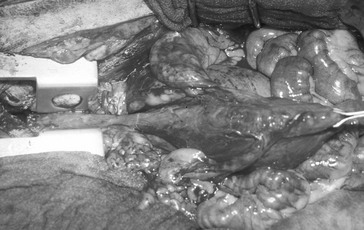
Chapter 213 An incision along the median raphe is made from the level of the caudodorsal aspect of the horizontal vaginal canal, descending to the dorsal commissure of the vulvar cleft. The incision is continued along the same plane of the skin incision through the vaginal musculature and mucosal layers. Placement of a flat instrument (e.g., scalpel handle) in the vestibule can be used to stabilize the tissues while the incision is made through the dorsal vestibular mucosa. Alternatively, Metzenbaum scissors can be used to cut the mucosal layer. Cautery, vessel ligation or compression of the vestibular wall using two Doyen bowel clamps (positioning one on each side with one blade in the vestibular lumen and one on the skin surface) can be used for hemostasis (Figure 213-1). Hemorrhage often is associated with surgery to this region because of the increased vascularity to the vaginal tissues. Exposure is maintained with the use of self-retaining retractors (i.e., Gelpi, Weitlander, or ring retractors) or stay sutures. A urinary catheter should be placed if there is potential for tissue manipulation around the urethra and urethral tubercle. Figure 213-1 An episiotomy over the dorsal aspect of the vulva allows access to the lumen of the vestibule/vagina. Two Doyen bowel clamps are placed on the edges of the incision (positioning one on each side with one blade in the vestibular lumen and one on the skin surface to control hemorrhage and allow visualization). An incision along the median raphe is made from the level of the caudodorsal aspect of the horizontal vaginal canal, descending to the dorsal commissure of the vulvar cleft. Digital palpation during the approach facilitates identification of the vagina and helps identify the location of interest (Figure 213-2, A). The incision is continued along the same plane of the skin incision until the muscular wall of the vagina/vestibule is reached. Cautery vessel ligation should be used for hemostasis. Exposure is maintained with the use of self-retaining retractors. Blunt dissection can be performed around the vagina as needed (Figure 213-2, B). Careful dissection along the ventral aspect of the vagina is necessary to avoid trauma to the urethra. A urinary catheter should be placed if there is potential for tissue manipulation around the urethra and urethral tubercle. Figure 213-2 Perineal approach to the vestibule/vagina. A, Digital palpation of the vestibule with an incision along the median raphe. B, Continued dissection along the midline to the vagina and careful dissection circumferentially around the vagina using right-angled forceps. A red rubber catheter is placed in the urethra for identification and protection during dissection. Alternatively an osteotomy through the pubic symphysis, separating the hemipelvis, can be performed. The flexibility of the pelvis allows the placement of retractors to separate the hemipelvis, giving exposure to the pelvic canal. Holes can be predrilled on either side of the pubic symphysis. Self-retaining retractors (i.e., Finochietto retractors) facilitate exposure (Figure 213-3). Care must be taken not to put excessive stress on the hemipelvis, which can create a fracture or sacroiliac luxation (especially in young dogs or cats). Closure of this approach begins with reduction of the pelvic floor, using 18- to 20-gauge cerclage wire. The predrilled holes allow for rapid and accurate alignment of the pubic and ischial rami. The obturator and adductor muscle fascia from either side is sutured to its contralateral partner along the midline. Closure of the linea, subcutaneous tissue, and skin is performed routinely. Because of the osteotomy, activity should be restricted for 4 months after surgery. In small patients the pubic symphysis does not have to be replaced. Closure of the obturator and adductor muscles along the midline provides adequate support of the pelvic floor.
Surgical Repair of Vaginal Anomalies in the Bitch
Surgical Approaches to the Canine Vagina
Caudal Approach with Episiotomy
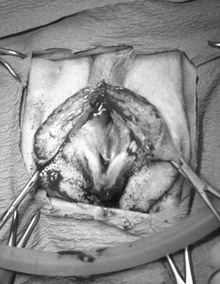
Perineal Approach with Episiotomy
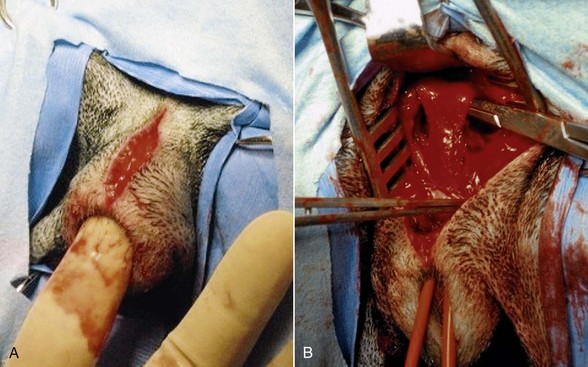
Ventral Approach
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Surgical Repair of Vaginal Anomalies in the Bitch
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue