42 Canine lens luxation
CLINICAL EXAMINATION
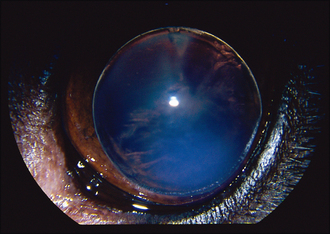
The lens can be visualized in the anterior chamber between the back of the cornea and the front of the iris (Figure 42.1). By viewing the patient from the side it should be possible to see the iris bowing back away from the cornea and the structure of the lens should be apparent. The size of the pupil is variable (if visible!) but is normally mid sized or dilated, and often fixed or poorly responsive to light. If fundus examination is possible it could be normal, or optic disc cupping might be noted (discussed further in the cases on glaucoma). Intraocular pressure measurement should be undertaken if possible, since this will have an important effect on the prognosis and management of the cases.
Positive diagnostic tests which can be performed in practice are simple – if there is a positive dazzle reflex in the affected eye, and a consensual pupillary light response in the unaffected eye, i.e. on shining a light into the affected eye the fellow pupil constricts, these both indicate that vision might be preserved with rapid referral for lendectomy. If neither test is positive, then the prognosis for vision is very poor, and any emergency surgery is only likely to salvage the globe.
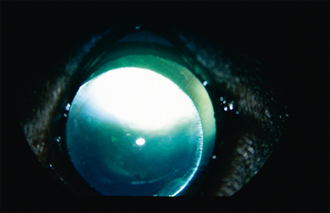
The fellow eye should be very carefully evaluated since primary lens luxation is a bilateral condition, although it is rare for both lenses to luxate simultaneously. The contralateral lens is frequently subluxated – this can be appreciated as iris wobble (iridodonesis) or lens wobble (phacodonesis) as the eye moves. The anterior chamber might be deep or shallow, depending on where the lens has slipped, and strands of vitreous are frequently visible in the anterior chamber. Pupillary dilation with tropicamide might allow the edge of the lens to be visualized – normally it slips slightly ventrolaterally, and stretched lens zonules can sometimes be noted (Figure 42.2). The worse affected eye (with the full anterior luxation) should not be dilated with tropicamide since this could both exacerbate any glaucoma and allow the lens to fall into the vitreous, making surgical retrieval much more difficult.
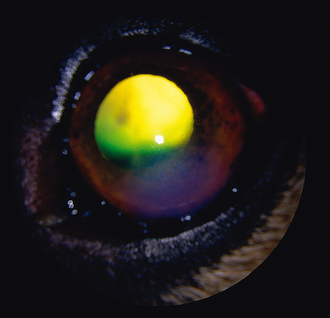
Some patients will not have an anterior but a posterior lens luxation. Typically with these the owner reports the eye was very sore and cloudy, but then became more comfortable, although it still did not look normal. In such cases the subcentral patch of corneal oedema will still be present but the lens is not visible in the anterior chamber (Figure 42.3). The iris normally wobbles (iridodonesis) on globe movement and the anterior chamber is often deep. By looking though the pupil from above, the lens can normally be seen lying in the ventral posterior segment. The different subtypes of lens luxation are shown in Figure 42.4.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree