7 Cheilitis in a guinea pig
Introduction
Guinea pigs generally fare well in captivity (Box 7.1), but are susceptible to many stressors. Careful attention should be paid to husbandry conditions both to reduce various diseases and also to optimize the environment during recovery.
BOX 7.1 Ecology of guinea pigs
• Originally from the Andes, guinea pigs are domesticated descendants of wild cavies. Therefore they do not exist naturally in the wild
• Normal habitat of cavies: grassy plains. Seek shelter in burrows, crevices or tunnels in vegetation. Crepuscular activity
• Social groups, usually consisting of several sows, one boar and offspring. Communicate primarily using vocalization
• Reproduction: gestation 59–72 days (average 63–68 days). Litter of 1–6 pups (average 3). Precocial young. Pelvic symphysis usually fuses at 9–12 months of age in the female, and dystocia is likely if the initial pregnancy occurs after this
Clinical Examination
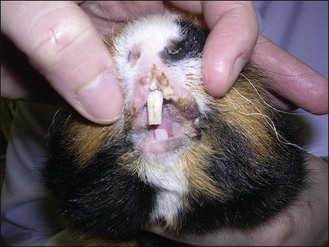
The guinea pig (Fig. 7.1) was examined with the following findings:
The companion animal had some lesions, but these were much less severe.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES
The differential causes for these crusting lesions were:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree