Chapter 2 Tissues and body cavities
Within the body individual cells are grouped together to form tissues and organs. Thus:
Body tissues
Each tissue type consists of three main components:
There are four main types of tissue:
Epithelial tissue
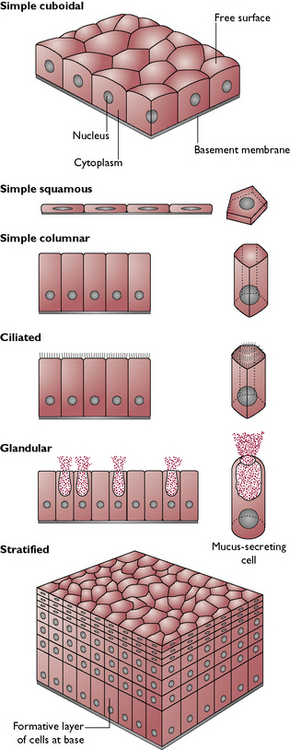
Epithelium may be described according to the number of layers of cells, i.e. its thickness:
Epithelium may also be described according to the shape of the cells within it (Fig. 2.1). There are three basic shapes of epithelial cell:
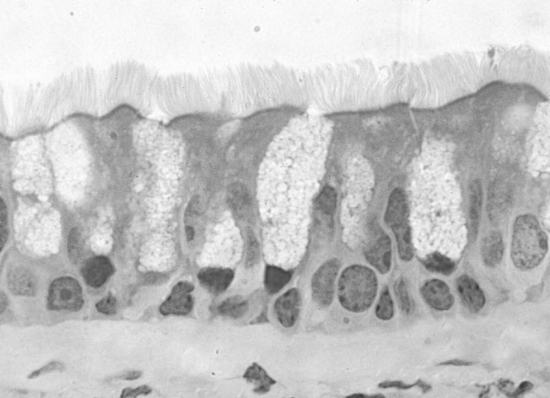
Fig. 2.3 Photomicrograph of the lining of the trachea showing a pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
(Taken from D. Samuelson. Textbook of Veterinary Histology. Saunders. 2007, p 43.)
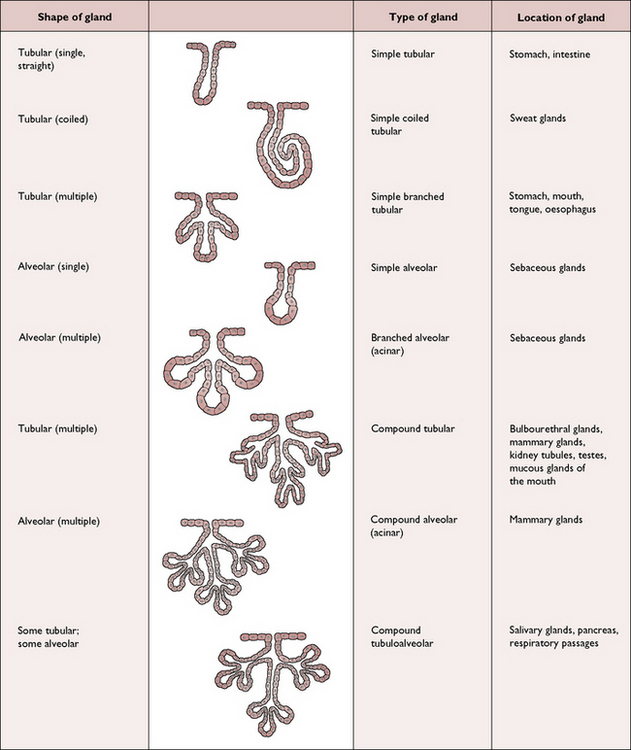
Glands
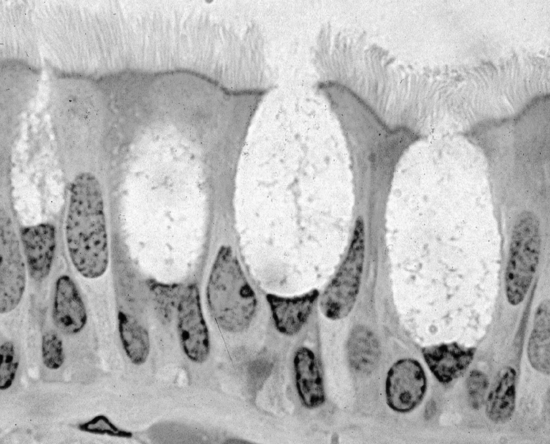
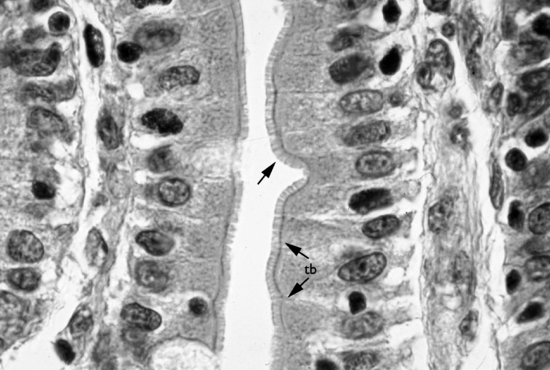
Fig. 2.4 Photomicrograph of goblet cells within a pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
(Taken from D. Samuelson. Textbook of Veterinary Histology. Saunders, p 64.)
Connective tissue
Connective tissue is responsible for supporting and holding all the organs and tissues of the body in place. It also provides the transport system within the body, carrying nutrients to the tissues and waste products away. Connective tissue consists of cells embedded in an extracellular matrix or ground substance. The properties of this ground substance depend on the type of connective tissue. There are many types of connective tissue which, in order of increasing density are:
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree