Chapter 11 Surgical procedures of the lens and cataract
Evolution of cataract surgery in dogs 307
Evolution of cataract surgery in horses 308
Development of the intraocular lens for the dog, cat, and horse 309
Patient selection for all species 314
Non-surgical treatment of cataracts 316
Surgical procedures for cataracts and lens removal 320
Choice of ophthalmic anesthesia and surgical exposure 321
Anterior chamber entry for cataract and lens extraction 322
Capsulorhexis and anterior capsulectomies 322
Phacoemulsification in small animals 327
Phacoemulsification in the horse 330
Intraocular lens implantation in small animals 334
Intracapsular cataract or lens extraction in small animals 334
Intracapsular cataract or lens extraction in the horse 335
Removal of the unstable lens in small animals 335
Intraocular lens implantation 339
Postoperative treatment and management in small animals 342
Postoperative treatment and management in the horse 342
Postoperative results and complications in small animals 343
Complications of cataract surgery in dogs 343
Postoperative results and complications after lens surgery in the horse 351
The future and challenges of cataract and lens surgery in animals 352
Introduction
Types of cataract classification
The different cataract classifications in animals include: 1) age of onset; 2) position within the lens; 3) degree of opacification; and 4) possible cause (Table 11.1). Hence, for the clinical description of a cataract, all methods are usually combined. For instance, the breed-specific cataract in Golden Retrievers is a juvenile, inherited, axial, posterior cortical and capsular incipient cataract. The early cataract secondary to diabetes mellitus in dogs and cats is an equatorial cortical incipient cataract.
Table 11.1 Different classifications for cataracts in animals
| Classification | Description |
|---|---|
| Age of onset | Congenital |
| Developmental (juvenile or adult) | |
| Senile | |
| Position within the lens | Anterior capsular |
| Anterior cortical | |
| Nuclear | |
| Posterior cortical | |
| Posterior capsular | |
| Equatorial and axial | |
| Degree of opacification and lens size | Incipient |
| Immature | |
| Mature (subdivision intumescent) | |
| Hypermature (subdivision Morgagnian) | |
| Resorbing | |
| Possible cause | Inherited |
| Associated with other ocular anomalies | |
| Secondary to retinal degeneration | |
| Secondary to trauma (direct/indirect) | |
| Viral | |
| Post-inflammatory | |
| Metabolic | |
| Toxic (infant formulas, radiation, drugs) |
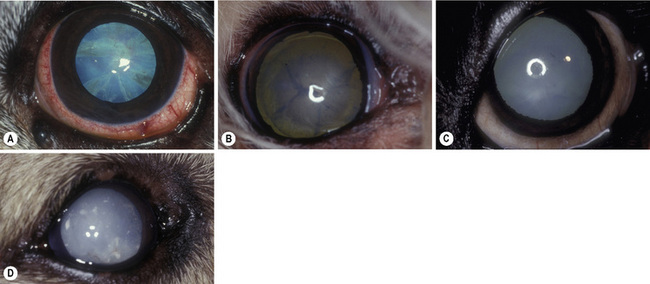
Relative to surgery, the classification system that assesses the degree of opacification (or maturity) of cataracts is most useful, as this quantification of lens opacity correlates to clinical vision (Fig. 11.1). Incipient cataracts are the earliest detectable lens opacities. Often appearing as vacuoles and water clefts, these opacities do not significantly impair clinical vision in dogs, cats, or horses. Immature cataracts have noticeable opacification and a tapetal fundic reflection. The animal still has clinical vision, but some visual impairment may be demonstrable, especially during daytime with miosis. With an immature cataract the lens is still normal in size. By indirect ophthalmoscopy, the ocular fundus is visible but some details may be hazy from lens opacification.
Development of the intraocular lens for the dog, cat, and horse
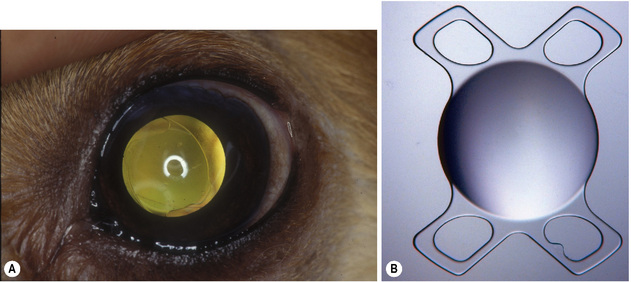
IOL in the dog
The materials from which IOLs are constructed may influence the development of postoperative capsular opacification (PCO) in dogs. Both the hard polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) and soft foldable (acrylic hydrophil) IOLs are now available for the dog, cat, and horse. Although the PMMA IOL, supported by two haptics, has been the most common IOL for the dog (Fig. 11.2), the foldable IOLs have recently also become popular. The 6–7 mm biconvex optical center of the IOL, or the optic, produces the refractive power of the IOL. The +41 diopter (D) canine IOL requires a fairly large optic (compared to humans); larger optics tolerate slight decentralization without significant optical aberrations. Currently, foldable acrylic IOLs are the most commonly implanted IOLs in dogs, cats, and horses. These allow for implantation through a smaller incision, resulting in less astigmatism, shortened surgical time, and possibly less PCO.
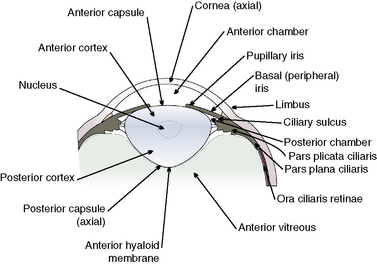
Surgical anatomy
To perform cataract surgery in animals, the anatomy of the peripheral cornea and limbus, iris and ciliary body, lens, and anterior vitreous is important (Fig. 11.3). Cataract surgeries gain access to the anterior chamber, pupil, and anterior lens capsule through corneal or limbal incisions. Sclerotomies and removal of cataracts through the pars plana ciliaris and equatorial or posterior lens capsule are technically difficult and not used. The corneal incision is performed in the most peripheral cornea, consisting of a combination of beveled and perpendicular incisions, or only a perpendicular incision. The combination method provides a larger tissue surface for closure of the cornea and is less likely to leak aqueous humor postoperatively.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree