56 Lupoid onychodystrophy
INTRODUCTION
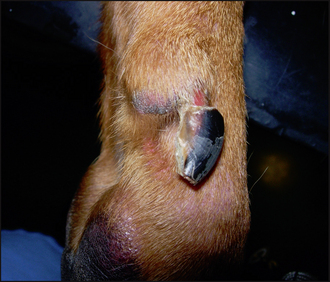
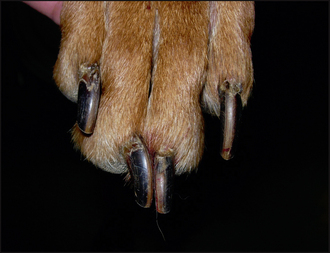
Lupoid onychitis, also known as symmetrical lupoid onychodystrophy, is considered to be an immune-mediated cutaneous reaction pattern. Often, the initial cause leads to secondary paronychia, which further contribute to the ongoing problem. The condition normally affects several claws on the feet, rather than just a single claw or a single foot and is characterized by progressive shedding of nails over a period of weeks to months with associated pain and paronychia. Histologically, it is characterized by a cell-rich interface dermatitis. Claw abnormalities are described using special terms and those used in this chapter are defined in Table 56.1.
Table 56.1 Various terms used to describe claw abnormalities in this case report
| Term | Visible abnormality of the claw |
|---|---|
| Onychitis | Inflammation of the claw |
| Onychodystrophy | Malformation of the claw |
| Onycholysis | Separation of claw from the claw bed |
| Onychomadesis | Sloughing of the claw |
| Paronychia | Inflammation of the claw bed |
| Onychalgia | Claw pain |
CASE HISTORY
The relevant history in this case was: