4 Spinal fracture in a rabbit
Clinical Examination
Examination at this point showed:
A spinal fracture was suspected.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES
The differentials for hindlimb paralysis are:
• Infectious or inflammatory central nervous system disease, e.g. encephalitozoonosis, toxoplasmosis, neosporosis, meningitis/encephalitis
• CNS disease, e.g. brain abscess or tumour, viral haemorrhagic disease (VHD), trauma, encephalitozoonosis
• Metabolic disease (resulting in ataxia or muscular weakness), e.g. hepatic lipidosis or hypokalaemia
• Terminal disease, e.g. septicaemia, renal or hepatic failure, cardiovascular disease, starvation, intestinal obstruction, VHD, predator attack
• Congenital or acquired skeletal abnormalities, e.g. splay leg (developmental condition), spondylosis, kyphosis, lordosis
Diagnosis
Acute injury causing vertebral fracture and spinal cord compression (see below for radiographs).
Anatomy and Physiology Refresher
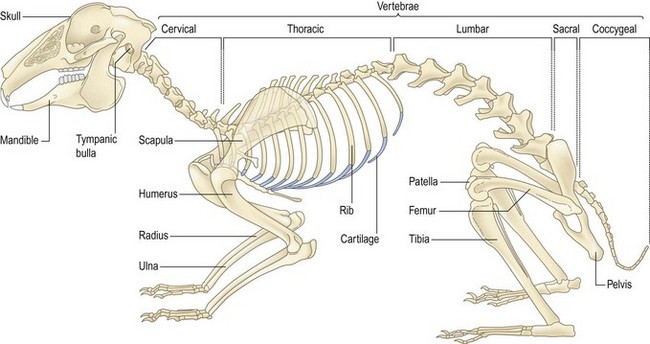
The skeleton in the rabbit is similar to other mammals (Fig. 4.1), with 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 7 lumbar, 4 sacral and 6 caudal vertebrae. Bone density in rabbits is relatively low, and accounts for only 6% of body mass. There is no cauda equina in rabbits; thus any injury along the vertebral column will affect the spinal cord and result in upper and lower motor neuron damage.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree