26 Urticaria, angio-oedema and anaphylaxis
Localized Reactions
Urticaria and Angio-oedema
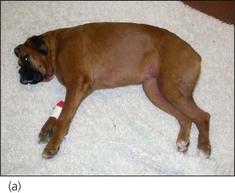
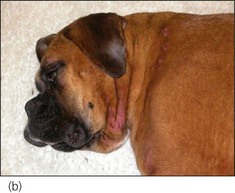
In angio-oedema, subcutaneous tissues and deep blood vessels become affected by the inflammatory process, resulting in oedema and consequent diffuse swelling that is usually not pruritic. Angio-oedema typically affects the face (especially around the eyes, mouth and ears) although other areas, in particular the extremities, may be involved (Figure 26.1).
Treatment of urticaria and angioedema is described in the case example.
Systemic Reactions – Anaphylaxis/Anaphylactic Shock
Maldistributive shock occurs and in addition a marked increase in capillary permeability causes significant loss of fluid from the intravascular to the extravascular compartment, resulting in hypovolaemic shock (see Ch. 2). The cardiovascular picture during anaphylaxis (hypoperfusion that is refractory to appropriate fluid therapy) is also a hallmark of maldistributive shock secondary to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) or sepsis (SIRS due to infection, most commonly bacterial). Thorough evaluation to exclude sepsis may be indicated in some cases prior to making a presumptive diagnosis of anaphylaxis.