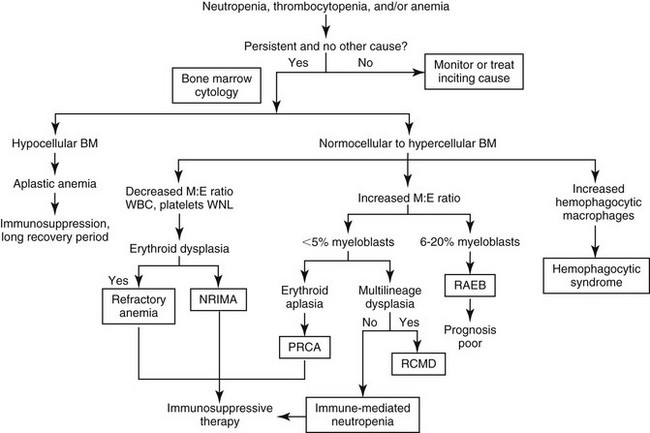
Chapter 68 The term bone marrow dyscrasia technically means any disease originating in the bone marrow. Dysmyelopoiesis is another term used to describe disorders stemming from bone marrow problems. This chapter describes bone marrow diseases that result in peripheral cytopenias and that require a bone marrow evaluation to determine the cause or classify the disorder. These diseases may be nonneoplastic (secondary dysmyelopoiesis) or neoplastic or “preneoplastic” (primary dysmyelopoiesis). Secondary dysmyelopoiesis includes immune-mediated or drug-induced phenomena, and preneoplastic or neoplastic diseases include myelodysplastic syndromes, acute and chronic myeloid leukemias, and acute and chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Determining the cause of the dyscrasia, whether it is primary or secondary, and its classification if it is myelodysplastic or leukemic influences treatment and prognosis. Clinical signs of bone marrow dyscrasias are related directly to the effects of the cytopenias or to the effects of proliferating hematopoietic cells (e.g., leukemia). For example, clinical signs in a dog with pure red cell aplasia may include nonspecific malaise progressing to exercise intolerance and severe lethargy related to the lack of oxygen-carrying capacity caused by anemia. Clinical signs of an acute leukemia that is infiltrating abdominal organs may be acute-onset lethargy, fever, anorexia, vomiting, cranial organomegaly, and biochemical abnormalities related to the organ that is infiltrated with neoplastic cells. An animal with drug-related neutropenia may have fever secondary to an opportunistic infection. Diagnosis of a bone marrow dyscrasia is based on a finding of one or more unexplained cytopenias or severe leukocytosis in a complete blood count, accompanied by characteristic features on cytologic evaluation of bone marrow. A flow chart for the diagnostic workup of unexplained cytopenias is presented in Figure 68-1. Figure 68-1 Diagnostic workup for unexplained cytopenias in peripheral blood. BM, Bone marrow; M:E ratio, myeloid to erythroid ratio; NRIMA, nonregenerative immune-mediated anemia; PRCA, pure red cell aplasia; RAEB, refractory anemia with excess blasts; RCMD, refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia; WBC, white blood cell count; WNL, within normal limits. Myeloid: Adjective referring to commitment of a progenitor to erythroid, granulocytic, monocytic, or megakaryocytic lineage. These progenitors may differentiate into any blood cell other than a lymphoid cell. It also refers to the granulocytic component of the precursor cell population in the myeloid:erythroid ratio determined during bone marrow cytologic evaluation. Lymphoid: Adjective referring to lineage commitment to any lymphoid cell line, including all B and T cells. Dysplasia: Abnormalities in the cytologic appearance of any maturational stage of bone marrow cells. Dyserythropoiesis: Dysplastic features of erythroid precursors. Includes binucleation, megaloblastosis (excess cytoplasm relative to nucleus), nuclear fragmentation, and asynchronous maturation (e.g., hemoglobinized cytoplasm with an immature nucleus). Dysgranulopoiesis: Dysplastic features of myeloid precursors. Includes small myeloblasts and promyelocytes, giant metamyelocytes and band cells, asynchronous maturation, and hypersegmentation of mature neutrophils. Primary myelodysplastic syndrome: One or more cytopenias, cell dysplasia, and maturation abnormalities in the marrow, not associated with infection, drug administration, a toxin, or other neoplasia. These are hematopoietic cell clonal disorders in human beings and are assumed to be clonal in dogs and cats. Leukemia: Clonal proliferation of hematopoietic cells of any lineage in the blood or bone marrow. Acute myeloid leukemia: Clonal proliferation of immature cells of erythroid, granulocytic, monocytic, or megakaryocytic lineage in the bone marrow. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Clonal proliferation of immature cells of lymphoid lineage in the bone marrow. Chronic myeloid leukemia: Clonal proliferation of hematopoietic cells that differentiate enough to appear mature in the peripheral blood. These cause extreme leukocytosis and are usually of a granulocytic, monocytic, or eosinophilic lineage. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (chronic lymphoid leukemia): Clonal proliferation of mature-appearing lymphoid cells arising from spleen or bone marrow. Blast cell: Earliest recognizable precursor of a certain cell lineage. A rubriblast is the earliest erythroid precursor and a myeloblast is the earliest granulocytic precursor. The reader is encouraged to consult a recent excellent review on the evaluation of bone marrow, including collection techniques (Moritz et al, 2010). A brief description of bone marrow collection for smears is given here. Bone marrow evaluation is indicated any time there is a cytopenia that cannot be explained by other clinical or laboratory findings. Some examples are persistent neutropenia without evidence of sepsis and nonregenerative anemia without evidence of renal failure, neoplasia, infection, or inflammatory disease. Bone marrow may be collected from dogs at the iliac crest, the proximal femur, or the ribs, and from cats at the iliac crest, proximal humerus, or trochanteric fossa. The skin at the site is shaved and aseptically prepared. Two percent lidocaine solution is used to provide local anesthesia in all tissue layers, including deep infusion to the periosteum. A sterile 16- to 18-gauge bone marrow needle with an interlocking stylet is used, and in general the animal is at least heavily sedated. The needle, with the stylet in place, is inserted into the skin at the site of aspiration and is seated on the bone. Slow twisting is used to insert the needle through the cortex into the marrow cavity. The stylet is removed, and a 10- to 12-ml syringe is placed in the needle hub. Strong aspiration is used to remove marrow. Only a small amount of marrow should be collected; otherwise hemodilution will occur and a poor-quality sample will result. No more than about 250 µl of marrow should be aspirated. For best staining quality, no anticoagulant should be used, but the marrow should be smeared on glass slides immediately. The smears should be stained within 24 hours of collection and evaluated by a veterinary clinical pathologist. The evaluation will include assessment of overall cellularity, presence or absence of iron stores, quantification of megakaryocytes, differential count of myeloid (granulocytic) and erythroid precursors (producing the myeloid:erythroid ratio), evaluation of the orderliness of precursor maturation, morphologic abnormalities, and the presence of abnormal (e.g., neoplastic) cells. A complete blood count must be performed within 24 hours of bone marrow collection. Nonregenerative immune-mediated anemia (NRIMA), primarily described in dogs, is secondary to an immune response against erythroid precursors in the bone marrow. Affected dogs may have a short to several-month history of lethargy, anorexia, weight loss, and exercise intolerance, and show pallor, systolic heart murmurs, and tachycardia on physical examination; these signs all are referable to severe anemia. Laboratory abnormalities include a severe, nonregenerative anemia and reticulocytopenia. Leukocyte counts typically are normal, although platelet counts may be decreased in a minority of dogs. Spherocytes are present in many dogs, and Coombs’ test yields positive results in over half of cases. The majority of bone marrow samples show erythroid hyperplasia, and there may be an expansion of immature erythroid precursors. Other cell lines are normal. Although over half of cases respond to immunosuppressive therapy, the mortality rate for this disease in one report was 28% (Stokol et al, 2000).
Bone Marrow Dyscrasias
Definitions
Bone Marrow Aspirate Cytologic Evaluation
Nonneoplastic Dyscrasias
Nonregenerative Immune-Mediated Anemia
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


