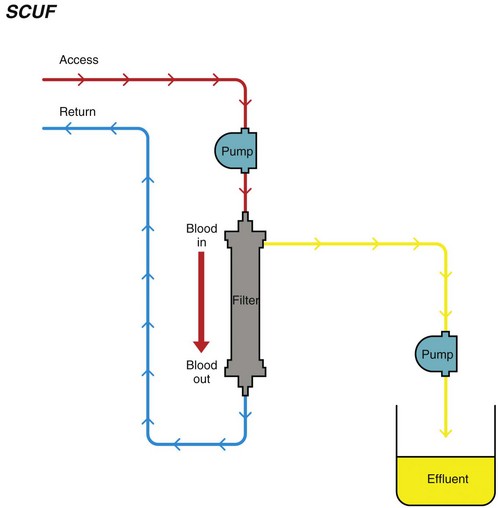
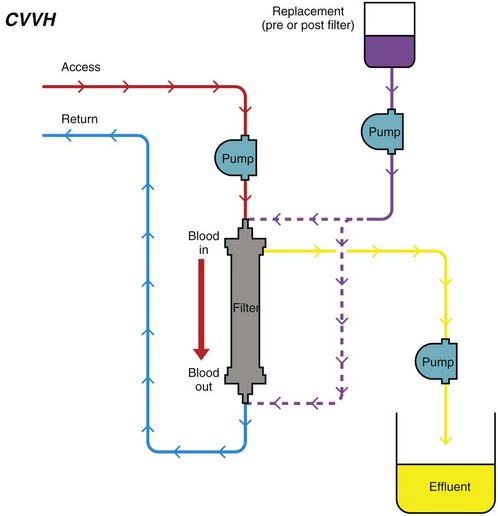
Chapter 192 Slow continuous ultrafiltration (SCUF) (Figure 192-1) is a purely convective modality in which a positive transmembrane pressure forces fluid (ultrafiltrate) out of the blood and the hemoconcentrated blood is returned to the patient. In human medicine, SCUF is used widely for the treatment of diuretic-resistant congestive heart failure. Its utility in veterinary medicine currently is under investigation. Figure 192-1 Slow continuous ultrafiltration (SCUF) is a purely convective modality that generates ultrafiltrate that is not replaced. (Used with permission, Veterinary Learning Systems.) Continuous venovenous hemofiltration (CVVH) (Figure 192-2) also is a purely convective modality; however, unlike SCUF, the ultrafiltrate is replaced with a sterile balanced electrolyte solution. The solution can be added to the blood before or after it passes through the dialyzer. In a postdialyzer configuration, a positive transmembrane pressure forces fluid out of the blood, which increases hemoconcentration. Before the patient’s blood is returned, replacement fluids are added to restore it to physiologic packed cell volume. This is an extremely effective way to remove uremic toxins; however, as the blood becomes hemoconcentrated, there is a risk that the dialyzer will sludge and clot. This limits the amount of fluid that can be removed by CVVH to approximately 25% of blood plasma volume. Alternatively, replacement fluids can be added to the blood before it passes through the dialyzer. The diluted blood then enters the dialyzer, where the excess fluid is removed by convection. Although this is less likely to result in dialyzer clotting, the prefilter arrangement is significantly less effective in removing uremic toxins. Figure 192-2 Continuous venovenous hemofiltration (CVVH) is a convective modality that generates ultrafiltrate. Unlike in slow continuous ultrafiltration, the ultrafiltrate is replaced with a sterile balanced electrolyte solution. This fluid can be added before or after the blood passes through the dialyzer. (Used with permission, Veterinary Learning Systems.)
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Modalities
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


