Chapter 1 • With the increasing availability of nucleic acid–based testing, cell culture is decreasingly used for diagnosis of infections caused by obligate intracellular pathogens in dogs and cats. • Cell culture remains an important technique for (a) confirmation of a diagnosis when the results of molecular testing or serology are unavailable or equivocal; (b) pathogen discovery; and (c) vaccine manufacture. For some pathogens, cell culture is the most sensitive and specific method for organism detection. • Before collection of specimens, veterinary clinicians should communicate with the laboratory that is to perform the culture to discuss the patient signalment, history, immune status, travel history, nature of the suspected infection, and number of animals affected. • Specimens are inoculated onto monolayers, and the infecting organism is identified based on the presence of characteristic cytopathic effect after a predictable incubation period, with or without confirmatory antigen staining, electron microscopy, or nucleic acid testing. • False-negative results may occur as a result of inadequate specimen collection, deterioration of organisms during transport, or culture contamination with bacteria or fungi. • Positive results do not imply that the organism detected is the cause of an animal’s signs, because some organisms can be present without causing disease. This is especially the case for animals with respiratory or gastrointestinal disease. Cell culture refers to the culture of nucleated (eukaryotic) cells under controlled conditions within the laboratory. Infectious agents that require living host cells for replication can only be isolated in cell culture. With the advent of molecular diagnostic assays based on nucleic acid detection, cell culture is being used less often for routine clinical diagnostic purposes, because of the long turnaround times (days to weeks), cost, and requirement for significant technical expertise to perform cell culture and interpret results (Table 1-1). Nevertheless, isolation of viral and intracellular bacterial and protozoal pathogens in cell culture remains an important technique for the discovery of new pathogens, identification of organisms involved in disease when the results of molecular testing or serology are unavailable or equivocal, the propagation of isolates for research purposes, the generation of organisms for vaccination purposes, and the establishment of the efficacy of novel antimicrobial drugs. Vaccines for dogs and cats that are propagated in cell culture include those for canine distemper, canine adenovirus infections, parvovirus infections, rabies, and feline viral and chlamydial respiratory tract disease. Veterinary clinicians should remain aware of situations where cell culture may be the best technique to identify the presence of an infectious agent and the optimum methods for collection and submission of specimens. Knowledge of cell culture methods can help veterinary clinicians to submit the optimum specimens and to understand laboratory turnaround times, potential complications, and how to interpret results. Although cell culture can be used to propagate intracellular bacteria and protozoa, it is most often used by clinicians for the diagnosis of viral infections. Active communication between the clinician and the laboratory that performs viral isolation is recommended. Successful detection of viruses is highly dependent on (a) collecting the appropriate specimens, (b) the timing of specimen collection, and (c) rapid and proper specimen transport and processing. Thus the actions of the veterinary clinician play a critical role in ensuring positive test results when a virus is present. The clinician should discuss with the laboratory what types of viruses are suspected in light of the animal’s clinical presentation. The patient signalment, history, clinical signs, immune status, travel history, and number of animals affected should be discussed to generate conclusions regarding the nature of the suspected infection (Box 1-1). Some viruses, such as feline coronavirus (FCoV), are difficult to isolate in cell culture or grow slowly, whereas others, such as feline calicivirus (FCV), replicate readily and rapidly in cell culture, and the sensitivity of cell culture is high. Viruses differ in respect to the cell type they prefer to replicate within. As a result, specimens should be sent to the laboratory with information on the specific viruses that are suspected. The timing of specimen collection is particularly important for viral infections. Specimens should be collected as early as possible following the onset of clinical signs, optimally within the first week, because viral shedding may commence before the onset of signs and continue for only a few days. The duration of viral shedding depends on the type of virus and the anatomic site sampled. When multiple animals are affected, collection of specimens from more than one animal may increase the chance that an isolate will be obtained. If possible, antibody testing using acute and convalescent phase serology should be performed concurrently to help confirm the diagnosis (see Chapter 2). Selection of the best specimen and collection site for culture is optimized based on knowledge of the pathogenesis of the infectious agent involved, because the optimum specimen collection site may not be the site where clinical signs are most severe. Attempts should be made during specimen collection to prevent contamination of the specimen with normal flora, although this is not always possible. Specimen size should also be maximized (for example, at least 5 mL of blood, body fluids, or lavage specimens, and ideally 8 to 10 mL of blood) to increase the chance of a positive isolation. In general, nasal or nasopharyngeal washes have been preferred over nasal swabs in human patients for isolation of respiratory viruses, but one study showed that nasal swab specimens were just as sensitive as nasopharyngeal washes for isolation of most respiratory viruses.1 Nasal or oropharyngeal swab specimens are collected by placing a long-shafted swab in the area to be sampled, rotating the swab against the mucosa, and allowing the secretions to be absorbed for approximately 5 to 10 seconds. Swabs and small tissue specimens for virus isolation should be placed in buffered virus transport medium, which contains antibiotics and protein. This can be obtained from the laboratory or purchased from other commercial sources. It is important that the medium used has not reached its expiry date. Table 1-2 provides a guide to the recommended specimen types for isolation of viruses or obligate intracellular bacteria from companion animals. Specimens should be labeled with the patient data, the site(s) from which the specimen(s) was collected, specific organisms suspected, and the time and date of specimen collection. Contained specimens should be placed inside leak-proof triple packaging and transported on wet ice or cold packs to the laboratory, especially if transport is expected to take longer than 1 hour. Absorbent materials should be placed within the secondary container in order to absorb any spills. If specimens are to be shipped, the specimen must be labeled and handled according to governmental and International Air Transport Association (IATA) regulations for shipping materials known to contain infectious substances, which are categorized as Category A or Category B. Category A infectious substances are those capable of causing permanent disability or life-threatening or fatal disease in otherwise healthy animals and humans.2 Most specimens submitted by veterinarians fall under Category B, which are those that do not fall under the criteria for inclusion in Category A. Updated documents providing guidance on regulations for the transport of infectious substances are provided online by the World Health Organization (WHO).2 Import permits may be required for interstate and international transportation. TABLE 1-2 Specimen Collection Guide for Diagnosis of Viral and Intracellular Bacterial Infections of Companion Animals Maintenance of Cell Cultures in the Laboratory In general, cells are grown as a monolayer on a plastic plate. The cells in the monolayer can be derived directly from an animal (primary cell culture), which tend to have a limited life span, or they may be immortalized (continuous cell lines). Primary cell cultures are needed for the isolation of some viruses, because the cells more closely resemble those present in vivo, and the replication of these viruses occurs more efficiently in primary cell lines than in continuous cell lines. Further subculture of primary cell lines often reduces their sensitivity to viral infection. Primary cell cultures are generated by placing tissues in cell culture media, often after treatment of the tissue with an enzyme such as trypsin or collagenase. Primary white blood cell cultures (such as peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures) are generated by separation of the white cells from the other cellular elements using density gradient centrifugation, and adding them to a culture medium. Ficoll, a highly branched polysaccharide, is an example of a medium used commonly for density gradient centrifugation. Primary cell cultures have been used widely for the isolation of intracellular pathogens of dogs and cats.3–6 Low-passage cell lines remain viable and sensitive to viral infections for 20 to 50 passages. Continuous cell lines are the type of cell line used most commonly for diagnostic, research, and commercial purposes. These are derived from cancer cells (such as the widely used HeLa cell line, derived from human cervical cancer cells of a patient named Henrietta Lacks),7 or they result from experimental induction of cellular mutations (for example, using a carcinogen). Continuous cell lines representing a wide variety of cell types are available from commercial suppliers (Table 1-3). Laboratories that perform virus isolation for disease diagnosis may need to simultaneously inoculate multiple cell lines, because different viruses prefer to replicate in differing cell types. Mixed cell cultures are also now available commercially to simultaneously facilitate isolation of multiple different viral pathogens. TABLE 1-3 Examples of Continuous Cell Lines Used for Isolation of Viruses and Intracellular Bacteria That Infect Dogs and Cats
Isolation in Cell Culture
Introduction
Specimen Collection and Transport
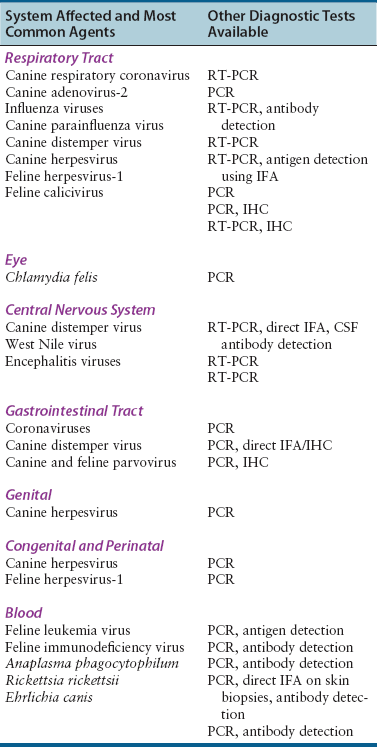
System Affected
Possible Agents
Specimen Type
Respiratory tract
Dogs: coronaviruses, canine adenovirus, influenza viruses, parainfluenza virus, CDV, canine herpesvirus
Cats: FHV-1, FCV, influenza viruses, FCoV
Oropharyngeal swabs
Nasal flushes, transtracheal wash or bronchoalveolar lavage specimens: ideally 5 to 10 mL of fluid
Lung tissue obtained at biopsy or necropsy, including an area adjacent to affected tissue
Eye
Dogs: canine herpesvirus, canine adenovirus
Cats: FHV-1, FCV, Chlamydia felis
Conjunctival swab, scraping or biopsy
Central nervous system
Dogs: CDV, West Nile virus, arboviruses
Cerebrospinal fluid: ideally at least 0.5 to 1 mL
Blood: 8 to 10 mL
Brain at necropsy
Gastrointestinal tract
Dogs: CDV, CPV, rotaviruses, canine coronavirus
Cats: FCoV, FCV, FeLV, rotaviruses, toroviruses
Feces: ideally an olive-sized portion of formed feces or 10 mL of liquid stool
Intestinal biopsies obtained using endoscopy or surgery, or intestinal tissue obtained at necropsy
Genital
Dogs: canine herpesvirus
Cats: Chlamydia felis
Vesicle scrapings, vaginal swabs
Congenital and perinatal
Dogs: canine herpesvirus
Cats: FHV-1, FeLV
Blood, tissues obtained at necropsy
Blood
Dogs: Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Rickettsia rickettsii, Ehrlichia canis
Cats: FeLV, FIV, FCoV
Blood: ideally 8 to 10 mL
Diagnostic Methods
Cell Line
Cell Origin
Pathogen(s)
Vero cells; recombinant Vero-SLAM cells
African Green monkey renal epithelial cells
CDV11,12
Rickettsia rickettsii13
Toxoplasma gondii14
Madin-Darby canine kidney cells (MDCK)
Kidney
CDV8,15
Canine adenovirus8,15
Canine herpesvirus-18,15
Parvoviruses8,16
Canine parainfluenza virus8
Canine calicivirus4
Rotaviruses17
Influenza viruses18
FeLV19
Neospora caninum20
Crandell-Reese feline kidney cells
Fetal kidney
FHV-121
FCV21,22
FCoV23
Parvoviruses24
FIV25
HL-60
Human leukemia
Anaplasma phagocytophilum26
A-72
Canine fibroma
Canine adenovirus27
Canine coronavirus27
Canine parainfluenza virus27
Canine herpesvirus27
McCoy
Mouse fibroblast
Chlamydia felis28
FCWF
Felis catus whole fetus, has characteristics of macrophages
FCoV29
FHV-130
DH-82
Monocyte/macrophage
Ehrlichia canis31
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Isolation in Cell Culture
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue