Fig. 45.1
Mouse lung tissues prepared by IVCT at 5 s (a), 1 min (b), and 5 min (c–f) after the melanoma cell injection. HE-stained morphological features (HE; a–d) and distributions of QDs (QD ; e, f). The section showing the red QD-fluorescence images with ultraviolet light (QD; e, f) is next to the serial paraffin section showing the HE-stained image (c, d). Black arrow: visceral pleura, Black arrowheads: melanoma cells with large nuclei, White arrowheads: grouping platelets, Black double-arrowheads: congested erythrocytes , White double-arrowheads: large platelet aggregates occupy their lumens, A: air space. Bars: 25 μm
45.3 Visualization of Platelet Activation at Five Minutes
Next, to evaluate the molecular cascade activation of platelets for signal transduction, the phosphorylation of Src was immunohistochemically examined. Platelets have been well documented to possess large amounts of Src-family kinases [14, 15], which generally have two phosphorylation sites of tyrosine (Y), Y418 and Y527 [16]. It has already been reported that the combination of Y418 phosphorylation and Y527 dephosphorylation indicates the full activation of Src, whereas another combination of both Y418 and Y527 phosphorylation indicates partial Src activation [14]. To confirm the existence of Src molecules in the present aggregated platelet s, we performed immunostaining for Src. At 5 min after the melanoma cell injection, large masses of platelet aggregates (white double-arrowheads in Fig. 45.2a) were strongly immunopositive for Src in some blood vessel s (black arrows in Fig. 45.2a). Such platelet aggregates were also fluorescently immunostained with anti-phosphorylated-Y418 (p418) antibody (green in Fig. 45.2d) inside the red fluorescence contours of platelets immunostained for CD42c (white arrowheads in Fig. 45.2d). Thus, it is suggested that Src-family kinases in the aggregated platelets were mostly in active molecular states. On the other hand, phosphorylation of Y527-Src (p527) was still detected in the aggregated platelets (black arrows in Fig. 45.2b). Many aggregated platelets were double immunopositive for both Y418 and Y527 phosphorylations. These findings indicate that Src in the aggregated platelets started partial activation at 5 min after the melanoma cell injection.
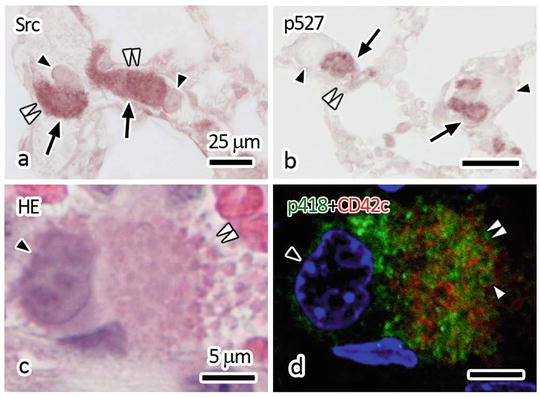

Fig. 45.2
Immunostaining images of Src (a) and p527-Src (b) and double fluorescent immunostaining image of p418-Src (green in d) and CD42c (red in d) with nuclear DAPI staining (blue in d). (c, d) The tissue sections were firstly immunostained and observed under a confocal laser scanning microscope (d) and subsequently stained with HE and observed under a light microscope (c). Black arrowheads: melanoma cell s , Black arrows: immune-positive reaction, White double-arrowheads: platelet aggregations, White arrowhead: immunopositive regions for p418-Src inside platelet cell membranes shown by the CD42c immunostaining. Bars: 25 μm in (a, b), 5 μm in (c, d)
45.4 Visualization of Fibrin Formation in Paraffin Sections
To verify such formation of fibrin thrombu s , a specific antibody against fibrin monomer , F405 antibody, was used for immunohistochemistry in the lung tissues at 5 min after the melanoma cell injection. Fibrin monomers are the earliest reaction products of fibrin molecules derived from fibrinogen , and the F405 antibody is a specific monoclonal antibody against them, which has been clinically used for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) as highly sensitive detection of DIC for human plasma samples [11]. Common microwave treatment in citrate buffer was essential to obtain immunoreactivity for the F405 antibody in paraffin-embedded tissue sections, even for the IVCT-FS-prepared samples. Serial paraffin sections of IVCT-prepared lung tissues, in which QDs had already been injected at 5 min after the melanoma cell injection, were immunostained for the fibrin monomer and fibrinogen (Fig. 45.3). In some large blood vessel s stacked with melanoma cells (arrowheads in Fig. 45.3a), fluorescent QDs red in color were rarely detected (Fig. 45.3c). However, in other alveolar capillaries connecting with large blood vessel s , QDs were clearly observed (white arrows in Fig. 45.3c). The fibrin immunostaining was often detected as spotty patterns between melanoma cells in the large blood vessels (black arrows in Fig. 45.3b). In the blood vessels, where fibrin was positively immunostained, the immunoreaction intensity of fibrinogen was very strongly detected (black arrows in Fig. 45.3d). The antibody against fibrinogen recognized fibrin and fibrinogen immunoreaction was widely positive in all fibrin-immunopositive areas, suggesting initiation of fibrin formation. Thus, the initial compact products of fibrin thrombus as well as fibrinogen accumulation were morphofunctionally visualized in the blood vessels of melanoma cell metastasis by IVCT.
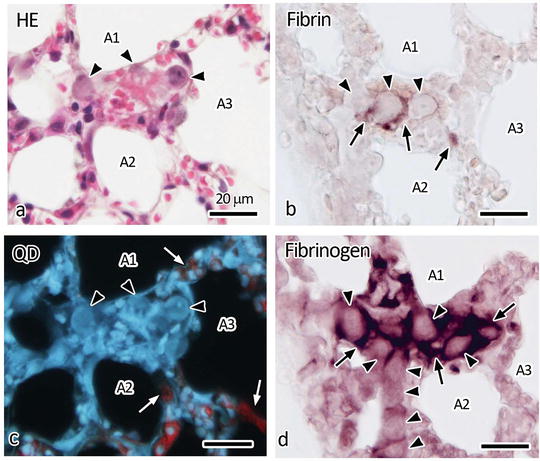

Fig. 45.3




Light microscopic images of living mouse lung tissues at 5 min after the melanoma cell injection. Serial sections are HE stained (a) and detected for QDs under UV light (c) or immunostained for fibrin with F405 antibody (b) and fibrinogen (d). Black arrows: immune-positive reaction, Black arrowheads: melanoma cells , White arrows: red fluorescent signals derived from QDs detected in some parts of alveolar capillaries connecting larger blood vessel s , A1–A3: air spaces in alveoli. Bars: 20 μm
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


