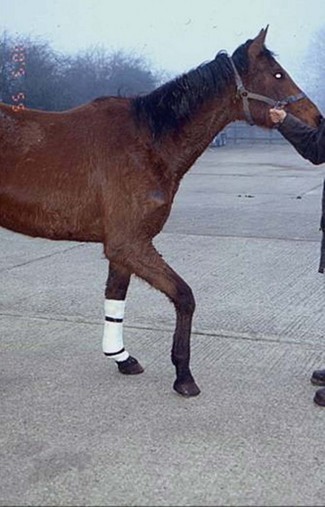
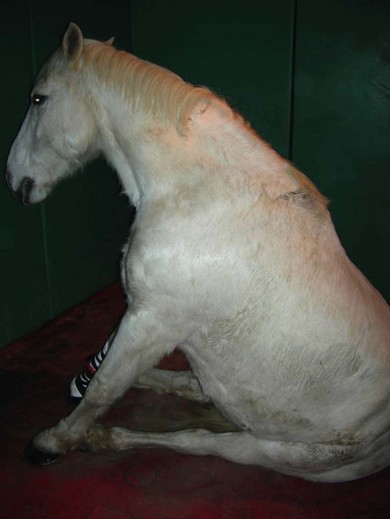
Chapter 21 21.1 Examination of the muscular system 21.2 Congenital/familial disease 21.3 Myopathy with physical causes 21.4 Myopathy of infectious origin 21.5 Myopathy of metabolic origin 21.6 Myopathy of nutritional origin 21.7 Ionophore antibiotic toxicity 21.8 Atypical myopathy (atypical myoglobinuria) 21.10 Causes of poor performance/exercise intolerance 21.11 Thermoregulatory problems 21.12 Exhausted horse syndrome • The horse should be evaluated initially from a distance. Symmetry, size and shape of the muscle groups should be assessed. • The various muscle groups and pairs of muscles are palpated to give an impression of tone, sensitivity, asymmetry or atrophy. The horse should be given time to relax so that apprehension to palpation does not elicit a false impression. • The horse is walked and examined for evidence of lameness, weakness or pain associated with movement. Differentiating between weakness caused by neurological disease and weakness caused by muscular disease can be difficult. Three enzymes are routinely measured in the evaluation of muscular disease: • CK is found predominantly in skeletal and cardiac muscle and in the brain. • When the muscle cell wall is disrupted, CK is released from the cytoplasm and enters the extracellular fluid. • Elevated serum CK is usually caused by myopathy rather than by neuropathy, since CK activity in nervous tissue is not sufficient to elevate serum concentrations. • Elevated serum concentrations of CK can be a sensitive indicator of muscle damage. Serum concentrations increase within hours of an insult to muscle. • Training, transport and strenuous exercise can cause a mild elevation in serum CK, whereas diseases such as exertional rhabdomyolysis or nutritional muscular dystrophy may cause CK concentrations of thousands to hundreds of thousands of IU/L. • Serum LDH activity is tissue non-specific, although muscle, liver and erythrocytes may be the major source of high activity. • Elevations of serum LDH can be seen in horses with exertional rhabdomyolysis and other causes of myodegeneration, myocardial necrosis and in association with liver disease. • To differentiate the source of LDH, it is helpful to separate it into its different isoenzyme forms by electrophoresis. • Concentrations of CK peak in 6 to 12 hours, and AST concentrations peak in 12 to 24 hours. • The half-life of CK is 1 to 2 days, and for AST it is 7 days. • Therefore, elevated CK levels indicate active muscle damage. If CK decreases or is normal and AST is high this indicates that myonecrosis is not continuing. If the injury is not progressive, CK will return to normal within 24 to 48 hours. • Collection and storage of blood samples are important. Ideally, samples should be transported to the laboratory immediately. Separation of the serum or plasma should be done as soon as possible since RBC lysis can lead to release of AST and LDH. • Primarily affects young horses less than 1 year of age. • Primarily affects the extensor muscles of the pelvic limbs resulting in a stiff gait. • Bilateral focal enlargement of the proximal caudal thigh and rump muscles gives the impression that the horse is overdeveloped or is ‘double muscled’. • Percussion of affected muscles induces a prolonged contraction resulting in raised lumps or ‘dimpling’ which lasts for a minute or more with eventual slow relaxation. • Clinical signs usually do not progress beyond 6 to 12 months of age but can involve multiple organ systems. • HYPP is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. • The gene responsible has been identified in descendants of the stallion Impressive. • The pathogenesis involves an altered permeability of muscle membranes to sodium and potassium by affecting the sodium ion channel. An uncontrollable influx of sodium causes depolarization of muscle fibres resulting in uncontrollable muscle twitching and weakness. • Recurrent episodes of muscle weakness, tremors and collapse. • Usually less than 4 years of age. HYPP has been recorded in horses as young as 2 months and as old as 15 years. • Signs often begin with stiffness, sweating and muscle fasciculations. • Some horses ‘dog-sit’; some become recumbent. • Occasionally episodes are accompanied by respiratory noises due to paralysis of the larynx and pharynx. • Horses remain bright and alert and respond to noise and painful stimuli. • During episodes of clinical disease there is an increase in PCV/total protein and potassium [hyperkalaemia (serum potassium 5.0 to 12.3 mEq/L)]. • DNA blood test is available at the University of California – Davis, and is the most reliable and effective way of identifying carriers of the HYPP gene. • HYPP can be tentatively diagnosed on the basis of the clinical signs and signalment. • Potassium chloride challenge test – involves administering 90–150 mg/kg of potassium chloride dissolved in water and given via a nasogastric tube following an overnight fast. A positive result is characterized by signs of HYPP in 2–4 hours. Known affected horses do not always test positive at the lower doses. Treatment: Prior to treatment, blood samples are obtained to determine the serum concentrations of potassium and muscle enzymes. Mild attacks (trembling but no recumbency):: • Exercise the horse by walking or lunging. This stimulates adrenaline, which aids in the replacement of intracellular potassium. • Feed grain because the carbohydrates will supply glucose which will stimulate insulin release which promotes potassium uptake by cells. • Acetazolamide orally. This carbonic anhydrase inhibitor will increase potassium excretion by the kidneys. Severe attacks (horse is recumbent and unable to rise):: • Insert an intravenous catheter. • Administer calcium gluconate 23%: 150 mL added to 1 to 2 L of 5% glucose per 500 kg body weight. The majority of affected horses will stand immediately following this treatment. • If there is no response to calcium gluconate, administer 1 litre of 5% sodium bicarbonate IV (1 mEq/L). • If there is no response, give 3 litres of 5% dextrose IV and monitor the serum potassium concentration. • Once diagnosed, most cases can be managed with dietary and exercise modifications. Decrease or eliminate alfalfa to decrease potassium concentration and replace with oat or grass hay or pasture turnout. • Pasture or paddock exercise is preferred to stall rest. • If conservative treatment is ineffective, oral acetazolamide can be administered two to three times a day. • Affected horses are usually large and well-muscled and have been exposed to prolonged or deep anaesthesia on a hard surface. • Muscle compression and prolonged immobility result in muscle ischaemia and hypoperfusion. • A history of gaseous anaesthesia, mechanical ventilation and mean arterial pressures of less than 65 mmHg for an extended period of time. • A localized form (‘compartmental syndrome’) is associated with damage within osteofascial compartments. • The generalized form is thought to be due to the combination of the compartmental syndrome, muscle sensitivity to anaesthesia, stress, lowered blood pressure and use of muscle relaxants during anaesthesia. Clinical signs: This disorder primarily affects the triceps, quadriceps, hind limb extensors, longissimus muscles, masseter and gluteal muscles. • Lateral recumbency affects the triceps, deltoid and hind limb extensors. • Dorsal recumbency affects the longissimus and gluteals. • Affected muscles can be flaccid or hard, hot and painful on deep palpation and are swollen. • The horse is weak and unable to support its weight on the affected limb. It may have a dropped elbow appearance or knuckling of both hind fetlocks (Figure 21.1). • Signs may first appear 30 to 60 minutes after standing. • There is usually recovery within 24 hours if only a single muscle group is involved. • Phenylbutazone or flunixin meglumine. • Dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) IV or topically to affected muscles. 2. Severe generalized acute rhabdomyolysis: • Goals are to prevent more muscle damage and acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria, to provide analgesia, and to relieve stress. • Xylazine, detomidine or romifidine. • Fluid therapy with a balanced electrolyte solution is indicated to prevent acute renal failure and to maintain normal electrolyte and acid/base balance. • Mannitol may be indicated in the severely affected horse.
Muscle disorders and performance problems
21.1 Examination of the muscular system
Clinical pathology
Interpretation of enzyme levels
21.2 Congenital/familial disease
Hyperkalaemic periodic paralysis (HYPP)
21.3 Myopathy with physical causes
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree