Chapter 12 Tropical freshwater fish
Around 80–90% of tropical freshwater fish are captive bred, with typical hot spots of production being Singapore (e.g. Fig. 12.1), Malaysia, Israel, Florida and the Czech and Slovak Republics. Some important fish to the industry are still wild-caught however, such as the cardinal tetra (Paracheirodon axelrodi) from the Amazon basin.
For general information on fish consultations, examination, nursing care and anaesthesia, see Chapter 11, Goldfish and Koi.
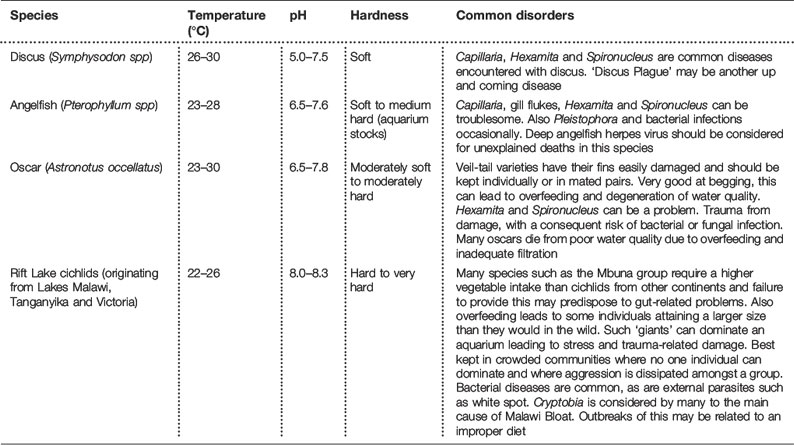
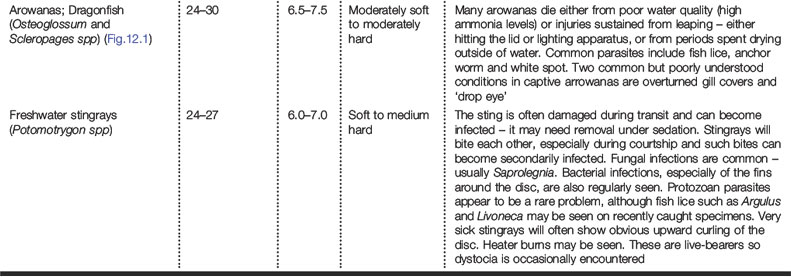
Recommended water quality parameters for different aquariums are listed in Table 12.1. Water hardness is measured in a variety of different ways with mg CaCO3 as international standard. Conversion factors from other units are given in Table 12.2. Common species of tropical freshwater fish presented to the veterinarian are listed in Table 12.3.
Table 12.1 Recommended parameters for: typical community aquarium; rift lake aquarium; discus aquarium
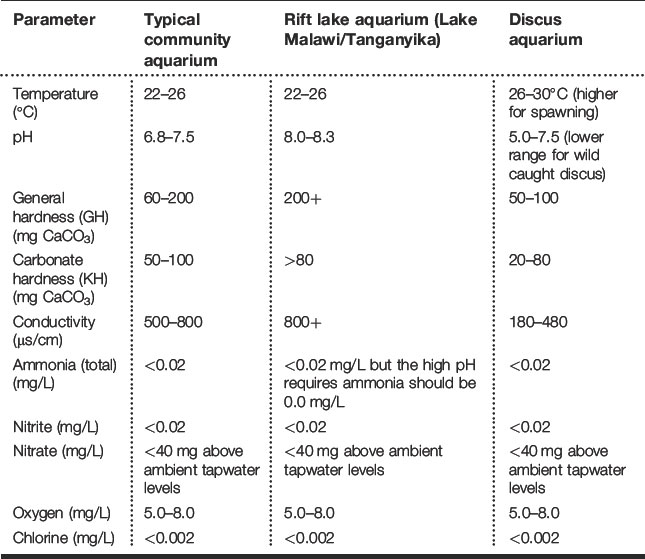
Table 12.2 Water hardness conversion factors
| Unit | Conversion factor to (mg CaCO3) |
|---|---|
| dH | 17.85 |
| Clark | 0.07 |
| f (French) | 0.1 |
| Hardness | 1 |
| Milliequivalent (mEq) | 0.02 |
Skin disorders
Structure and function of skin (see Ch. 11, Goldfish and Koi).
Differential diagnoses for skin disorders
Erosions and ulceration including fin rot
Nodules and non-healing wounds
Changes in pigmentation and colour
Ectoparasites
Neoplasia
Other findings on clinical examination
Investigations
Treatment/specific therapy
Table 12.4 Recommended dose rate for benzalkonium chloride
| Benzalkonium chloride concentration (mg/L) | Duration of bath (min) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 5–10 |
| 5 | 30 |
| 2 | 60 |
| 1 | Several hours |
Table 12.5 Recommended chloramine-T concentrations for different pH and water hardness combinations
| pH | Concentration in soft water (mg/L) | Concentration in hard water (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| 6.0 | 2.5 | 7.0 |
| 6.5 | 5.0 | 10.0 |
| 7.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 |
| 7.5 | 18.0 | 18.0 |
| 8.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 |