chapter 15 Small Animal Skull
Introduction
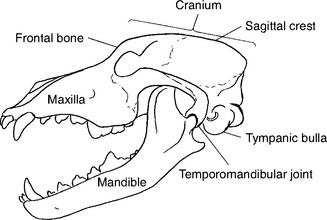
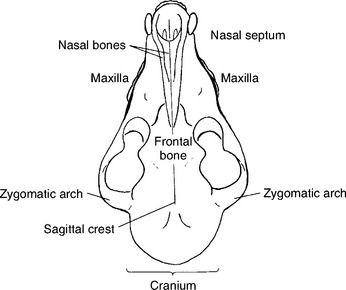
The anatomy of the skull is complicated, and radiography of the area can be just as complex. Familiarity with the anatomy of the small animal skull assists the correct positioning of various views (Figs. 15-1 and 15-2). Furthermore, veterinary radiography deals with many breeds and species and the number of physical variations in skull anatomy adds to the complexity of positioning. Compare the skull of a collie with that of a Boston terrier—the difference is enormous. However, the principles presented here can be applied to any small animal breed and species.
Lateral View
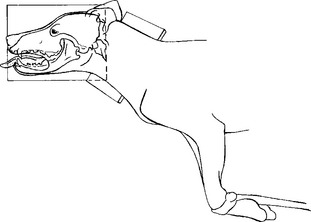
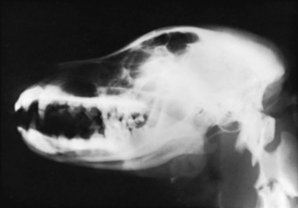
The patient should be placed in lateral recumbency with the affected side of the skull toward the cassette (Figs. 15-3 and 15-4). To eliminate rotation of the skull, a foam pad of suitable thickness is placed under the ramus of the mandible. The nasal septum should be parallel to the surface of the cassette. From the view of the x-ray tube (bird’s-eye view), the mandibular rami should be superimposed. Placing a pad under the cranioventral cervical region and pulling the front limbs caudally may help maintain the skull in a true lateral position. The field of view should include the entire head from the tip of the nose to the base of the skull.
BEAM CENTER: Lateral canthus of eye
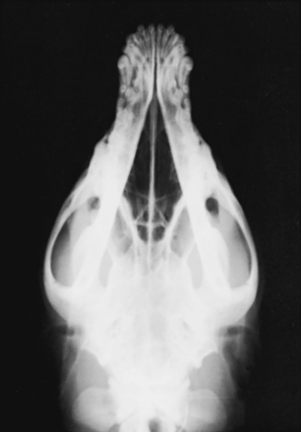
Dorsoventral View
The patient is placed in sternal recumbency with the head resting on the cassette (Figs. 15-5 and 15-6). Gentle pressure can be placed over the cervical region with a sandbag to keep the skull next to the cassette in a dorsoventral position. The front limbs can remain in a natural position alongside the head but out of view of the x-ray beam. Check the final positioning by looking in a rostrocaudal direction. The sagittal plane of the head should be perpendicular to the cassette. If the head consistently rotates to one side or the other, a strip of adhesive tape can be placed over the cranium in the desired position. The field of view should include the entire head from the tip of the nose to the base of the skull.
BEAM CENTER: Lateral canthus of eye
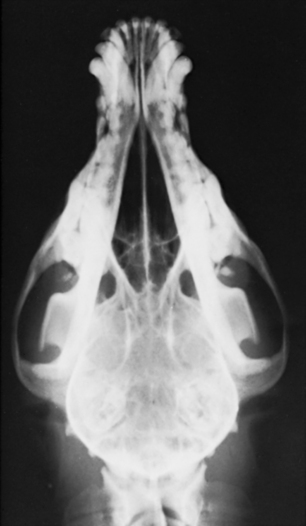
Ventrodorsal View
The patient is placed in dorsal recumbency (Figs. 15-7 and 15-8). A V trough or sandbags may be used to keep the animal in position. The front limbs are extended caudally and secured. A foam pad should be placed under the midcervical region to properly position the skull on the cassette. The nose must remain parallel to the cassette, and the skull must be balanced in a true ventrodorsal position. Rotation of the skull is a problem with animals that have a prominent external occipital protuberance. A thin sponge pad placed under the cranium helps prevent this type of rotation. The field of view should include the entire head from the tip of the nose to the base of the skull.
BEAM CENTER: Lateral canthus of eye
Rostrocaudal View
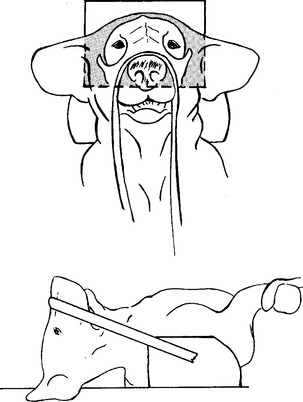
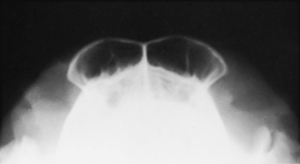
The patient is placed in dorsal recumbency with the nose pointing upward (Figs. 15-9 and 15-10). The front legs should be pulled caudally alongside the body. The nose is positioned perpendicular to the cassette. A length of roll gauze or tape can be tied around the nose to stabilize the patient in this position. The frontal sinuses should be centered on the cassette, and the field of view should include the entire forehead of the patient. The collimator central beam should be aimed perpendicularly to the cassette and centered between the eyes.
BEAM CENTER: Through center of frontal sinuses, between eyes
Rostrocaudal View
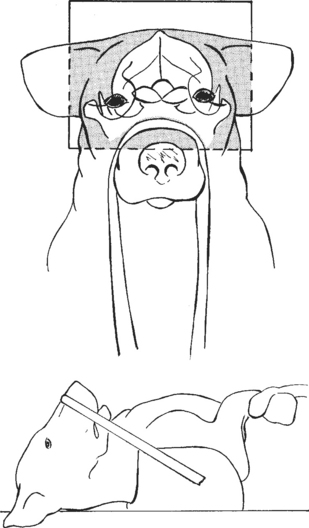
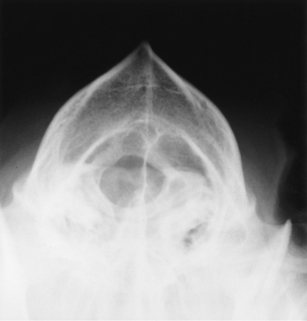
The patient is placed in dorsal recumbency with the nose pointing upward and the front limbs pulled caudally alongside the body (Figs. 15-11 and 15-12). This view is similar to the frontal sinus projection, except that the angle of the nose is directed slightly in a caudal direction. With a length of roll gauze or tape, the nose is pulled caudally approximately 10 to 15 degrees. If an endotracheal tube is in place, care must be taken not to crimp the tube while flexing the animal’s neck. The cranium should be centered to the cassette, and the field of view should include the entire cranium.
BEAM CENTER: Midpoint between eyes