Fig. 17.1
Light micrographs of serial paraffin sections of living mouse thymic tissues prepared by IVCT, which are stained with H&E (a, b) or immunostained for albumin (c, d), IgG1 (e, f), IgA (g, h), and IgM (i, j). Each micrograph (b, d, f, h, j) is a highly magnified view of area enclosed in squares in a, c, e, g, and i, respectively. Co cortex, M medulla, Cp capsule. All the proteins—albumin, IgG1, IgA, and IgM—are immunolocalized in blood vessel s at low magnification (arrowheads in a, c, e, g, i). At a higher magnification, both albumin and IgG1 are evenly immunolocalized in the interstitium of whole cortex (arrows in d, f). Inset in d shows immunocontrol without the primary antibody at the same magnification. However, both IgA and IgM immunostaining are detected less in the subcapsular cortex (arrows in h, j). Bars a, c, e, g, i 100 μm; b, d, f, h, j 50 μm
17.3 Distribution of Extrinsic BSA in Living Mouse Thymus
By IVCT, it has become clear that the injected BSA diffused out from blood vessel s of the corticomedullary area s but not from blood capillaries in the subcapsular areas of cortex. As shown in Fig. 17.2b, it did not leak out through the blood capillaries until 2 h after BSA injection. However, it leaked out earlier through the blood capillaries of connective tissues at 1 h with the same BSA concentration, as previously reported [19]. In addition, immunoreactive intensities of intravenously injected BSA in the interstitium were variously detected, depending on time intervals after the injection and also BSA concentration (Figs. 17.2 and 17.3). Therefore, these findings are compatible with the existence of functional barriers along blood capillaries of the subcapsular cortex , although molecular permeability through blood vessels in the corticomedullary areas is higher than that in the thymic cortex, as already reported [20]. As shown with albumin and BSA immunolocalizations in the thymic cortex of living mice prepared with IVCT, it is concluded that soluble serum protein s have difficulty in directly entering the thymic cortex because of the blood–thymus barrier , but they are diffused throughout the whole cortex from the corticomedullary areas.
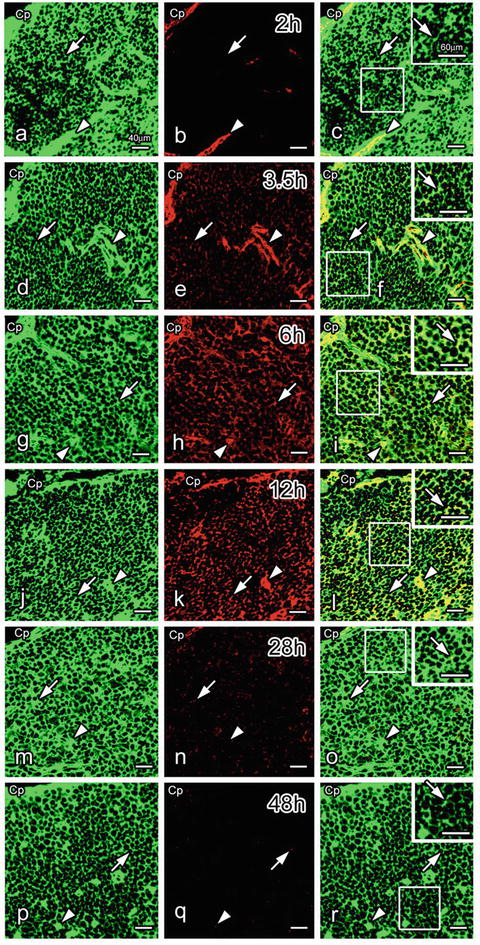

Fig. 17.2




Double immunofluorescence staining of thymic cortical tissues prepared with IVCT for albumin (green in a, d, g, j, m, p) and intravenously injected bovine serum albumin (BSA; red in b, e, h, k, n, q) at 2 (a–c), 3.5 (d–f), 6 (g–i), 12 (j–l), 28 (m–o), or 48 (p–r) h after BSA injection. Albumin (a, d, g, j, m, p) is immunolocalized in blood vessel s (arrowheads) and the interstitium of the whole cortex (arrows). At 2 h, BSA immunoreactivity is detected only in blood vessels (arrowheads in b, c). However, it is weakly detected in the interstitium at 3.5 h (arrows in e, f) in addition to the blood vessels (arrowheads in e, f). At 6 and 12 h, it is more widely seen in the interstitium (arrows in h, i, k, l), although it is detected less in the blood vessels (arrowheads in n, o, q, r) and the interstitium (arrows in n, o, q, r) at 28 and 48 h. Cp capsule. Bars 40 μm, insets 60 μm
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


