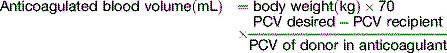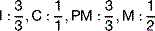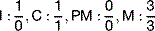Chapter 1 Ferrets
Ferrets (Mustela putorius furo) are thought to be a domesticated form of the European polecat (M. putorius) and, not surprisingly, have a history extending back alongside the domestic rabbit. Originally kept as working animals, selective breeding for colour varieties and temperament has resulted in a significant rise in their being kept as pets and show animals.
Table 1.1 The ferret: Key facts
| Average life span (years) | 5–8+ | |
| Weight (kg) Male | 1.0–2.0 kg | |
| Female | 0.5–1.0 kg | |
| Body temperature (°C) | 37.8–40 | |
| Respiratory rate (per min) | 33–36 | |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 180–250 | |
| Gestation (days) | 41–42 | |
| Age at weaning (weeks) | 6–8 | |
| Sexual maturity | 4–8 months (in the first spring following birth – typically March) | |
Consultation and handling
Always weigh the ferret whenever examined, to monitor weight trends. A healthy ferret above ground walks with a dorsal flexure in its back. Hind-leg paresis can be a non-specific sign of ill-health in the ferret due to weakness of the muscle groups needed to maintain this position.
Nursing care
Thermoregulation
For general principles, see Thermoregulation under ‘Nursing Care’, in Ch. 2, Rabbits.
Fluid therapy
The normal maintenance daily water intake for ferrets is 75–100 mL/kg per day. In ferrets, the choice of fluid used is indicated as with other mammals. Fluid replacement calculations are as for other species. All fluids should be warmed to 38°C.
Recommended fluid replacement rates for ferrets
Nutritional support
Analgesia
Analgesic doses for ferrets are given in Table 1.2.
Table 1.2 The ferret: Analgesic doses
| Analgesic | Dose |
|---|---|
| Buprenorphine | 0.01–0.03 mg/kg s.c., i.m., i.v. every 8–12 h |
| Butorphanol | 0.1–0.5 mg/kg s.c., i.m. or i.v. every 2–4 h |
| Carprofen | 1.0–2.0 mg/kg s.c., i.m. every 12–24 h |
| Ketoprofen | 1.0 mg/kg s.c., i.m. every 12–24 h |
| Meloxicam | 0.1–0.3 mg/kg s.c. or p.o. every 24 h |
| Morphine | 0.5–5.0 mg/kg s.c., i.m. every 2–6 h |
| Pethidine | 5–10 mg/kg s.c., i.m., i.v. every 2–4 h |
| Nalbuphine | 0.5–1.5 mg/kg i.m., i.v. every 2–3 h |
Anaesthesia
Ferrets have a very short gut transit time of around 3 h, therefore if starved overnight there is a high risk of hypoglycaemia. Therefore, do not starve preoperatively.
Skin disorders
Findings on clinical examination
Investigations
Treatment/specific therapy
Respiratory tract disorders
Findings on clinical examination
Investigations
Treatment/specific therapy
Gastrointestinal tract disorders
The permanent incisors erupt at around 6–8 weeks while the other permanents are usually through by 10 weeks.