Chapter 91 Serotonin Syndrome
• Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine [5-HT]) syndrome is a drug-induced condition resulting from excess serotonergic agonism of the central and peripheral nervous system serotonin receptors.
• Serotonin syndrome can result from overdoses of serotonin reuptake inhibitors, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressant medications, lithium, dietary supplements, or administration of multiple serotonergic medications.
• Clinical signs reported in companion animals due to accidental ingestion of serotonergic medications include nervous system signs (seizures, depression, tremors, hyperesthesia, ataxia, paresis, disorientation, coma, hyperreflexia, mydriasis, blindness), gastrointestinal tract symptoms (vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, ptyalism, flatulence, bloat), hyperthermia, and death.
SEROTONIN AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF SEROTONIN SYNDROME
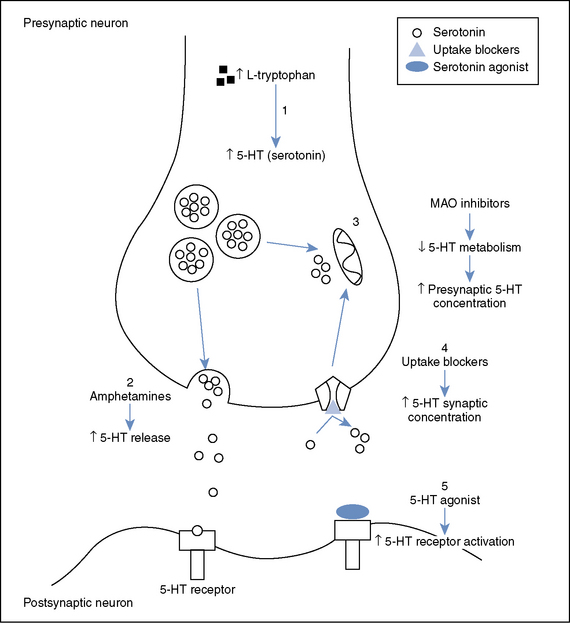
Serotonin is formed in the body by hydroxylation and decarboxylation of the essential amino acid tryptophan. Increased intake of tryptophan in the diet can increase brain serotonin levels because the enzyme, tryptophan hydroxylase, does not normally reach saturation levels.7 Serotonin is synthesized in the cytosol in neurons, stored in vesicles at the nerve terminal, and released into the synaptic cleft where it binds to the postsynaptic receptor, mediating neurotransmission. After release, much of the serotonin is recaptured by an active reuptake mechanism and inactivated by monoamine oxidase to form 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. This substance is then eliminated in the urine (Figure 91-1).7
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree