CHAPTER 3 Intraoral Radiographic Anatomy of the Cat
MAXILLARY CANINE TEETH
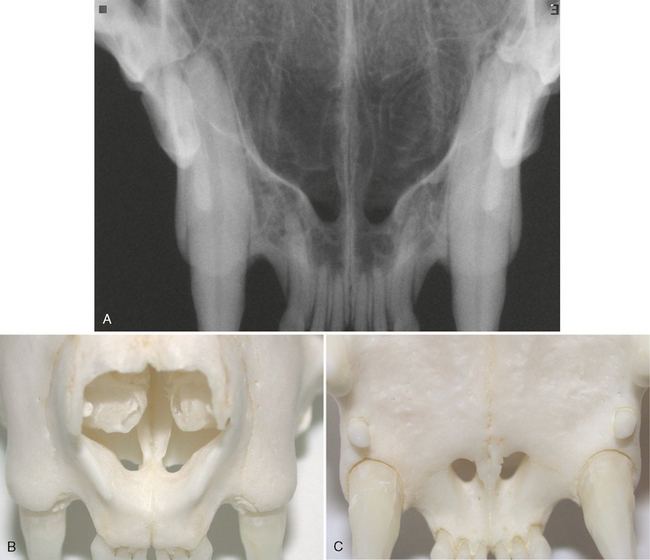
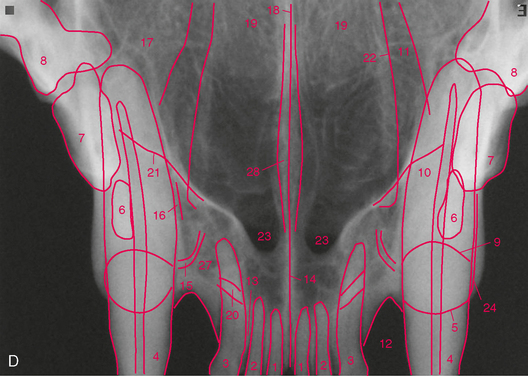
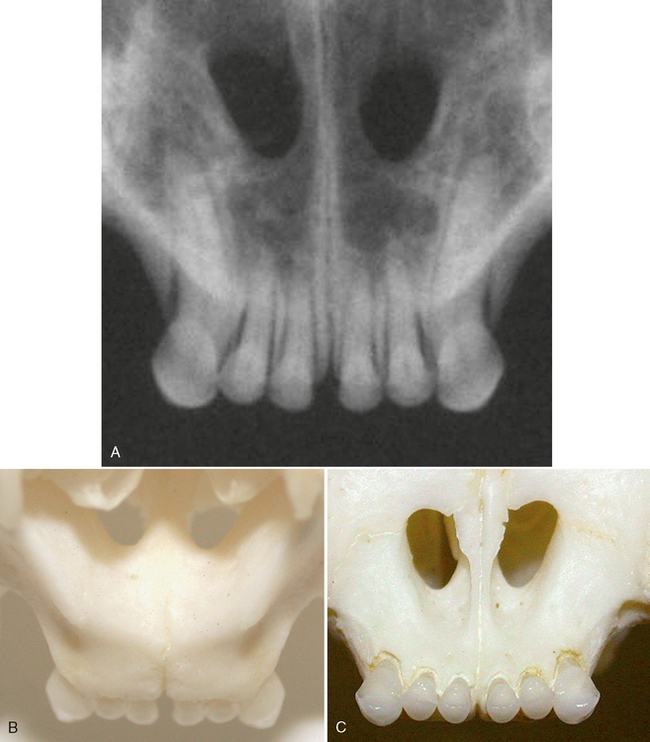
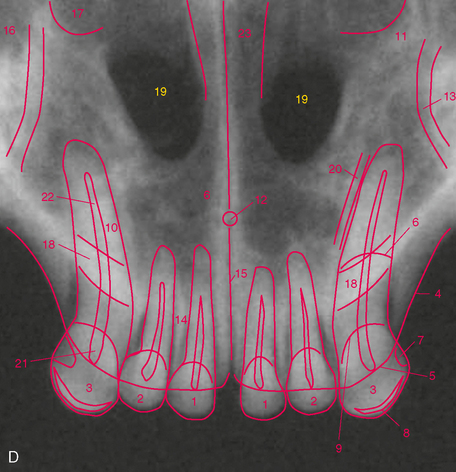
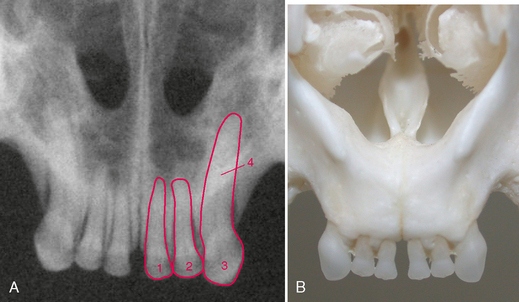
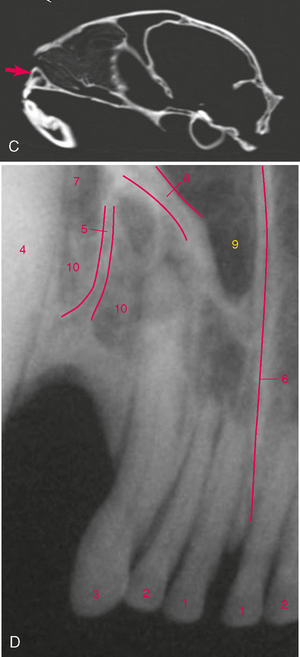
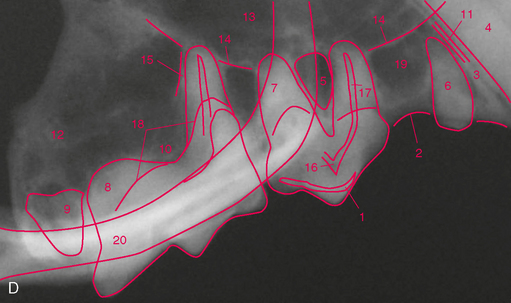
FIGURE 3-5 Normal adult cat canine teeth. A, Radiograph of the skull of an adult cat showing the canine teeth and surrounding structures. B, Dorsal view of prepared skull. C, Ventral (mirror) view of skull. D, Same radiograph as A.
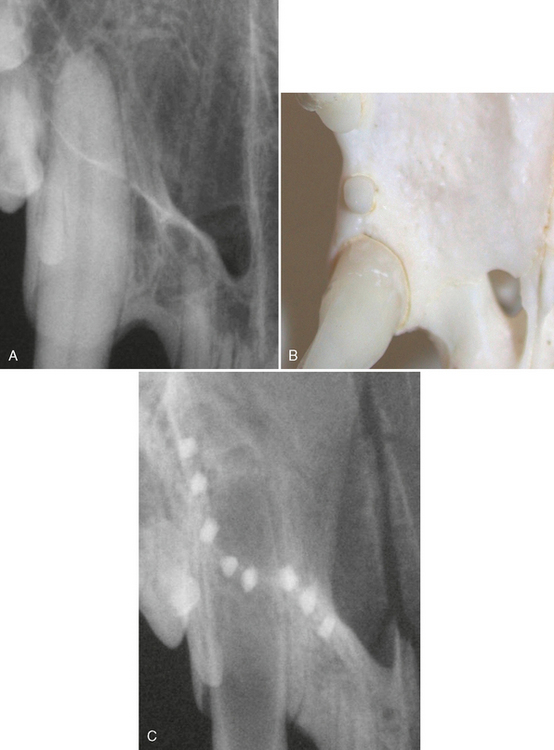
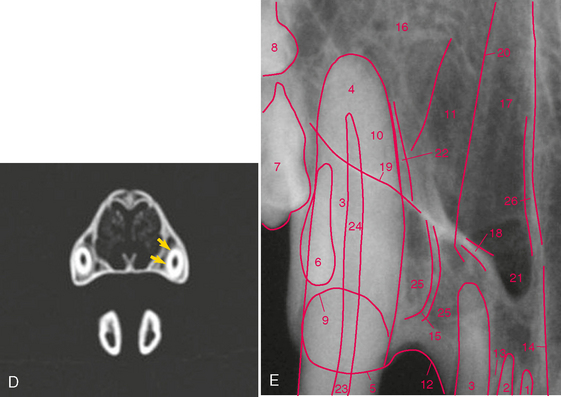
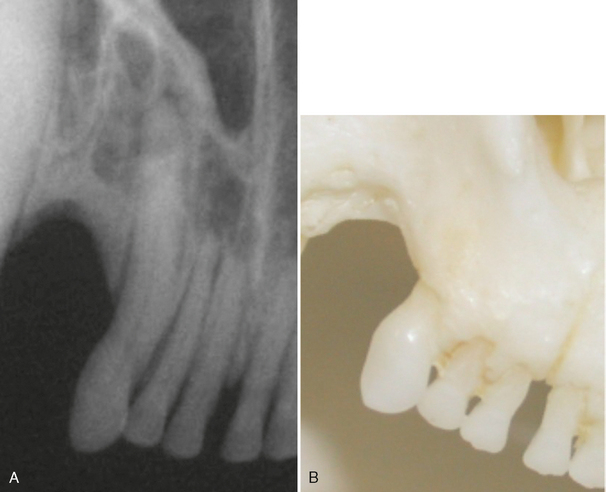
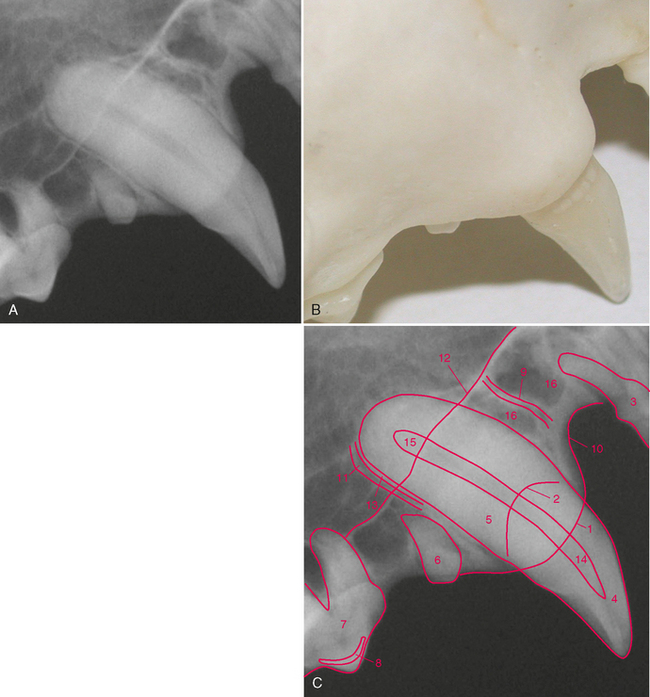
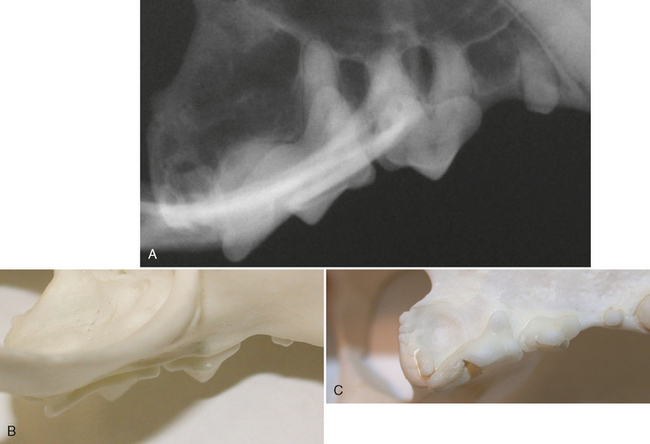
FIGURE 3-6 Normal adult cat canine tooth. A, Radiograph of the maxillary right canine tooth. B, Palatal view of prepared skull specimen. C, Radiograph illustrating the nasal surface of the alveolar process of the maxilla. Holes were drilled into the nasal surface of the maxilla bone where the nasal and palatal portions meet and these were filled with gutta percha. D, CT scan, transverse plane at mid-root of canine teeth (arrows). E, Same radiograph as in A.
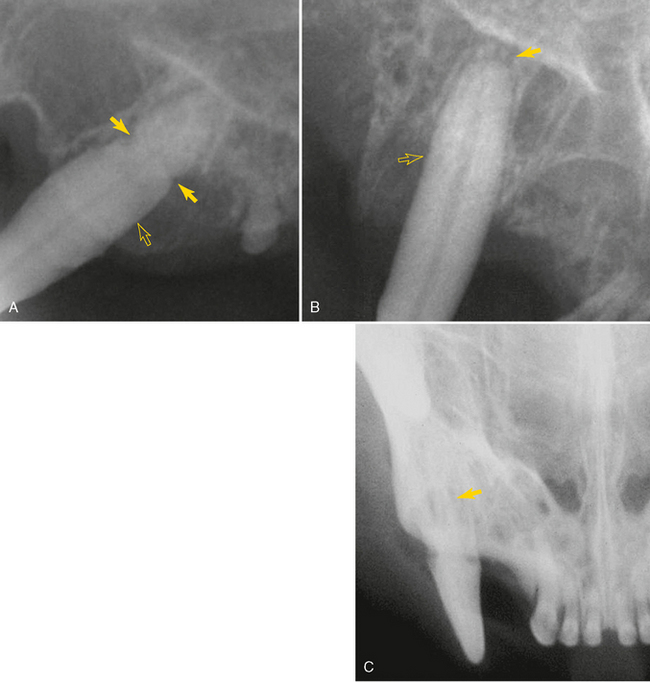
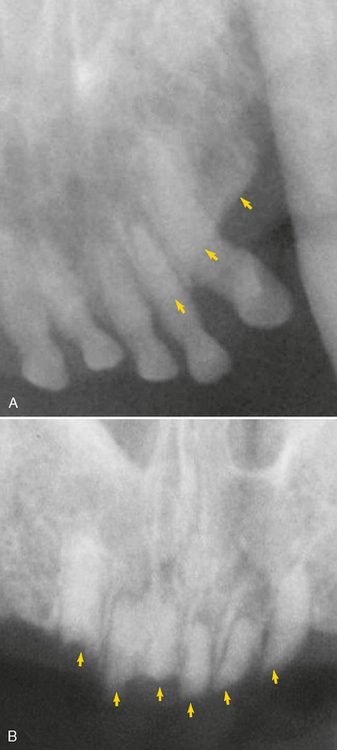
FIGURE 3-8 Radiographs of feline canine teeth demonstrating commonly found abnormalities. A, Radiograph of the left maxillary canine tooth in an adult cat demonstrating severe alveolar (attachment) bone loss (open arrow) and external root resorption (arrow) associated with severe periodontitis. B, Radiograph of right maxillary canine revealing loss of apical lamina dura (arrow) (endodontic disease, see Chapter 6) and alveolar bone loss (open arrow) (periodontitis, see Chapter 5). C, Radiograph of maxillary right canine revealing severe root resorption (arrow) typically seen with tooth resorption in feline canine teeth (see Chapter 7).