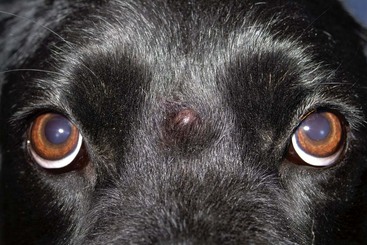
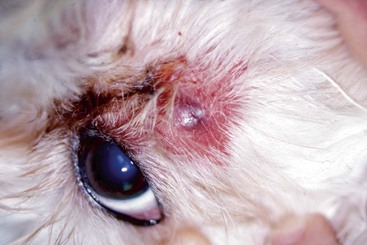
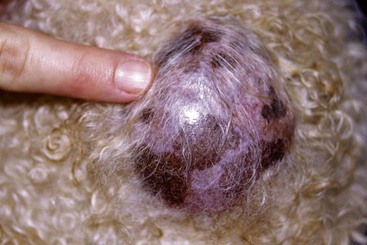
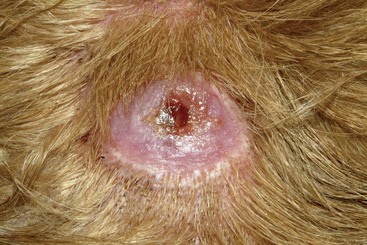
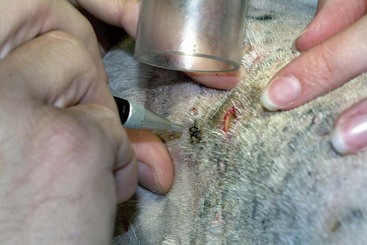
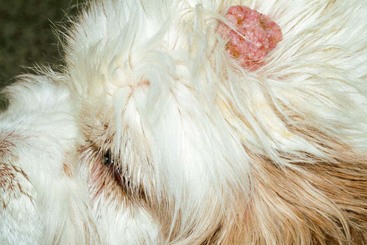
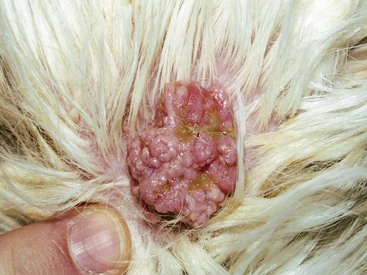
CHAPTER | 14 Neoplastic and Nonneoplastic Tumors
Intracutaneous Cornifying Epithelioma (keratoacanthoma, infundibular keratinizing acanthoma)
Diagnosis
Treatment and Prognosis
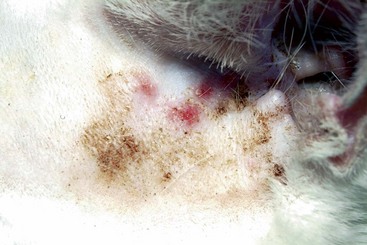
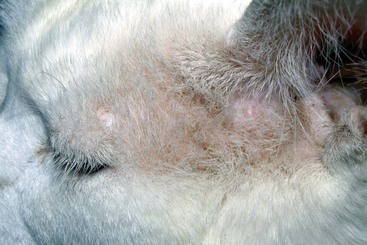
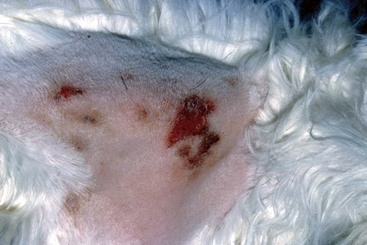
Feline Solar Dermatosis
Diagnosis
Treatment and Prognosis
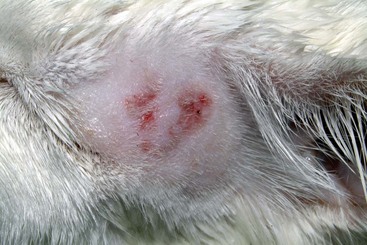
FIGURE 14-4 Feline Solar Dermatosis.
Same cat as in Figure 14-3. The crusts have been removed, revealing the erythematous papular lesions.
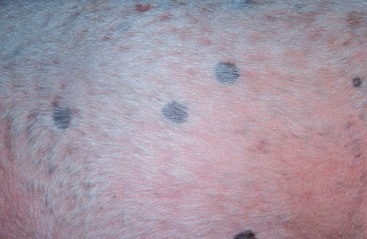
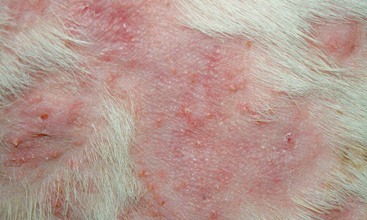
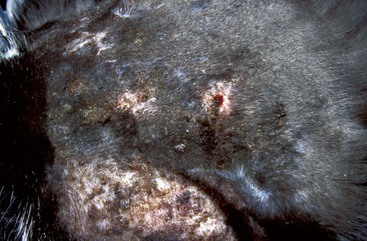
Canine Solar Dermatosis
Diagnosis
Treatment and Prognosis

FIGURE 14-9 Canine Solar Dermatosis.
Generalized alopecia and erythema covering the face and trunk of a Bull terrier.
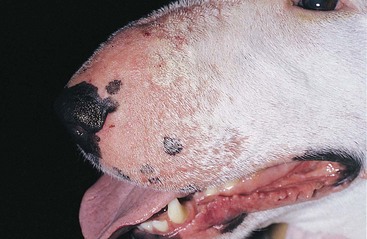
FIGURE 14-10 Canine Solar Dermatosis.
Alopecia and erythema with papular dermatitis on the muzzle.
(Courtesy D. Angarano.)
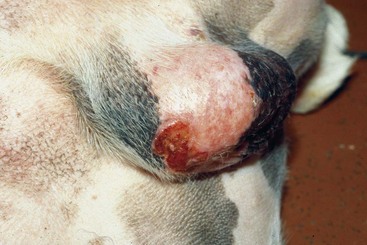
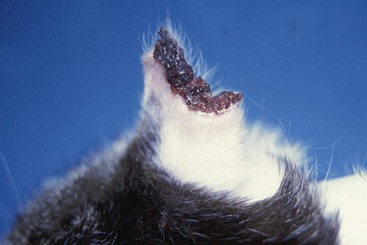
FIGURE 14-14 Canine Solar Dermatosis.
This focal area of ulceration on the scrotum of a Boxer had progressed to squamous cell carcinoma.
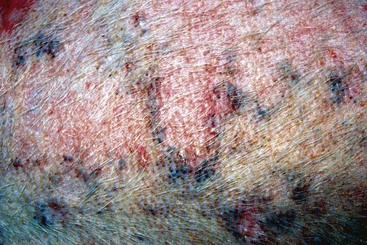
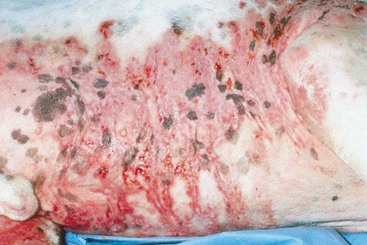
FIGURE 14-18 Canine Solar Dermatosis.
Severe erythematous dermatitis with a coalescing papular rash caused by sun exposure.
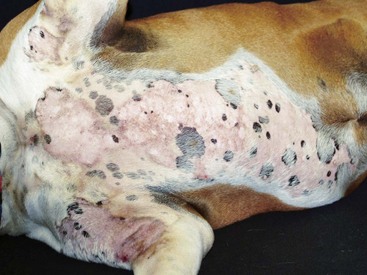
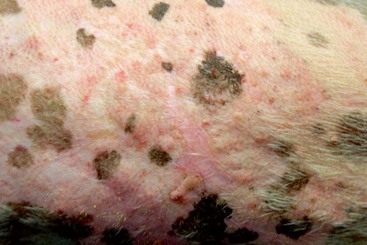
FIGURE 14-19 Canine Solar Dermatosis.
