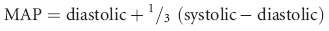Chapter 203 Hemodynamic Monitoring
BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING
Hypotension is defined as systolic blood pressure less than 80 mmHg or mean arterial pressure of less than 60 mmHg in either species. Causes of hypotension include decreased cardiac output secondary to reduced circulating volume, myocardial failure, severe bradyarrhythmia or tachyarrhythmia, or decreased systemic vascular resistance due to peripheral vasodilation secondary to sepsis or systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Treatment of hypotension should always be aimed at correcting the underlying problem (see Chapter 6, Hypotension).
Invasive Blood Pressure Monitoring
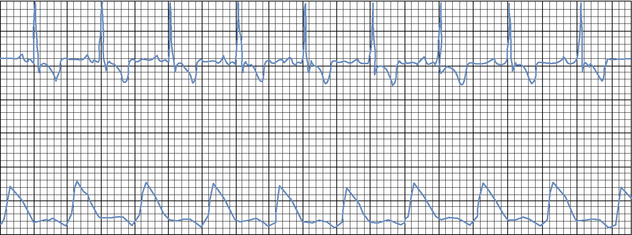
When a display monitor is employed, continuous direct arterial pressure monitoring allows for observation of pressure changes and trends (Figure 203-1). Another advantage of an arterial catheter is that it can be used to obtain blood samples for arterial blood gas analysis and laboratory testing. Despite its many advantages, direct monitoring should be limited to critically ill patients that will benefit from having their blood pressure measured frequently over a defined period, such as during anesthesia in a patient with a high anesthetic risk or while hospitalized in an intensive care unit.
Direct arterial blood pressure monitoring in patients with hypovolemic or septic shock is extremely helpful in guiding volume replacement and the use of pressors to maintain an acceptable systemic blood pressure. By evaluating the pressure waveform with various arrhythmias, the clinician can distinguish which ones are causing poor pressures or even pulse deficits, and this can influence the decision as to whether or not to initiate treatment. Direct arterial blood pressure monitoring is not indicated in active, relatively healthy patients because of possible morbidity from arterial catheter placement and risk of the patient pulling the catheter out or disconnecting the arterial line and causing significant hemorrhage. Animals with arterial catheters must be strictly supervised at all times (see Chapter 49, Arterial Catheterization).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree