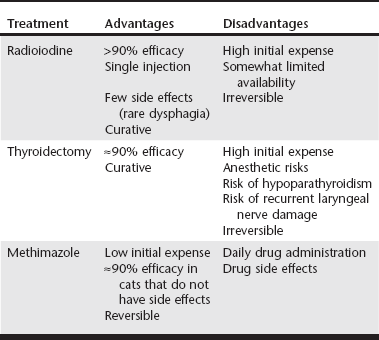
Web Chapter 19 Hyperthyroidism is the most common endocrine disorder in cats, affecting approximately 2% of all cats presenting to veterinary teaching hospitals. Management options include radioiodine therapy, thyroidectomy, and medical treatment with antithyroid drugs such as methimazole. More recently diet has also been advocated in select cases (see Web Chapter 20). Radioiodine is considered the treatment of choice for hyperthyroidism based on its high efficacy and relative lack of complications (Web Table 19-1). However, in some situations methimazole therapy may be preferred over radioiodine. Methimazole is useful before thyroidectomy to normalize serum thyroxine (T4) concentrations and reduce the risk of tachyarrhythmias during anesthesia. Methimazole, which is reversible, is similarly indicated in cats with renal insufficiency, either for long-term therapy or as a “clinical test” to determine whether serum T4 can be safely lowered without causing renal decompensation. Practical considerations such as lack of a convenient referral center with a radiation license, client fears about radiation or quarantine, or initial cost to the client may also drive the use of methimazole. Typical starting doses of methimazole range from 1.25 to 2.5 mg per cat twice daily (Web Table 19-2). More frequent dosing (three times daily) is rarely necessary. Higher doses of 5 mg two to three times daily, used in original cases of cats with relatively high serum T4 concentrations, are probably not needed for initial therapy of cats with mild-to-moderate hyperthyroidism and could potentially increase the risk of renal decompensation from a rapid fall in serum T4. Starting dosages can be titrated upward if there is an inadequate initial response to lower doses of methimazole over 2 to 4 weeks. In cats that tolerate methimazole without side effects, efficacy is greater than 90%. WEB TABLE 19-2 Drugs Useful in the Medical Management of Hyperthyroidism GI, Gastrointestinal; T3, triiodothyronine; T4, thyroxine; AV, atrioventricular. In humans, methimazole has a long residence time in the thyroid gland and can exert antithyroid effects for 24 hours or more; therefore methimazole can be given once daily in humans with remission rates that are comparable to divided daily dosing. However, when our group studied 40 hyperthyroid cats we found that once-daily dosing (5 mg) was less effective than divided dosing (2.5 mg twice daily), with only 54% of cats achieving a euthyroid state after 2 weeks of once-daily treatment compared with 87% of cats treated with divided dosing (Trepanier et al, 2003). Therefore, unless clients are unable to dose more frequently than once daily, divided twice-daily dosing of methimazole may be preferred to maximize efficacy. Dosing less frequently than once daily is unlikely to be effective because serum T4 concentrations rise to pretreatment hyperthyroid values within 48 hours after discontinuing methimazole. Increases in serum alkaline phosphatase (SAP) and bilirubin, or alanine aminotransferase (ALT), are observed in approximately 2% of cats treated with methimazole (Peterson, Kintzer, and Hurvitz, 1988); liver biopsy may show hepatic necrosis and degeneration. Liver enzyme elevations are usually reversible over several weeks following drug discontinuation, although nutritional and fluid support may be required. Rechallenge can lead to recurrent hepatopathy, and future drug avoidance is generally recommended. In rodent models methimazole hepatotoxicity is exacerbated by glutathione depletion (Mizutani et al, 1999). The role of glutathione depletion, or supplementation, in methimazole-associated hepatotoxicity in cats has not been evaluated. Anorexia, vomiting, and lethargy are seen in approximately 10% of cats treated with methimazole. Simple gastrointestinal (GI) upset is most common in the first 4 weeks of treatment and can resolve with a dosage reduction. These signs may be caused in part by direct gastric irritation from the drug, since transdermal administration of methimazole is associated with significantly fewer GI side effects than the oral route (Sartor et al, 2004). Methimazole and to a lesser extent propylthiouracil (PTU) inhibit vitamin K–dependent clotting factor activation (γ-carboxylation) and epoxide reductase (necessary for vitamin K recycling, and the same enzyme targeted by warfarin) at high concentrations. In a study of 20 hyperthyroid cats treated with methimazole, there were no significant changes in prothrombin time or activated partial thromboplastin time, but one cat developed a prolonged protein-induced by vitamin K antagonism (PIVKA) clotting time (Randolph et al, 2000). No cats had clinically significant bleeding. This suggests a possible but apparently uncommon “warfarin-like” effect of methimazole in cats. This reaction is rare enough not to warrant routine monitoring but should be considered in any cat presenting with hemorrhage that is also being treated with methimazole.
Medical Treatment of Feline Hyperthyroidism*
Methimazole Actions, Dosing, and Efficacy
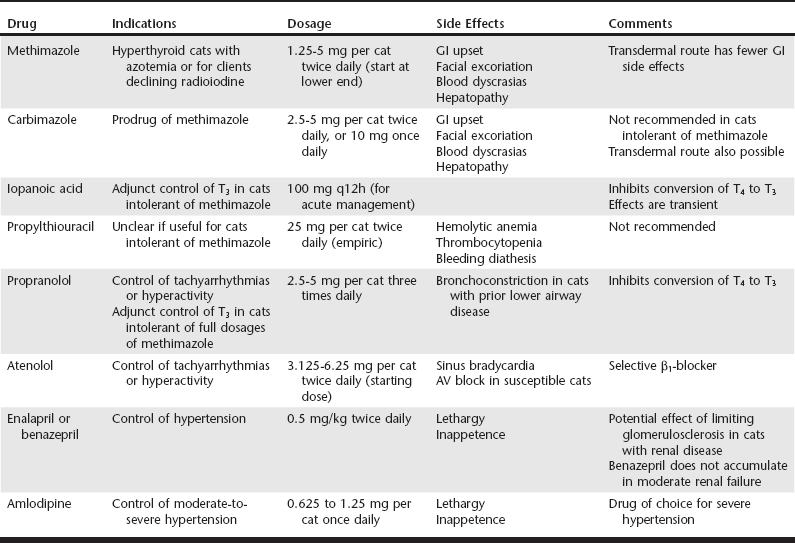
Methimazole Side Effects
Hepatotoxicity
Simple Gastrointestinal Upset
Coagulation Abnormalities
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree