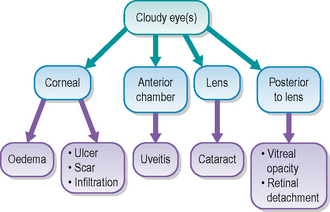
26 Corneal endothelial dystrophy
CLINICAL EXAMINATION
Intraocular examination is unremarkable – details might be hazy but the use of distant direct ophthalmoscopy will help to determine whether the lens is clear or is cataractous, while indirect ophthalmoscopy will assist in evaluating the fundus.