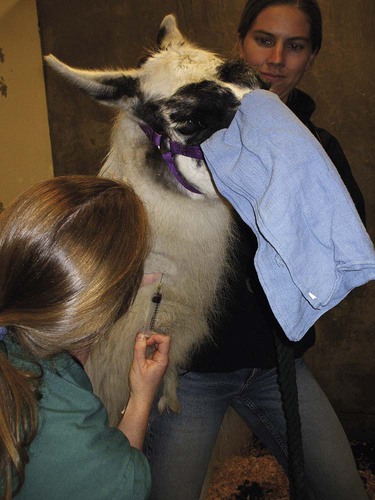
After completing this chapter, you will be able to • Set up and prepare the patient for each procedure, perform the procedure (when appropriate), or assist the clinician in performing diagnostic sampling and medication procedures • Properly insert and maintain an intravenous catheter and monitor the catheter for complications • Explain the rationale and indications for each of the clinical procedures described • Set up materials and equipment and prepare the patient as needed for the procedure • Provide assistance to the veterinarian when performing the procedure or perform the procedure when it may be appropriate for a veterinary technician to do so • Perform or assist necropsy and sample collection procedures and maintain a safe environment during these procedures The low neck jugular venipuncture should be performed with the animal in stocks or performed against a fence or wall if the camelid is halter broke. To begin, elevate the camelid’s head. The anatomical location of interest for this method of collection is the enlarged transverse process of the sixth cervical vertebrae. The jugular vein lies just medial to this process. Care should be taken to avoid the carotid artery, which is also located just medial to the process and can be identified by its pulsating. The technician should begin by occluding the vein. Confirmation of the jugular can be identified visually by observation of its filling when it is occluded between the fifth and sixth cervical vertebrae (Fig. 19-1). The needle then can be inserted. Use of an 18- to 20-ga × Arterial blood sampling can readily be performed from the low neck jugular venipuncture location, which allows for readily palpatable pulsing, as in the low neck venipuncture location. Tables 19-1 and 19-2 list normal blood chemistry values for llamas and alpacas, respectively. TABLE 19-1 Llama’s Complete Blood Count Normal Values TABLE 19-2 Normal Blood Chemistry Values for Llamas
Camelid Clinical Procedures
Diagnostic Sampling
Venous Blood Sampling
Low Neck Jugular Technique
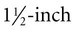 needle is recommended.
needle is recommended.
Arterial Blood Sampling
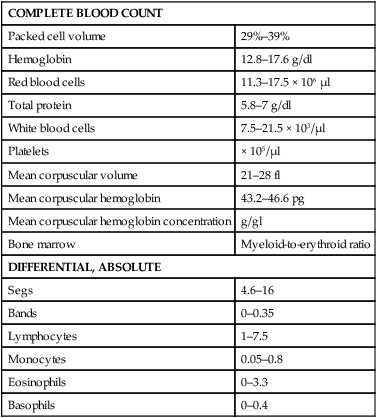
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
Packed cell volume
29%–39%
Hemoglobin
12.8–17.6 g/dl
Red blood cells
11.3–17.5 × 106 µl
Total protein
5.8–7 g/dl
White blood cells
7.5–21.5 × 103/µl
Platelets
× 105/µl
Mean corpuscular volume
21–28 fl
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin
43.2–46.6 pg
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
g/gl
Bone marrow
Myeloid-to-erythroid ratio
DIFFERENTIAL, ABSOLUTE
Segs
4.6–16
Bands
0–0.35
Lymphocytes
1–7.5
Monocytes
0.05–0.8
Eosinophils
0–3.3
Basophils
0–0.4
Blood urea nitrogen
13–32 mg/dl
Creatinine
1.5–2.9 mg/dl
Glucose
90–140 mg/dl
Albumin
3–5 g/dl
Total bilirubin
0–0.1 mg/dl
Aspartate aminotransferase
110–250 µ/L
γ-Glutamyl transferase
5–29 µ/L
Creatine kinase
30–400 µ/L
Alkaline phosphatase
30–780 µ/L
Lactate dehydrogenase
50–300 µ/L
Sodium
147–158 mEq/L
Potassium
4.3–5.6 mEq/L
Chloride
106–118 mEq/L
Calcium
7.7–9.4 mg/dl
Phosphorus
4.6–9.8 mg/dl
Magnesium
1.5–3 mg/dl ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Camelid Clinical Procedures

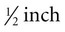 thick, which can make the procedure more difficult. However, the more challenging aspect is the location’s protection provided by the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae. To begin drawing blood from the high neck location, place the head of the animal so that the nose is completely perpendicular to the cervical vertebrae. The nose should not be tipped up or down. Palpate the sternomandibularis tendon. From this anatomical landmark, draw a line along the tendon and insert the needle at the location just dorsal and caudal. Insert the needle where the two lines connect.
thick, which can make the procedure more difficult. However, the more challenging aspect is the location’s protection provided by the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae. To begin drawing blood from the high neck location, place the head of the animal so that the nose is completely perpendicular to the cervical vertebrae. The nose should not be tipped up or down. Palpate the sternomandibularis tendon. From this anatomical landmark, draw a line along the tendon and insert the needle at the location just dorsal and caudal. Insert the needle where the two lines connect.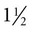 -inch-long needle. Digital pressure should be applied following needle withdrawal to help prevent hematoma formation. Hematoma formation is more common in camelids than in other species, especially neonates, so care should be taken to prevent hematoma formation.
-inch-long needle. Digital pressure should be applied following needle withdrawal to help prevent hematoma formation. Hematoma formation is more common in camelids than in other species, especially neonates, so care should be taken to prevent hematoma formation.