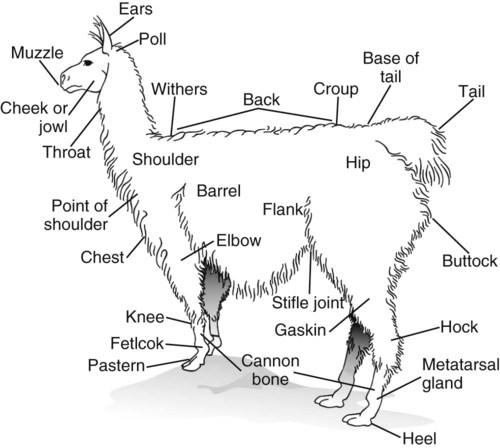
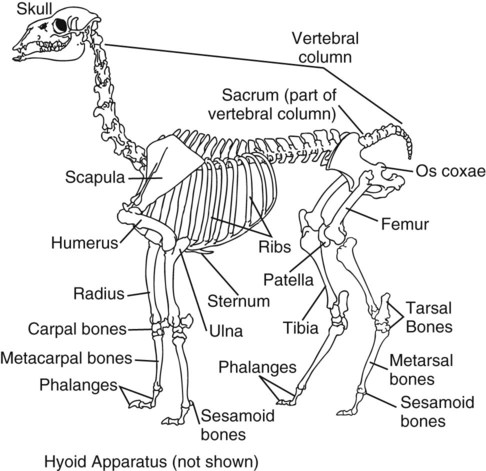
When you have completed this chapter, you will be able to • Know and understand the zoologic classification of the species • Know and be able to proficiently use terminology associated with this species • Know normal physiologic data for the species and be able to identify abnormal data • Identify and know the uses of common instruments relevant to the species • Describe prominent anatomical or physiologic properties of the species • Identify and describe characteristics of common breeds • Describe normal living environments and husbandry needs of the species • Understand and describe specific reproductive practices of the species • Understand specific nutritional requirements of the species Box 18-1 lists common terminology used to describe the age and breeding status of llamas and alpacas. Table 18-1 lists normal physiologic data for llamas and alpacas. TABLE 18-1 Alpaca typically are smaller than llamas, but the main difference is within their fibers. Llamas have a dual-fiber coat. Llamas have a fine covering, but it is intermingled with long guard hairs. Alpaca fiber does not contain these long guard hairs. On average the alpaca stands 34 to 36 inches at the withers (shoulders), whereas the llama stands 42 to 48 inches at the withers (Fig. 18-3). Breeding information for llamas and alpacas is given in Table 18-2. The normal reproductive course for any large animal species was discussed in Chapter 3. The following reproductive procedures are variations that exist among species. TABLE 18-2 Semen collection from camelids can be performed using an artificial vagina or electroejaculation.
Camelid Husbandry
Zoologic Classification
Llama
Kingdom
Animalia
Phylum
Chordata
Class
Mammalia
Order
Artiodactyla
Family
Camelidae
Genus
Lama
Species
Glama
Terminology and Physiologic Data
Temperature
99–101.5°F
Pulse rate
60–90/min
Respiratory rate
10–30 breaths/min
Adult weight
Llamas: 280–450 lb
Alpaca: 150–185 lb
Classification
Reproduction
Type of estrous cycle
Polyestrus
Age of female at puberty
Llama: 6–12months
Alpaca: 1 year
Age of male at puberty
Llama:2–3 years
Alpaca: 2–3 years
Time of first breeding
2.5–3.5 years
Estrous cycle frequency
8–12 days
Duration of estrus
4–5 days
Time of ovulation
Induced ovulator
Artificial insemination: 24–36 hours after induced ovulation
Optimal time of breeding
Induced ovulator
Gestation period
335–-365 days
Birth weight
Alpaca: 12 lb
Llama: 15 lb
Litter size
1–2; twinning is more common in llama
Weaning age
5–6 months
Semen Collection
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Veterian Key
Fastest Veterinary Medicine Insight Engine