Chapter 209 Intracranial Pressure Monitoring
INTRODUCTION
Although a growing number of studies in humans have suggested decreased mortality rates and improved long-term outcome with ICP-guided therapy, a randomized clinical trial showing that ICP monitoring improves outcome has not been done. The “Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury” (published in 1995 and revised in 2007) outline the evidence-based recommendations for using ICP monitoring to improve the treatment and outcome from severe brain injury.4 Similar guidelines and recommendations were published in 2004 for the management of severe brain injury in infants and children. As yet, no specific guidelines have been established in veterinary medicine for treating severe brain injury. The standard of care has been primarily that of repeated and careful assessments of an animal’s neurologic status in an attempt to detect increases in ICP. Unfortunately, most clinical signs indicating life-threatening intracranial hypertension (ICH) occur as a result of damage to brain tissue, and therapies administered at this point often are ineffective. There are potential benefits gained by monitoring ICP, especially when one expects prolonged and/or life-threatening ICH (Box 209-1).4,5
DETERMINATION OF INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
Intracranial Pressure
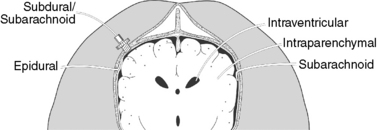
Locations for Monitoring Intracranial Pressure in the Brain
ICP monitoring commonly is done through a burr hole in the skull or a craniectomy site. It can be measured directly or reflected through measurement of CSF pressure or brain tissue pressure.2,3 CSF pressure measurements can be taken from the lateral ventricles or the cerebral subarachnoid space; brain tissue pressure measurements are taken intraparenchymally from within a cerebral hemisphere. Measurement of ICP from the brain’s surface may be taken epidurally or subdurally over a cerebral convexity1,2,4 (Figure 209-1).
Types of Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Devices
Pressure transducers convert ICP into a graded electrical signal that is recorded and displayed. They can be situated either intracranially or extracranially depending on the system used. Extracranial strain gauge type transducers communicate with the intracranial compartment via fluid-filled tubing and require that ICP measurements be taken at fixed reference points. Pressure transducers situated intracranially are incorporated into the tip of a catheter and implanted into one of several compartments of the brain. Some of the important considerations in choosing a transducer are listed in Box 209-2.2-4