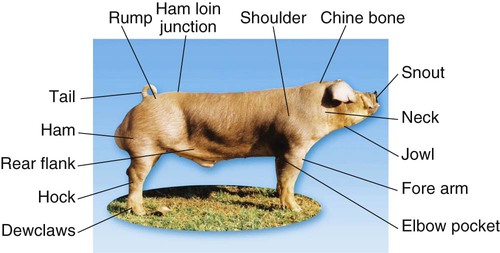
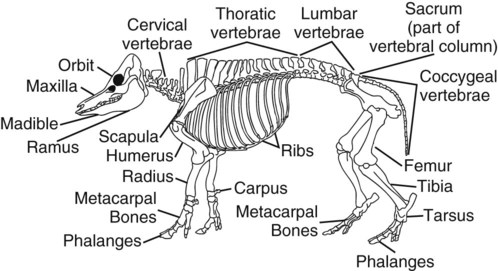
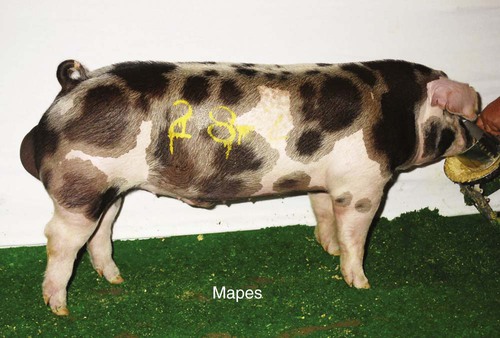
When you finish this chapter, you will be able to • Know and understand the zoologic classification of the species • Proficiently use terminology associated with this species • Describe physiologic data for the species and identify abnormal data • Identify the common instruments relevant to the species and their uses • Describe prominent anatomical or physiological properties of the species • Identify and describe characteristics of common breeds • Describe normal production and husbandry needs for the species • Describe specific reproductive practices of the species Box 22-1 lists common terminology used to describe the age and breeding status of swine. Table 22-1 list normal physiologic data for swine. TABLE 22-1 The American Landrace originated in Denmark. The hog is white. It is long bodied, and the large ears lop forward and down. The Landrace sow is noted for its mothering ability. The breed is also known for its large litters and length of side. The breed association is the American Landrace Association, Inc. Disqualifications for registry are black hair, erect ears, and less than six teats on a side. This is considered a maternal breed and is mostly used for crossing with other breeds (Fig. 22-3). The Berkshire originated in England in and around Berkshire and Wiltshire counties. It is a medium-sized hog that produces an acceptable carcass. The animal is black with six white points, four white feet, and some white on the face and the tail. The head is slightly dished, and the ears are erect. The breed association is the American Berkshire Association. Disqualifications for registration are swirls on the back or sides and large amounts of white hair on the body. Selection has placed emphasis on fast and efficient growth, meatiness, and good reproduction. This is considered a terminal breed (Fig. 22-4). The Chester White originated in Chester County, Pennsylvania. Producers refer to this breed as “Chesters.” The breed is a mixture of Yorkshire, Lincolnshire, Cheshire, and Bedfordshire lines. The color of the breed is white, and the ears droop forward. The breed is noted for its mothering ability. The breed association is the Chester White Swine Record Association. Disqualifications for registry include swirls on the back and sides or any other color than white. This breed is considered a maternal breed (Fig. 22-5). The Duroc breed originated from red hogs raised in New Jersey and New York. The breed was originally called the Duroc-Jersey, but the Jersey was later dropped. The color of the Duroc is red. Shades vary from light to dark, with a medium cherry being the preferred shade. The Duroc has ears that droop forward. The breed has good mothering ability, growth rate, and feed conversion. It is one of the most popular breeds of swine in the United States. Swine of this breed can be registered with the United Duroc Swine Registry. Disqualifications for registry include swirls on the back and sides or white hair on the body. This breed is considered a terminal breed (Fig. 22-6). The Hampshire breed originated in England and was developed in Kentucky. It was previously known as the Thin Rind. The Hampshire is black, with a white belt that encircles the forepart of the body. The forelegs are included in the white belt. The Hampshire has erect ears. The breed is noted for its rustling (foraging) ability, muscle, and carcass leanness. It is a popular breed and is used in many crossbreeding programs. The breed association is the Hampshire Swine Registry. Disqualifications for registry include cryptorchidism, swirls on back or sides, incomplete belt, or white belt more than two thirds back on the body. White is permitted on the hind limbs as long as it does not go above the bottom of the ham or touch the belt. Other disqualifications include white on the head (except on the front of the snout), black front legs, white going above the bottom of the ham, or white on the belly extending the full length of the body. The Hampshire is considered a terminal breed (Fig. 22-7). The Hereford was developed in Missouri, Iowa, and Nebraska. The breed was founded with use of Duroc, Poland China, some influence of Chester White, and Hampshire hogs. The Hereford is red with a white face. The ears are