Chapter 84 Calcium Channel and β-Blocker Drug Overdose
METHOD OF ACTION
Calcium Channel Blockers
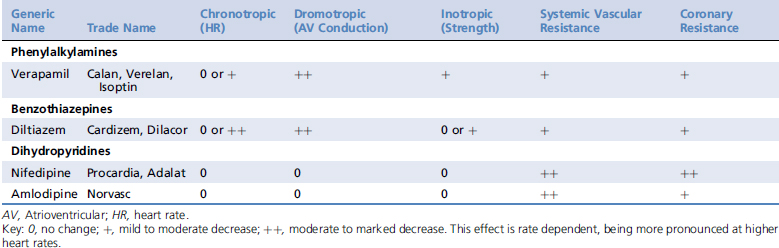
Calcium channel blockers exert most of their effects on cardiac myocytes, pacemaker cells, and vascular smooth muscle. They are classified into three major groups based on their structure, including the phenylalkylamines (e.g., verapamil), the benzothiazepines (e.g., diltiazem), and the dihydropyridines (e.g., amlodipine). Structural differences among the classes are associated with distinct binding sites on the calcium channel, resulting in differing potencies and tissue affinities (Table 84-1). Their structural heterogeneity leads to functional heterogeneity with regard to their vasodilator potency and their cardiac inotropic, chronotropic, and dromotropic effects.1-3
Table 84-1 Expected Cardiovascular Effects of Calcium Channel Blocking Agents in Healthy Animals2,3,34