Severe erythema affecting only the nonpigmented areas of skin on the ventrum of a Boxer.
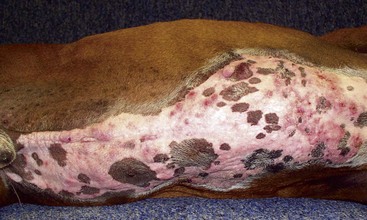
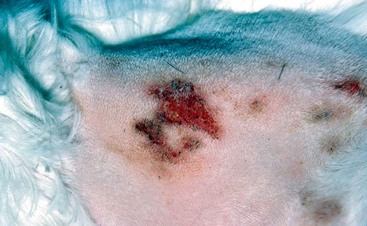
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Diagnosis and Staging
Treatment and Prognosis
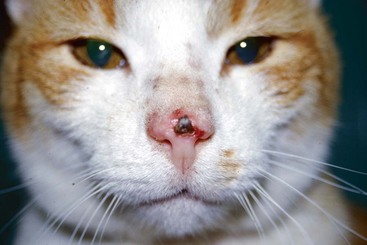
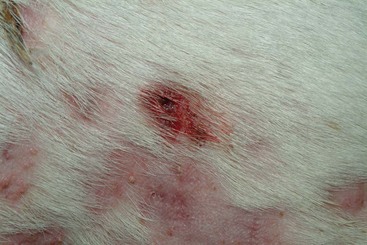
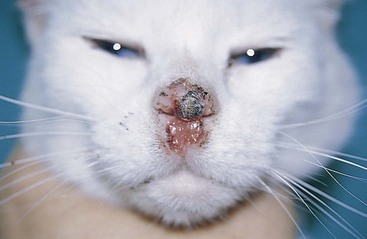
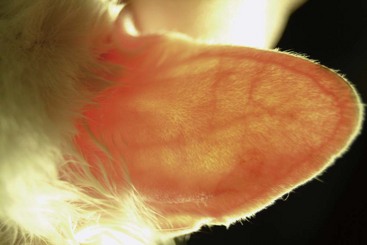
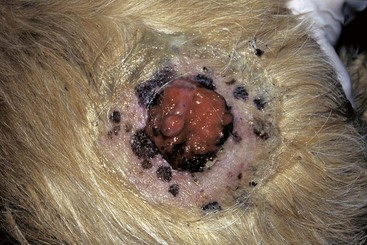
FIGURE 14-21 Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
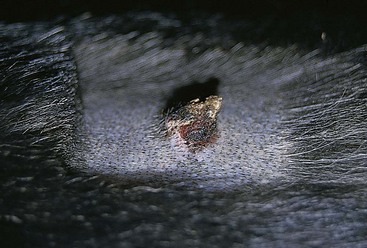
A small, ulcerated tumor on the nonpigmented nasal planum of a cat.
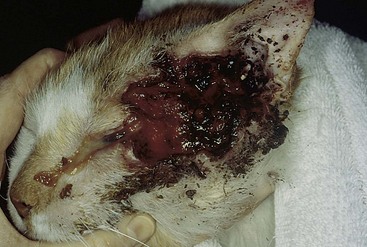
FIGURE 14-24 Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Severe tissue destruction and tumor proliferation on the face and periocular tissue of a cat.
(Courtesy S. McLaughlin.)
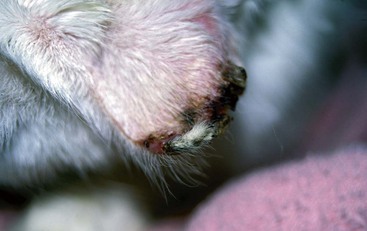
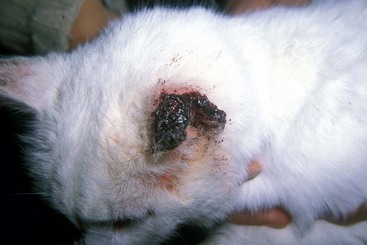
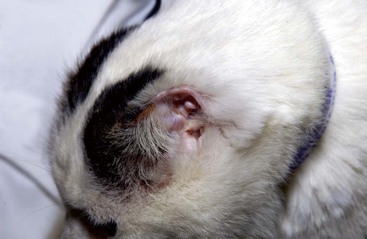
FIGURE 14-25 Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
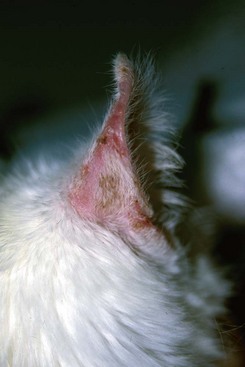
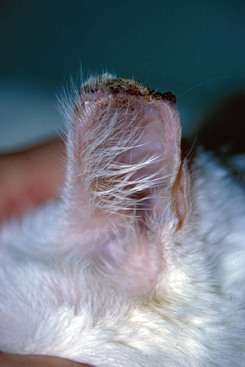
Necrosis and crusting of the distal ear margin of an adult white cat.
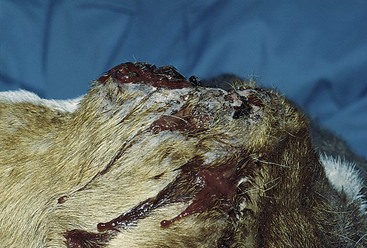
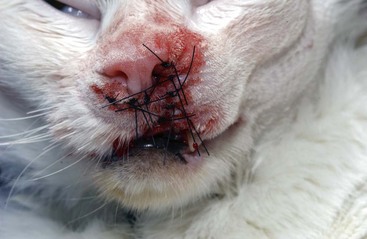
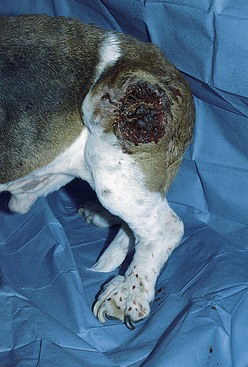
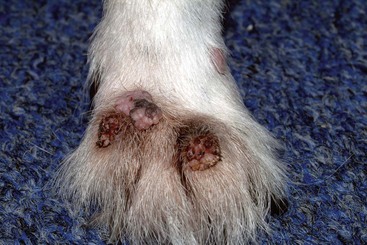
FIGURE 14-30 Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Close-up of the dog in Figure 14-29. This raised tumor has a deep ulcer, with tissue destruction forming a central crater.
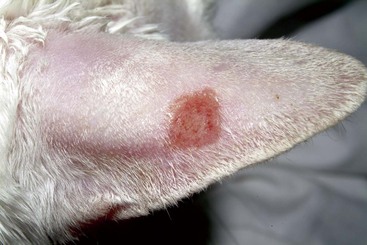
FIGURE 14-33 Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Same cat as in Figure 14-32. The tumor has been ablated, leaving a focal area of ulceration.
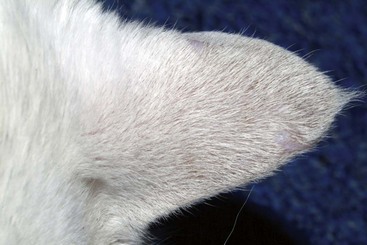
FIGURE 14-34 Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Same cat as in Figure 14-32. Three weeks after treatment, the focal area has healed and the hair is regrowing. Early detection and therapeutic intervention provide better cosmetic outcomes.
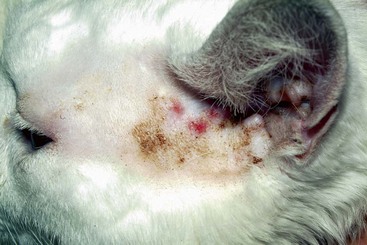
FIGURE 14-35 Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Multifocal squamous cell carcinoma on the preauricular area of a white cat.
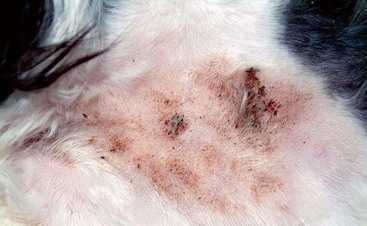
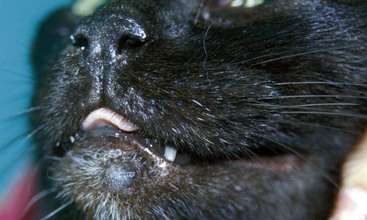
Bowen’s Disease/Multifocal Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
Treatment and Prognosis
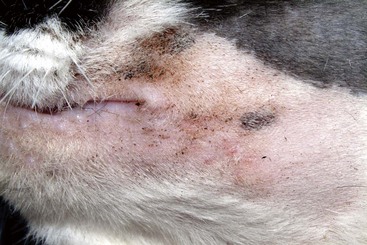
FIGURE 14-38 Bowen’s Disease.
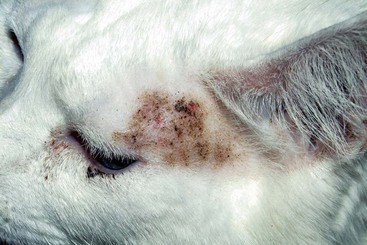
Multifocal, crusting, papular lesions on the face. Note the mild, subtle nature of the lesions.
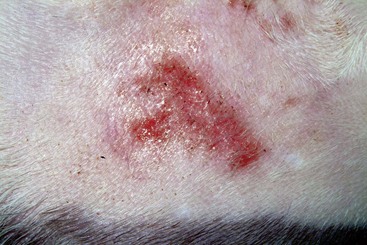
FIGURE 14-41 Bowen’s Disease.
Coalescing papules formed a plaque on the nonpigmented skin of this cat.
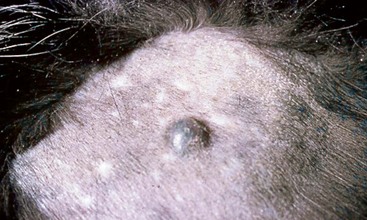
Basal Cell Tumor/Carcinoma
Diagnosis
Treatment and Prognosis
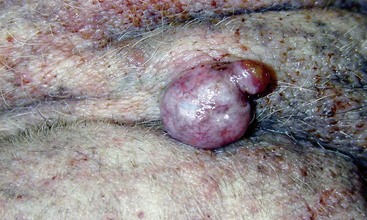
Hair Follicle Tumors
Features
Diagnosis
Treatment and Prognosis
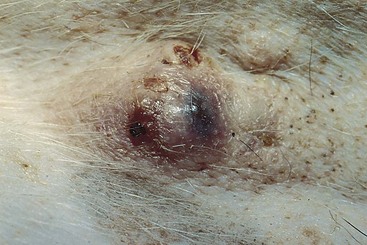
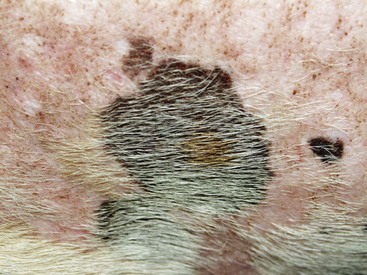
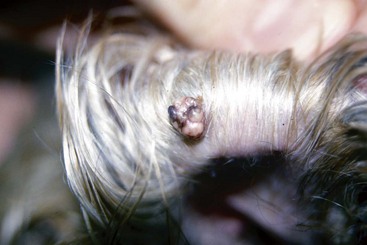
FIGURE 14-47 Hair Follicle Tumors.
A small, pigmented nodule. Note the similarity to basal cell tumors, apocrine tumors, and melanoma.
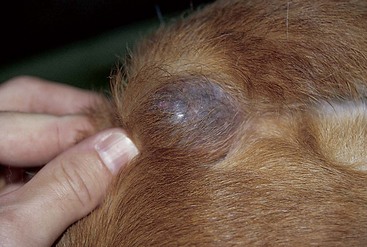
FIGURE 14-48 Hair Follicle Tumors.
This large cyst on the ventral thorax of an aged hound mix was associated with a follicular tumor.
Sebaceous Gland Tumors
Diagnosis
 Sebaceous hyperplasia/adenoma: cells exfoliate in groups and appear similar to normal sebaceous cells, with foamy pale blue cytoplasm and small dark nuclei.
Sebaceous hyperplasia/adenoma: cells exfoliate in groups and appear similar to normal sebaceous cells, with foamy pale blue cytoplasm and small dark nuclei. Sebaceous epithelioma: small, fairly uniform, sometimes melanotic epithelial cells with low numbers of sebaceous cells
Sebaceous epithelioma: small, fairly uniform, sometimes melanotic epithelial cells with low numbers of sebaceous cells Sebaceous hyperplasia: multiple enlarged mature sebaceous lobules with a single peripheral layer of basaloid germinal cells and a central duct. No mitotic figures are seen.
Sebaceous hyperplasia: multiple enlarged mature sebaceous lobules with a single peripheral layer of basaloid germinal cells and a central duct. No mitotic figures are seen. Sebaceous adenoma: similar to hyperplasia but with increased numbers of basaloid germinal cells and immature sebocytes. Low mitotic activity and loss of organization are noted around the central duct.
Sebaceous adenoma: similar to hyperplasia but with increased numbers of basaloid germinal cells and immature sebocytes. Low mitotic activity and loss of organization are noted around the central duct. Sebaceous epithelioma: multiple lobules of basaloid epithelial cells interspersed with reactive collagenous tissue and secondary inflammation. Fairly high mitotic activity has been demonstrated. Scattered areas of sebaceous differentiation, squamous metaplasia, or melanization may be observed.
Sebaceous epithelioma: multiple lobules of basaloid epithelial cells interspersed with reactive collagenous tissue and secondary inflammation. Fairly high mitotic activity has been demonstrated. Scattered areas of sebaceous differentiation, squamous metaplasia, or melanization may be observed.Treatment and Prognosis
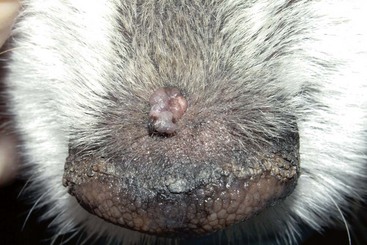
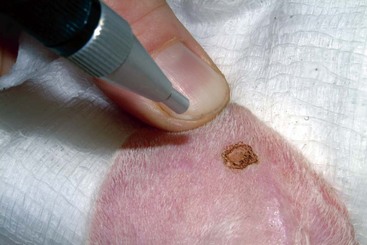
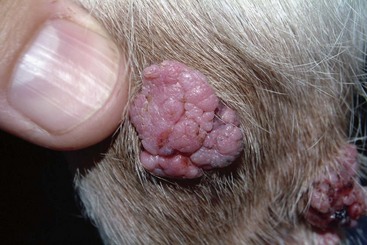
FIGURE 14-52 Sebaceous Gland Tumors.
This sebaceous adenoma on the nasal planum demonstrates the characteristic cauliflower appearance.
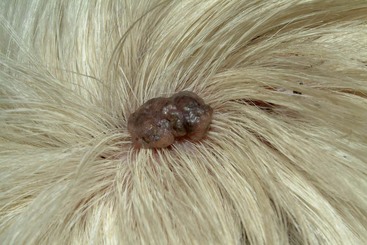
FIGURE 14-53 Sebaceous Gland Tumors.
This sebaceous adenoma had persisted for several years with little progression.