Chapter 45 Gastric Cytoprotective Agents
Introduction
The gastric mucosa has several intrinsic properties that protect it from autodigestion, including intact apical cell membranes, tight junctions, bicarbonate secretion, mucus production, rich blood supply, active cell renewal, surface active phospholipids, and endogenous prostaglandins. Gastric ulceration is believed to have its origins in the disruption of the mucosal barrier, or as a result of excessive acid secretion (Box 45-1), and is more commonly reported in dogs than in cats.1–4 History and physical examination, as well as full metabolic assessment, will help to rule out systemic disease and drug administration as the underlying cause. Strenuous exercise, particularly in sled dogs, is associated with increased intestinal permeability and gastrointestinal ulceration.5,6 The use of corticosteroids in dogs with intervertebral disk disease has been associated with severe gastrointestinal ulceration.7 If no underlying cause is identified abdominal ultrasound combined with further testing, such as endoscopy or gastric biopsy, may be required.
Box 45-1
Differential Diagnoses of Gastric Ulceration
For many of the conditions listed in Box 45-1 the true incidence of ulceration is unknown, especially with regards to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID) toxicity. NSAIDs (particularly aspirin) are reported to exert their adverse effects by direct toxicity to the gastric mucosa as well as by inhibition of the cyclooxygenase pathways, thereby reducing endogenous prostaglandin and mucus production.8 It may well be that the superficial gastric erosions reported and identified in animals given NSAIDs are not clinically significant.
In addition to the conditions detailed in Box 45-1, gastric cytoprotective agents have been used in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroesophageal reflux may occur secondary to general anesthesia (especially when the animal has not been fasted),7 protracted vomiting disorders, or physical defects such as hiatal hernias.9 Ingestion of caustic substances such as clindamycin or generic doxycycline capsules in cats may cause severe esophagitis requiring gastric antisecretory therapy.10,11
It is important to bear in mind that ideal treatment goals for specific gastric conditions have not been established in veterinary medicine. In human medicine it is recommended that the gastric pH should be increased to more than 4 for approximately 16 to 22 hours per day in the treatment of gastroesophageal disease, as well as in critically ill patients, whereas for conditions of gastrointestinal hemorrhage the pH should be as high as 6 to promote hemostasis.12 Similar standards have not yet been developed for most companion animal disease conditions.
Oral Antacids
Mechanism of Action
Antacids react chemically with gastric acid to reduce the overall acidity of the stomach. Antacids do not directly decrease acid secretion. The most commonly used antacids are aluminum hydroxide (Al[OH]3), magnesium hydroxide (Mg[OH]2), and calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Many of these are available as over-the-counter formulations for the symptomatic relief of gastroesophageal reflux and dyspepsia, and are often formulated with other drugs (see Box 45-1). They are given orally as tablets or liquids and are often flavored for palatability. There is little absorption from the gastrointestinal tract so the risk for adverse systemic effects is minimal.
The use of antacids for stomach ulceration is based on the premise that buffering or decreasing gastric acid will permit ulcer healing.13 However, ulcer healing seen with aluminum hydroxide may not be related to gastric acidity,14 as it may also release prostaglandin (PG) E2 into the gastric lumen and submucosa.15 The significance of this finding requires further investigation. There is very little scientific literature assessing the efficacy of local antacids for dog and cat gastric ulceration.
Dose
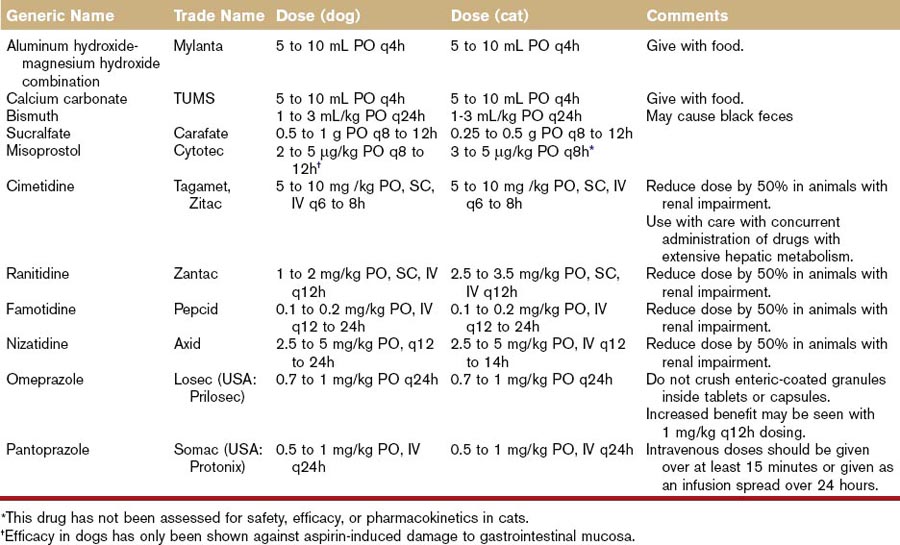
The onset and duration of antacid effect in humans is rapid and extends from 20 minutes to 3 hours, depending on the preparation that has been used.16 Antacids act locally so the presence of food will delay gastric emptying, thereby prolonging the effect of these drugs.17 This short duration of action, which presumably also occurs in dogs and cats, necessitates that these drugs be taken often. Dose recommendations are estimations only and have not been scientifically determined for dogs or cats (Table 45-1).
Contraindications and Side Effects
The cations in antacids are capable of binding to fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines and may decrease the systemic absorption of this drug class. Ketoconazole and itraconazole, which depend on gastric acidity for oral absorption, will show decreased systemic absorption when given concurrently with any drug capable of reducing gastric acidity. Recommendations to prevent decreased bioavailability of these drugs that are based on controlled animal studies do not exist, but human recommendations are that these drugs be given parenterally (if appropriate) or orally a few hours before or after administration of the antacid.16 In dogs, the bioavailability of oral propranolol in the presence of aluminum hydroxide or magnesium hydroxide is reduced.18
Magnesium hydroxide has mild laxative effect whereas aluminum hydroxide has a mild constipating effect. These two salts are often given together in the same formulation such that changes in fecal consistency are uncommon. It has been suggested that magnesium-containing antacids should be avoided in patients with renal failure to avoid hypermagnesemia that may lead to central nervous system toxicity.19 Calcium carbonate reacts with stomach acid to liberate carbon dioxide, and belching may be noted.19 Aluminum hydroxide is capable of binding to phosphates and is sometimes used for cases of hyperphosphatemia.20 Aluminum toxicity to with aluminum hydroxide antacids has been reported.21
Antacids have sometimes been singled out as drugs that produce significant rebound gastric acid hypersecretion once therapy has stopped, however, this hypersecretion may simply be a function of gastric hypoacidity caused by many of the gastric acid-lowering drugs.22
Prostaglandin Analogues
Mechanism of Action
Gastric prostaglandins play an important role in gastric mucosal defense in that they increase mucosal blood flow, mucus production, and bicarbonate secretion.23,24 The most commonly studied and used prostaglandin analogue in veterinary medicine is misoprostol, an analogue of prostaglandin E1.25–28
Dose
Beneficial effects have been reported at a dose of 3 µg/kg body weight every 8 to 12 hours in dogs,8 with a half-life of approximately 30 minutes, and a duration of action of 3 to 6 hours.29 Only oral formulations for this purpose are available. No known pharmacokinetic or safety studies have been performed in cats, but the anecdotal dose is recommended to be 2 to 5 µg/kg body weight every 12 hours.8
Rational Use
The veterinary application of this drug originated from its use in people to prevent NSAID-induced gastric injury, although it is not clear how superior it is to other gastric cytoprotective agents.30,31 NSAIDs are frequently used in older animals and may inhibit tissue cyclooxygenase pathways.2,32 In most in vivo veterinary assessments of this drug, misoprostol was given along with a nonsteroidal drug, usually aspirin, and compared with placebo. Despite slight variation in study design, it has been shown that there was significantly less gastroduodenal hemorrhage and vomiting in the misoprostol group over 14-day25 to 30-day26 periods. The benefit of misoprostol is less convincing in studies of dogs given corticosteroids because of intervertebral disk disease.7,33 This may be due to differences in the pathogenesis of glucocorticoid-induced gastric ulceration or additional neurogenic factors. Based on these studies, it would seem prudent to only recommend the prophylactic use of misoprostol in dogs receiving NSAID therapy that are at high risk of developing gastric ulceration. However, its use is not generally supported in healthy animals receiving cyclooxygenase-2–specific antagonists or animals receiving glucocorticoids alone.
Contraindications and Side Effects
The use of this drug is contraindicated in dogs receiving gentamicin or other nephrotoxic drugs, as it has been shown to potentiate nephrotoxic effects.27 Side effects that have been reported include intestinal cramping and diarrhea, caused by the stimulation of migrating motor complexes. The incidence of diarrhea is dose dependent, especially when the recommended dosage is exceeded.28 Because of the potential to induce abortion, the drug should not be handled by women who are pregnant or trying to conceive.
Chemical Diffusion Barriers
Mechanism of Action
Bismuth is capable of binding to an ulcer bed, providing a protective coating. In addition, it can enhance bicarbonate secretion and local prostaglandin synthesis, and adsorb the proteolytic enzyme pepsin.34
Sucralfate is a complex of sucrose octasulfate and aluminum hydroxide that in the presence of acid dissociates into these two components. Sucrose octasulfate will polymerize into a sticky, viscous, yellow-white gel that is strongly anionic and electrostatically binds to cationic tissue proteins of ulcerated mucosa. The ulcerated site covered by this “liquid band aid” is protected from backward diffusion of hydrogen ions. It seems likely that both the sucrose octasulfate and aluminum hydroxide components contribute to cytoprotection.35 Sucralfate has additional cytoprotective roles that may involve mucosal synthesis of protective prostaglandins, secretion of mucus and bicarbonate, and increases in epidermal growth factor. It has little effect on stomach acidity.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree