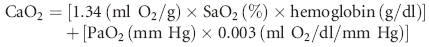Chapter 19 Oxygen Therapy
• Hypoxemia occurs in a variety of critical illnesses. Oxygen supplementation can improve oxygen delivery and decrease the incidence of lactic acidosis.
• Supplemental oxygen administration should be provided whenever a patient’s partial pressure of arterial oxygen (PaO2) is less than 70 mm Hg, oxygen saturation (SaO2) is less than 93% on room air, and in cases of significant anemia or cardiovascular instability.
• Noninvasive means of oxygen supplementation, including flow-by, mask, hood, and oxygen cage, are a simple means of providing an oxygen-enriched environment to a critically ill patient.
• Nasal and nasopharyngeal oxygen supplementation require minimal equipment and are well tolerated by many hypoxemic patients.
INTRODUCTION AND INDICATIONS FOR OXYGEN THERAPY
where (SaO2) is arterial oxygen saturation and (PaO2) is partial pressure of arterial oxygen.