TABLE 16-1 Normal Electrolyte Composition of Serum (mEq/L) I Anesthesia, surgery, and many of the diseases for which surgical intervention is required disturb cardiac function, smooth muscle vascular tone, blood flow distribution, plasma electrolyte concentrations and acid-base balance potentially altering the effective circulating blood volume (the volume circulating). A Many diseases produce changes in the relative or absolute blood volume, electrolyte concentrations, and acid-base balance (Table 16-2) TABLE 16-2 Common Diseases And Expected Electrolyte Abnormalities ↑, Increased serum concentration; ↓, decreased serum concentration; —, normal serum concentration. B Common side effects of anesthesia 1. Inhalant and/or IV anesthesia a. Decrease myocardial contractility, cardiac output and tissue perfusion b. Produce vasodilation; relative hypovolemia; hypotension is one of the most common, if not the most common side effects of general anesthesia in most species c. Depress minute ventilation; respiratory acidosis may occur d. Decrease urine production and renal concentrating ability 2. General anesthesia usually depresses sympathoadrenal and compensatory reflex responses to hypotension, hypercapnia, and hypoxemia C Imbalances associated with or caused by surgery II Fluid loss leads to a decrease in the “effective” circulating blood volume eventually resulting in a decrease in cardiac output, a redistribution of blood to vital organs (heart, brain, lung), and the development of metabolic acidosis III Fluid administration in young or small animals (<3 kg) should be supplemented with a source of calories (dextrose) and monitored closely to prevent hypothermia and/or overhydration IV The administration of large quantities of room-temperature fluids to any animal can produce hypothermia and hemodilution, resulting in coagulation abnormalities I Total body water represents 55% to 75% of body weight (use 60%), primarily depending on the animal’s age and percentage of body fat II Extracellular water (ECW): the water outside cells and constituting the blood (plasma; red blood cells [RBCs]) volume and interstitial fluid volume. ECW ranges from 23% to 33% of body weight (use 30%); the percentage is greater in very young animals III Interstitial water constitutes 15% to 25% of body weight IV Plasma water constitutes approximately 5% of body weight V Extracellular water equals plasma water plus interstitial water VI Intracellular water constitutes 35% to 45% of body weight VII Blood volume constitutes 8% to 10% of body weight (approximately 90 mL/kg of body weight), depending on the hematocrit; hematocrit measures how much space in the blood is occupied by RBCs and is also referred to as the packed red cell volume or packed cell volume (PCV) and abbreviated as Hct or Crit I Extracellular water contains large quantities of salt: sodium and chloride ions. The extracellular fluids (plasma and interstitial fluid) also contain smaller quantities of other solutes A Blood contains RBCs and plasma. Plasma is a complex fluid that contains water and other solutes including electrolytes (see Table 16-1), proteins (albumin), large glycoproteins (antibodies: immunoglobulins), glucose and many other substances 1. Plasma osmolarity is a measure of the concentration of substances such as sodium, chloride, potassium, urea, glucose, and other ions in blood. It is calculated as the osmoles of solute per kilogram of solvent. 2. The plasma osmolarity is sensitive to changes in hydration status during dehydration and rehydration. The normal plasma osmolarity ranges from 280 to 300 mOs/kg II Intracellular water contains large quantities of potassium ions I Correct dehydration and electrolyte and acid-base imbalances 12 to 24 hours before anesthesia when possible II Do not attempt to replace dehydration or chronic fluid losses acutely; severe dilution of plasma proteins, RBCs, and electrolytes may be produced (see Table 16-2) A Normal daily fluid maintenance rates vary as follows: B Calculation of replacement fluid volume in dehydrated animals 1. Body weight (kg) × % dehydration (figured as a decimal) = fluid deficit (L) (e.g., 20 kg × 10% dehydration = 2 L fluid deficit); reassess periodically to determine the response to volume administered 2. Fluid administration to correct dehydration should be administered over a 6- to 12-hour period or added to the maintenance fluid volume and administered over a 24-hour period III Monitor hemodynamics, pulmonary, and renal function when administering fluids rapidly 1. Monitor arterial BP; systolic BP >90 mm Hg; mean BP >60 mm Hg 2. Auscultate the chest; if the total protein (TP) drops below 3.5 g/dL from fluid administration, pulmonary edema may occur 3. Central venous pressure (0.5 to 5.0 cm H2O) or pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (5 to 10 mm Hg) can be monitored, although their predictive value for determining rates and volumes of fluid administration is low unless fluids are administered in excess or the animal develops right heart failure 4. Measures of systolic arterial pressure variation (SPV) or pulse–oximeter-derived plethysmographic variability index (PVI) provides valuable information regarding fluid requirements and the effectiveness of fluid administration (see: Chapter 14) 1. Improve or reestablish renal perfusion and urine production (0.5 to 2.0 mL/kg/hr) before anesthesia 2. Administer mannitol at 1 to 2 g/kg IV over a 30-minute period to induce urine production in animals with normal hydration C Pulmonary function—overhydration can lead to pulmonary edema initially exemplified by increases in respiratory rate, increased breathing effort (abdominal contraction) and increased lung (bronchovesicular) sounds (Box 16-1).
Perioperative Fluid Administration
Overview
General Considerations (Table 16-1)
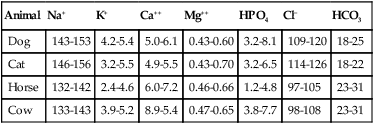
Animal
Na+
K+
Ca++
Mg++
HPO4
Cl−
HCO3
Dog
143-153
4.2-5.4
5.0-6.1
0.43-0.60
3.2-8.1
109-120
18-25
Cat
146-156
3.2-5.5
4.9-5.5
0.43-0.70
3.2-6.5
114-126
18-22
Horse
132-142
2.4-4.6
6.0-7.2
0.46-0.66
1.2-4.8
97-105
23-31
Cow
133-143
3.9-5.2
8.9-5.4
0.47-0.65
3.8-7.7
98-108
23-31
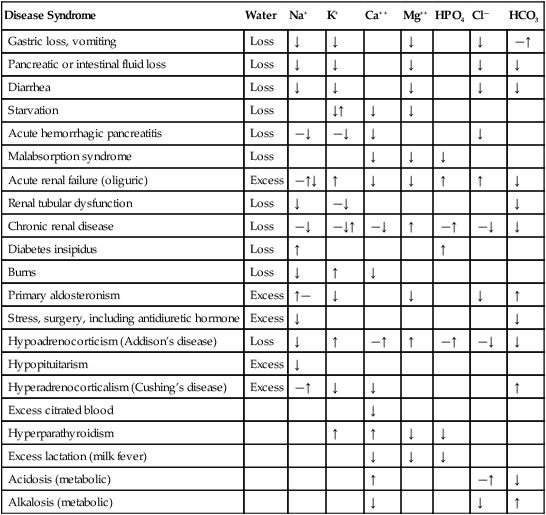
Disease Syndrome
Water
Na+
K+
Ca++
Mg++
HPO4
Cl—
HCO3
Gastric loss, vomiting
Loss
↓
↓
↓
↓
—↑
Pancreatic or intestinal fluid loss
Loss
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
Diarrhea
Loss
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
Starvation
Loss
↓↑
↓
↓
Acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis
Loss
—↓
—↓
↓
↓
Malabsorption syndrome
Loss
↓
↓
↓
Acute renal failure (oliguric)
Excess
—↑↓
↑
↓
↓
↑
↑
↓
Renal tubular dysfunction
Loss
↓
—↓
↓
Chronic renal disease
Loss
—↓
—↓↑
—↓
↑
—↑
—↓
↓
Diabetes insipidus
Loss
↑
↑
Burns
Loss
↓
↑
↓
Primary aldosteronism
Excess
↑—
↓
↓
↓
↑
Stress, surgery, including antidiuretic hormone
Excess
↓
↓
Hypoadrenocorticism (Addison’s disease)
Loss
↓
↑
—↑
↑
—↑
—↓
↓
Hypopituitarism
Excess
↓
Hyperadrenocorticalism (Cushing’s disease)
Excess
—↑
↓
↓
↑
Excess citrated blood
↓
Hyperparathyroidism
↑
↑
↓
↓
Excess lactation (milk fever)
↓
↓
↓
Acidosis (metabolic)
↑
—↑
↓
Alkalosis (metabolic)
↓
↓
↑
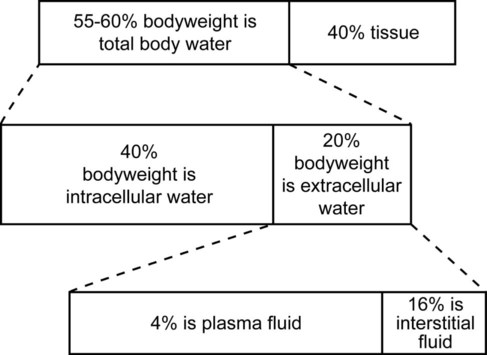
Normal Body Water Distribution (Fig. 16-1)
Electrolyte Distribution
Principles of Fluid Administration
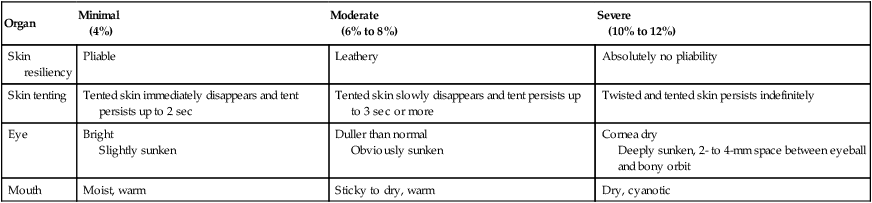
Organ
Minimal
(4%)
Moderate
(6% to 8%)
Severe
(10% to 12%)
Skin resiliency
Pliable
Leathery
Absolutely no pliability
Skin tenting
Tented skin immediately disappears and tent persists up to 2 sec
Tented skin slowly disappears and tent persists up to 3 sec or more
Twisted and tented skin persists indefinitely
Eye
Bright
Slightly sunken
Duller than normal
Obviously sunken
Cornea dry
Deeply sunken, 2- to 4-mm space between eyeball and bony orbit
Mouth
Moist, warm
Sticky to dry, warm
Dry, cyanotic