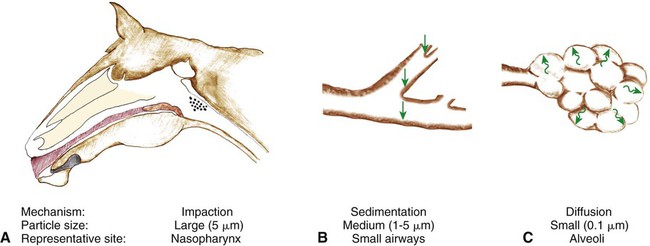
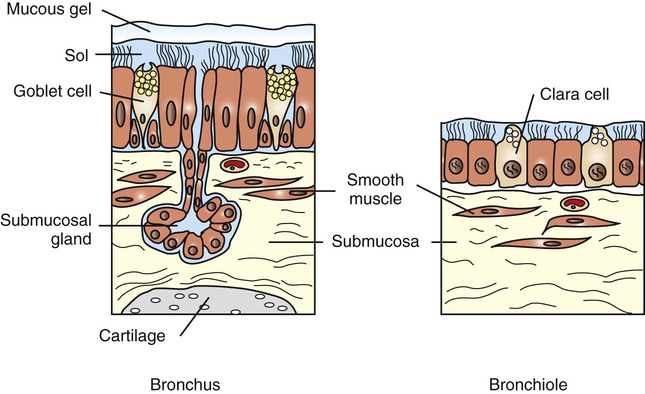
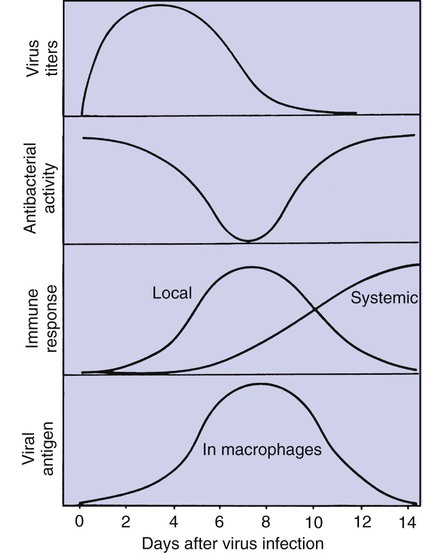
Defense mechanisms of the respiratory system 1. The extensive, delicate gas exchange surface of an animal’s lung is protected by a variety of specific and nonspecific defense mechanisms. 2. Particle deposition onto the mucociliary system depends on particle size and occurs by impaction, sedimentation, and diffusion. 3. The respiratory tract is lined by a mucociliary blanket consisting of a ciliated epithelium overlaid with a layer of mucus. 4. Alveolar macrophages scavenge particles deposited on the alveolar surface. 5. Cytokines and chemokines coordinate the defense mechanisms of the lung. 1. The lung continuously produces lymph as a result of the net fluid movement from the pulmonary microvasculature into the pulmonary interstitium. 2. Pleural fluid originates by filtration from capillaries in the parietal pleura and is reabsorbed through stomata that connect to lymphatics. Metabolic functions of the lung 1. The lung removes many hormones and toxins from the blood and inactivates many others. Particles and aerosols are removed from the air when they contact the moist epithelial surface of the tracheobronchial tree (Figure 50-1). The distance that particles and aerosols travel into the tracheobronchial tree depends on particle size. Larger particles, greater than 5 µm in diameter, contact the airway wall by inertial impaction. Inertial impaction occurs at the bends in the large airways because large particles traveling at high velocity have so much momentum that they fail to negotiate the turns. At sites of inertial impaction there are accumulations of lymphoid tissue, such as tonsils and bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue, presumably to orchestrate an immune response to the material landing on the airway surface. As airflow rates diminish deeper in the lung, particles 1 to 5 µm in diameter settle onto the walls of the airways by sedimentation. The smallest particles reach the peripheral airways and alveoli, where they either contact the epithelial surface by diffusion or are exhaled again. Inhaled drugs must be delivered in a form with a particle size of 1 to 5 µm to be deposited onto the airway wall and remain in the lungs. Particles deposited on the epithelial surface of the respiratory tract are transported on the mucociliary escalator to the pharynx, where they are then swallowed. The mucociliary system consists of sol and gel mucus layers overlying epithelial cells (Figure 50-2). The low-viscosity sol layer, in which the cilia beat, bathes the surface of the epithelial cells. On its forward stroke, the extended cilium catches the overlying viscous gel layer, in which inhaled particles are entrapped, and propels it up the tracheobronchial system or through the nasal cavity. Because the total surface area of the peripheral airways is so much greater than that of the trachea, differential rates of mucus transport are necessary in small and larger airways to prevent the accumulation of mucus in the trachea. Clearance rates and the beating frequency of cilia are slower in bronchioles than in bronchi and trachea. In large mammals, gravity also plays an important role in speeding mucociliary clearance. If a horse is prevented from lowering its head, the rate of mucociliary clearance is reduced. As a consequence, the number of bacteria in the trachea increases and this can lead to pneumonia. Inability of horses to lower their heads in a horse trailer may explain why transportation over long distances is the greatest risk factor for development of pneumonia in horses. Respiratory tract mucus originates from several sites (see Figure 50-2). In respiratory bronchioles the conciliated Clara cells are a source of the fluid that lines the airways. In the larger airways, goblet cells produce mucous secretions. In the bronchi, submucosal bronchial glands produce both serous and mucous secretions. Secretion is under autonomic regulation. Throughout the respiratory tract, transepithelial movement of water and ions can change the composition of the mucus layer. Ion and fluid exchange is assisted by microvilli on the surface of epithelial cells. Macrophages have adapted to the high oxygen levels of the alveolus, and their role as phagocytes is depressed by hypoxia. Macrophage function is also suppressed by endogenous glucocorticoids that are released from the adrenal glands at times of stress and by synthetic corticosteroids that are used to relieve inflammation (e.g., in arthritis). Stress-induced suppression of macrophage function contributes to respiratory disease in animals transported for long distances. In addition, excessive administration of synthetic corticosteroids can make animals more susceptible to bacterial infections of the lung. Viral infections also suppress macrophage function; this occurs approximately 7 days after virus inoculation (Figure 50-3) and contributes to the secondary bacterial infections that usually follow viral respiratory disease.
Nonrespiratory Functions of the Lung
Defense Mechanisms of the Respiratory System
The Extensive, Delicate Gas Exchange Surface of an Animal’s Lung Is Protected by a Variety of Specific and Nonspecific Defense Mechanisms
Particle Deposition onto the Mucociliary System Depends on Particle Size and Occurs by Impaction, Sedimentation, and Diffusion
The Respiratory Tract Is Lined by a Mucociliary Blanket Consisting of a Ciliated Epithelium Overlaid with a Layer of Mucus
Alveolar Macrophages Scavenge Particles Deposited on the Alveolar Surface
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Nonrespiratory Functions of the Lung
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue