Chapter 3 Electrocardiography
INDICATIONS AND ROLE OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM IN CLINICAL PRACTICE
PRINCIPLES OF ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
Standard Lead Systems
• The standard leads are I, II, III, aVR, aVL, and aVF (Figure 3-1, Box 3-1). Placement of electrodes to generate each lead is illustrated in Figure 3-2.
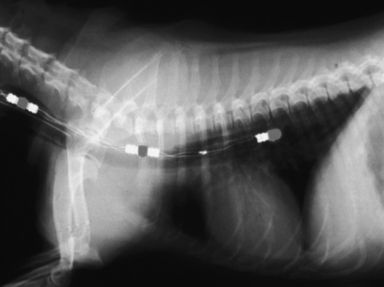
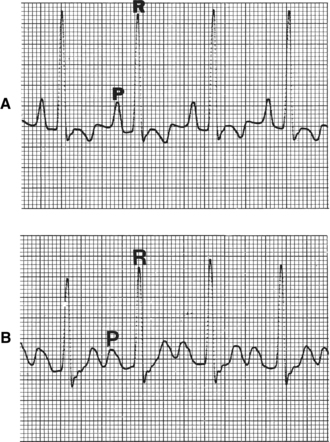
• Esophageal ECG electrode lead for surgical monitoring (Figure 3-3.) This technique is very useful as complexes recorded are increased in size, providing an increased accuracy for diagnosing an arrhythmia during surgery.
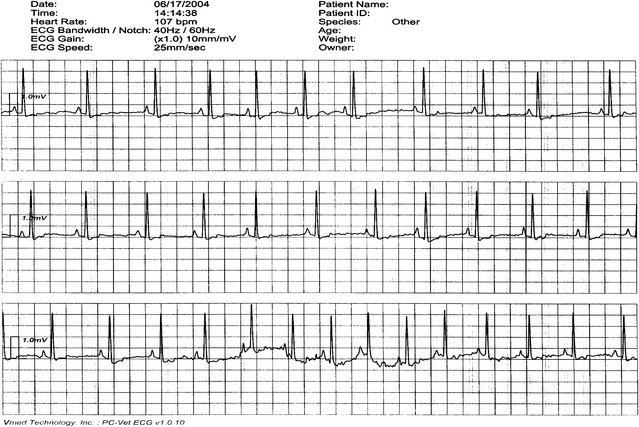
• Hand-held, wireless ECG and ECG real time computer display represents new technology for recording electrocardiograms (Figures 3-4 and 3-5.)
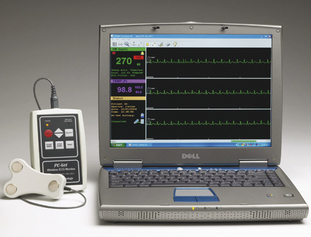
Figure 3-4 Hand-held, wireless ECG and ECG real time computer display.
(Courtesy Vmed Technology, Redmond, Wash. www.vmedtech.com.)
RECORDING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
CARDIAC CONDUCTION AND GENESIS OF WAVEFORMS
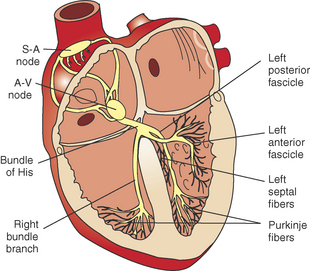
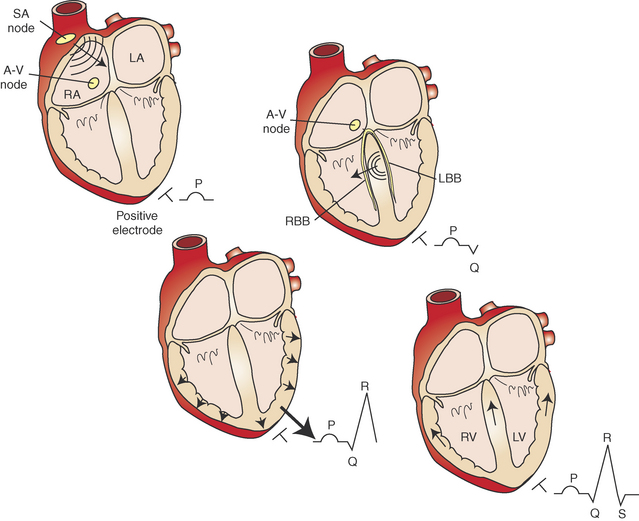
• The function of the cardiac conduction system is to coordinate the contraction and relaxation of the four cardiac chambers (Figures 3-6 and 3-7).
• For each cardiac cycle, the initial impulse originates in the sinoatrial (SA) node located in the wall of the right atrium near the entrance of the cranial vena cava. This impulse is rapidly propagated through the atrial myocardium, resulting in depolarization of the atria. Depolarization of the atria results in the P wave and atrial contraction. The initial SA nodal impulse is small and does not produce an electrocardiographic change on the body’s surface.
EVALUATION OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
• Determine the approximate mean electrical axis (MEA)
• The MEA refers to the direction of the net ventricular depolarization and refers solely to the QRS complex. If there is significant right ventricular hypertrophy, then the MEA will shift to the right. Because the left ventricle is normally the dominant ventricle, the normal MEA is to the left. A degree system is used—if the MEA is directly to the left, then it is said to be 0 degrees; if the MEA is directly downward, then it is 90 degrees, and if it is directly to the right, then it is 180 degrees. The MEA of the normal dog is 40 to 100 degrees. For the cat, the MEA is more variable, ranging from 0 to 160 degrees.
• The MEA may be determined using the six standard leads and the Bailey axis system (see Figure 3-1). If there is a lead with isoelectric QRS complexes, then the MEA equates to the lead on the Bailey axis perpendicular to the isoelectric lead.
• The MEA may also be determined by plotting the net amplitude of a lead I QRS complex (horizontal axis) and the net amplitude of a lead aVF QRS (vertical axis). The intersection will provide the vector equal to the MEA (see Figure 3-1).
Table 3-1 Normal Canine and Feline ECG Values*
| Canine | Feline | |
|---|---|---|
| Heart rate (HR) | Puppy: 70-220 bpm | 120-240 bpm |
| Toy breeds: 70-180 bpm | ||
| Standard: 70-160 bpm | ||
| Giant breeds: 60-140 bpm | ||
| Rhythm | Sinus rhythm | Sinus rhythm |
| Sinus arrhythmia | ||
| Wandering pacemaker | ||
| P wave | ||
| Height | Maximum: 0.4 mV | Maximum: 0.2 mV |
| Width | Maximum: 0.04 s (Giant breeds 0.05 s) | Maximum: 0.04 s |
| PR interval | 0.06-0.13 s | 0.05-0.09 s |
| QRS | ||
| Height | Large breeds: 3.0 mV maximum† | Maximum: 0.9 mV |
| Small breeds: 2.5 mV maximum | ||
| Width | Large breeds: 0.06 s maximum | Maximum: 0.04 s |
| Small breeds: 0.05 s maximum | ||
| ST segment | ||
| Depression | No more than 0.2 mV | None |
| Elevation | No more than 0.15 mV | None |
| QT interval | 0.15-0.25 s at normal HR | 0.12-0.18 s at normal HR |
| T waves | May be positive, negative, or biphasic | usually positive and < 0.3 mV |
| Amplitude range ± 0.05-1.0 mV in any lead | ||
| Not more than ¼ of R wave amplitude | ||
| Electrical axis | +40 to + 100 | 0 ± 160 |
| Chest leads | ||
| CV5RL (rV2) | T positive; R < 3.0 mV | |
| CV6LL (v2) | S < 0.8 mV; R < 3.0 mV | R < 1.0 mV |
| CV6LU (V4) | S < 0.7 mV; R < 3.0 mV | R < 1.0 mV |
| V10 | QRS negative; T negative except in Chihuahua | T negative. R wave/Q wave < 1 |
S, Second.
* Measurements are made in lead II unless otherwise stated.