Chapter 6 Diseases of the Integumentary System
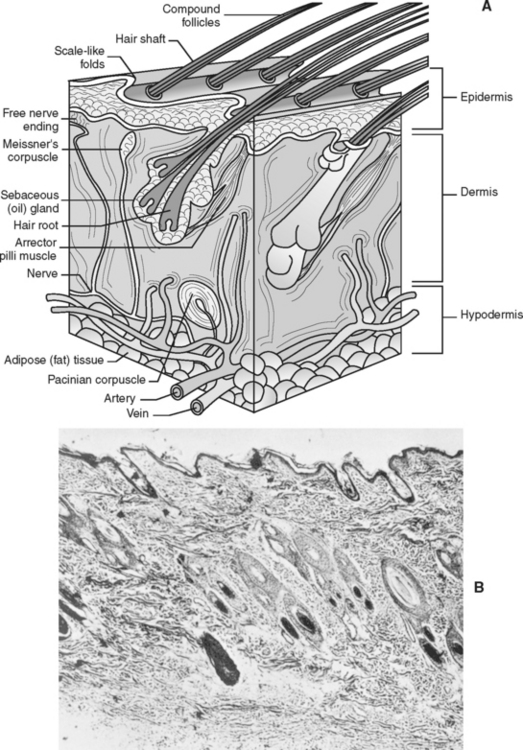
The skin makes up the largest organ system in the body. It comprises approximately 24% of the total body weight of a newborn puppy and about 12% of the body weight of an adult animal. It consists of three distinct layers: the epidermis, the dermis, and the hypodermis, or subcuticular layer (Fig. 6-1) (refer to an anatomy and physiology textbook for the exact function of each layer). The skin serves as a barrier between the animal’s body and the environment. It not only protects the animal from physical, chemical, and microbiological injury, but the sensory organs found in the skin allow the animal to feel pain, heat, cold, touch, and pressure. The skin is also a storage depot for electrolytes, water, proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, and it assists in the activation of vitamin D by solar energy.
The hypodermis stores fat for insulation and energy reserves. The animal’s skin has many functions:
ECTOPARASITES
Ear Mites (Otodectes cynotis)
Ear mites live on the surface of the skin in the external ear canal, feeding on epidermal debris (Fig. 6-2).

Figure 6-2 Adult male ear mite, Otodectes cynotis.
(From Hendrix CM, Robinson E: Diagnostic parasitology for veterinary technicians, ed 3, St Louis, 2006, Mosby, by permission.)
DIAGNOSIS
TREATMENT
Thiabendazole/neomycin/dexamethasone (Tresaderm): 5 to 15 drops twice a day topically to ear canals
Piperonyl butoxide, pyrethrins (Otomite): 4 to 15 drops daily in ear canals
Ivermectin (off-label uses): 300 μg/kg subcutaneously (SQ) or orally (PO) (repeat in 14 days)
Fleas (Ctenocephalides spp.)
Fleas are blood-sucking ectoparasites that feed sporadically on mammals and birds (Fig. 6-3). Fleas produce severe skin irritation as a result of their frequent bites. Flea saliva is highly antigenic in some animals and will produce an allergic dermatitis. Fleas can act as vectors for diseases and as intermediary hosts for the dog tapeworm (Dipylidium canium). Pets, as well as their environment, can become infested with massive numbers of fleas.
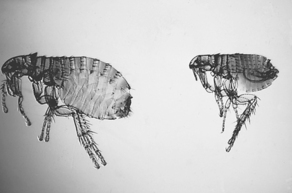
Figure 6-3 Adult male and female Ctenocephalides felis, cat fleas, the most common flea found on dogs and cats.
(From Hendrix CM, Robinson E: Diagnostic parasitology for veterinary technicians, ed 3, St Louis, 2006, Mosby, by permission.)
CLINICAL SIGNS
TREATMENT
Systemics
Program: Lufenuron, the active ingredient, is absorbed by the fatty tissue and slowly distributed to the bloodstream. This ingredient interferes with the synthesis of chitin, a necessary element in flea development. It is given by tablet once monthly or every 6 months by injection to cats. It takes 30 to 60 days to reach full effectiveness. Adult fleas may continue to be seen on the animal.
Frontline: Apply monthly to skin.
INFORMATION FOR CLIENTS
Ticks (Ixodes spp. and Argasid spp.)
Ticks are seen commonly on outdoor dogs and cats, especially during the summer months. These blood-sucking, arthropod parasites are not host specific and will infest all warm-blooded animals in the area (including humans). Heavy infestation may produce anemia in the host. Ticks also can transmit many bacterial, viral, rickettsial, and protozoan diseases. Lyme disease is one high-profile example of tick-borne disease. Ticks are divided into two main families: Ixodidae (hard ticks) and Argasidae (soft ticks). Most of the commonly found ticks belong to the Ixodidae family. Some of the best known members of this family include Rhipicephalus sanguineus (the brown dog tick (Fig. 6-4), Dermacentor variabilis (the American dog tick), and Amblyomma spp. All but Rhipicephalus spp. gain access to the host outdoors. Rhipicephalus spp. typically inhabit buildings and kennels. One soft tick, the spinose ear tick (Otobius megnini) can be found in the ear canals of dogs and cats in the southwestern United States.
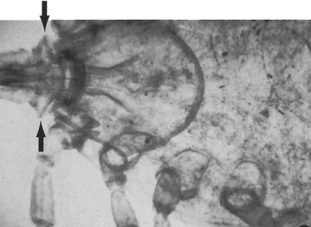
Figure 6-4 Rhipicephalus sanguineus (brown dog tick) invades both kennel and household environments.
(From Hendrix CM, Robinson E: Diagnostic parasitology for veterinary technicians, ed 3, St Louis, 2006, Mosby, by permission.)
TREATMENT
Durakyl Pet Dip (DVM Pharmaceuticals, Miami, Fla.)
VIP Flea and Tick Powder (Veterinary Products Laboratories, Phoenix, Ariz.)
Permectrin Pet, Yard, and Kennel Spray (Bio-Ceutic, St Joseph, Mo.)
Information for Clients
Demodectic Mange
Demodex canis, a cigar-shaped mite, lives within the hair follicles of most dogs and some cats (Fig. 6-5). These mites spend their entire life cycle on the host. In most dogs, the immune system holds the number of mites in check; however, in dogs with compromised immune systems (such as puppies with poor nutrition or other parasites, or dogs with chronic disease), the number of mites becomes excessive, causing disease. There appears to be a hereditary predisposition to demodectic mange, and certain breeds seem to be at greater risk.
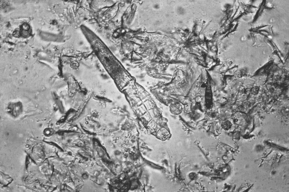
Figure 6-5 Adult Demodex canis. These mites resemble eight-legged alligators.
(From Hendrix CM, Robinson E: Diagnostic parasitology for veterinary technicians, ed 3, St Louis, 2006, Mosby, by permission.)
CLINICAL SIGNS (LOCALIZED DEMODEX)
DIAGNOSIS
TREATMENT
Generalized or severe localized
Sarcoptic Mange (Scabies)
Scabies is an intensely pruritic, contagious disease of animals. The mite, Sarcoptes scabiei var. canis, has a rounded body with four pairs of legs (Fig. 6-6). The female mite burrows into the epidermis and lays eggs. This burrowing produces intense itching and inflammation within the skin. Scabies can occur in dogs of any age, sex, or breed. Humans may experience development of visible lesions after exposure to infected animals; however, the mites do not survive off the animal host for longer than a few days. If the owner experiences development of small, red papules on his or her skin, a medical doctor should be consulted.
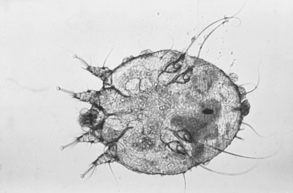
Figure 6-6 Adult Sarcoptes scabiei mite that causes scabies, an intensely pruritic disease.
(From Hendrix CM, Robinson E: Diagnostic parasitology for veterinary technicians, ed 3, St Louis, 2006, Mosby, by permission.)
DIAGNOSIS
INFORMATION FOR CLIENTS
Cuterebra “Warbles”
The Cuterebra fly lays eggs in the soil. These eggs mature into a larval stage similar to a grub that directly penetrates the host’s skin (Fig. 6-7, see also Color Plate 5). Here, in a subcutaneous pocket, the larva continues to mature, finally leaving the wound to become an adult fly. A fistula or opening in the swelling allows the larva to breathe while maturing; the larva can be seen moving up and down in the opening to the fistula.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree