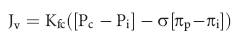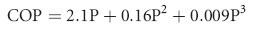Chapter 205 Colloid Osmotic Pressure And Osmolality
• Determination of colloid osmotic pressure (COP) can guide artificial colloid therapy in veterinary patients.
• Estimation of COP via equations using the patient’s albumin and globulin concentrations are unreliable, particularly in critically ill patients that may have altered albumin-to-globulin ratios.
• Maintenance of a goal COP of at least 15 mm Hg in whole blood for both dogs and cats reduces the risk of edema formation and secondary organ dysfunction associated with edema.
• Plasma osmolality can be estimated from an equation or measured directly via a freezing point depression osmometer.
COLLOID OSMOTIC PRESSURE
Starling Hypothesis
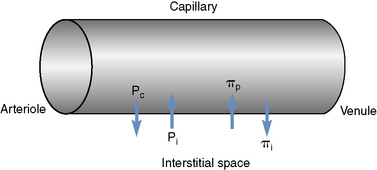
This equation shows the importance of plasma COP in maintaining a normal fluid balance between the intravascular space and the interstitial space (Figure 205-1). If the COP in the capillaries drops lower than the COP in the interstitium, fluid will move out of the vessels and edema formation will be favored.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree