Chapter 11 Goldfish and koi
This chapter covers those disorders likely to be seen in goldfish and koi, which constitute the most popular section of fish-keeping. Tolerance of wide temperature ranges means that these species can be kept outside, as well as inside, in most temperate countries such as Europe and North America. However, they are also happy at more tropical temperatures and in those countries such as Singapore, Malaysia and southern China where they are kept alongside ‘tropical species’. Hence, this disorders chapter should be read in conjunction with that on Tropical Freshwater Fish.
Consultation and handling
The key to successful fish-keeping, and a major stumbling point, is water quality. Recommended water-quality parameters for koi and goldfish are listed in Table 11.1.
Table 11.1 Recommended water quality parameters for koi and goldfish
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 10–30 (preferred range = 22–28 for Koi) |
| pH | 6.0–8.4 (preferred 7.0–8.0) |
| Hardness (CaCO3) (mg/L) | 100–250 |
| Conductivity (mS/cm) | 180–480 |
| Ammonia (total) (mg/L) | <0.02 |
| Nitrite (mg/L) | <0.2 |
| Nitrate (above ambient tapwater levels) (mg/L) | <40 |
| Oxygen (mg/L) | 5.0–8.0 |
| Chlorine (mg/L) | 0.002 |
Adapted from Jepson (2001).
If possible, fish should be examined in their home aquarium or pond. However, if the pond is large it may pay to ask for the fish to be caught and separated before arrival, as much time can be wasted attempting to catch the fish. Ponds are rarely built with recapture in mind. Once caught, place the fish on a damp towel for examination. If necessary sedate with MS222 or benzocaine (see ‘Anaesthesia’, below).
Blood sampling
This is best done under anaesthesia (see below). Blood can be drawn using a well-heparinized syringe from the ventral tail vein, which runs midline just below the caudal vertebrae. In small fish this can be accessed via the ventral midline while in larger fish, a lateral approach is often better. This same approach can be used for intravenous injections.
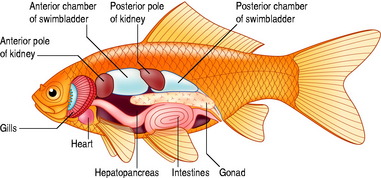
For the internal anatomy of a goldfish, see Figure 11.1.
Nursing care
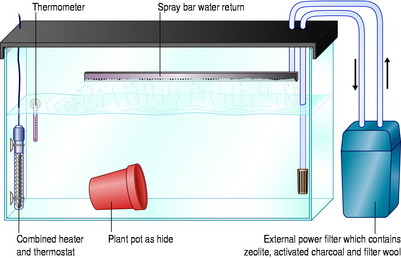
Provision of optimal water quality is essential to maximize recovery. A separate hospital aquarium or vat can be used but the water quality in this facility should be as good as in a main display (Fig. 11.2). The water should be filtered, but because of the use of medications such as antibiotics, biological filtration cannot be used. After each patient, the aquarium or vat should be dismantled and cleaned out with an iodine-based disinfectant.
Antibiotics can be administered either by:
Anaesthesia
There are a number of anaesthetic preparations and protocols described, but the author has found tricaine methane sulphonate and benzocaine to be the most useful.
Anaesthetic protocol for fish anaesthesia
Induction
Maintenance
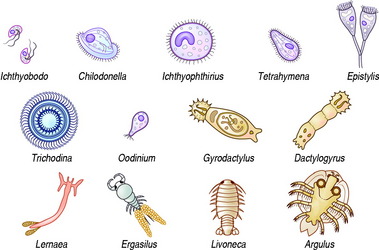
Skin disorders
Skin structure
The skin is a large and complex organ that is constantly in contact with the immediate environment of the fish. Its functions include an osmotic barrier, disease barrier, protection, intra-specific signaling and camouflage. Histologically it consists of: