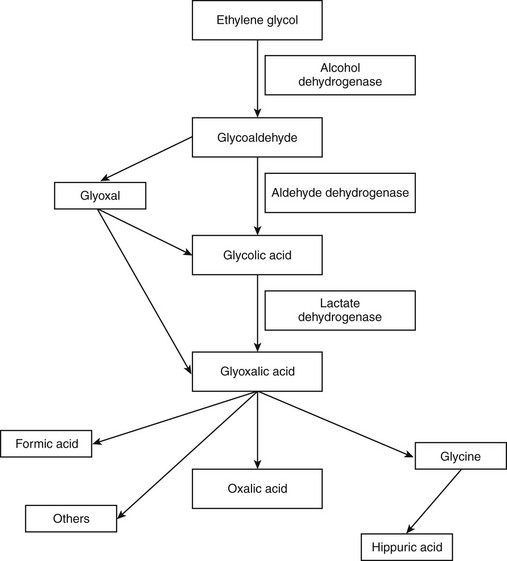
Chapter 36 EG is absorbed rapidly from the gastrointestinal tract, particularly on an empty stomach. Peak plasma concentrations occur within 3 hours of ingestion. Metabolism begins within hours of ingestion and occurs predominantly in the liver, with minor renal and gastric metabolism. The metabolic pathway of EG is illustrated in Figure 36-1. The metabolism of EG to glycoaldehyde and then glycolic acid to glyoxylic acid are both rate-limiting steps. Oxalic acid is the most important final metabolite of EG. The plasma half-life of EG is approximately 3 hours, and elimination is almost complete within 24 hours. EG and its metabolites are eliminated in the urine.
Automotive Toxins
Ethylene Glycol
Toxicity and Toxicokinetics
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Veterian Key
Fastest Veterinary Medicine Insight Engine