forward and drooping. The breed registry is the National Hereford Hog Registry Association. To be eligible for registry, Hereford hogs must be at least two thirds red and have some white on the face. Herefords are prolific, good mothers, and have good rustling ability. Disqualifications for registry include no white on the face, less than two thirds of the body red, swirls on the body, or less than two white feet (Fig. 22-8). The Poland China originated in the Ohio counties of Butler and Warren. The breed was developed with the use of lines from Russian, Byfield, Big China, Berkshire, and Irish Grazer bloodlines. The Poland China is black with six white points. The white points include the feet, tip of the nose, and the tip of the tail. The Poland China has forward-drooping ears. Poland China is one of the larger breeds of hogs. It is used in many crossbreeding programs. The breed association is the Poland China Record Association. Disqualifications for registry include fewer than six teats on a side, swirls on the upper half of the body, hernia, or cryptorchidism. The absence of any of the white points is not objectionable nor is an occasional splash of white on the body. The Poland China breed is considered a terminal breed (Fig. 22-9). The Spotted swine was developed in Indiana. Many producers refer to this breed as “Spots.” It was created by crossing hogs of Poland China breeding with spotted hogs being grown in the area and later with the use of Gloucester Old Spots. The color of the Spotted breed is black and white. To be eligible for registry, at least 20% but not over 80% of the body must be either black or white. The body type of the Spotted breed is similar to that of the Poland China. It has forward-drooping ears. Breeders strive to produce a large-framed hog with efficient gains and good muscling. The breed association is the National Spotted Swine Record. Disqualifications for registry include brown or sandy spots, swirls on any part of the body, and cryptorchids. The breed is considered a terminal breed (Fig. 22-10). The Tamworth hog originated in Ireland. It is one of the oldest of the purebred breeds. The Tamworth is red with shades varying from light to dark. The ears are erect, and it has a long head and snout. The sows are good mothers and have large litters. The breed is noted for its foraging ability. The breed association is the Tamworth Swine Association. Disqualifications for registry include swirls on the sides and back and inverted teats (Fig. 22-11). The Yorkshire hog originated in England, in the county of Yorkshire. The Yorkshire is white. The skin sometimes has black pigmented spots called “freckles.” The breed association is the American Yorkshire Club. Hogs with black spots can be registered, but this trait is considered undesirable. The ears are erect, and the face is slightly dished. Yorkshires have large litters, high feed efficiency, rapid growth, good mothering ability, and long carcasses. They are often used in crossbreeding programs. Disqualifications for registry include swirls on the upper third of the body, hair other than white, blind or inverted teats, fewer than six teats on a side, hernia, and cryptorchidism. The breed is considered a maternal breed (Fig. 22-12). The North American Potbellied Pig Association describes the potbellied pig as weighing no more than 95 lb and having a maximum height of 18 inches. Although some pigs stay small, between 40 and 50 lb, most pigs weigh closer to 120 lb. This breed of pig is not used for production of meat; it is more commonly kept as a pet. Most potbellied pigs are purchased between 6 to 8 weeks of age and are spayed or neutered within the first few months. Fifty percent of potbellied pigs are abandoned or sent to another home in the first year of life. This occurs because of unrealistic expectations of the owners and their unwillingness or inability to meet the pig’s needs (Fig. 22-13).
Porcine Husbandry
Terminology and Physiologic Data
Temperature
101–103.5°F
Pulse rate
60–90/min; 200–280/min in newborns
Respiratory rate
10–24/min; up to 50/min in very young swine
Adult weight
Varies by breed
Swine Breeds
Common Swine Breeds
American Landrace
Berkshire
Chester White
Duroc

Hampshire
Hereford
Poland China
Spotted Swine
Tamworth

Yorkshire

Potbellied Pig

![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Porcine Husbandry