Fig. 1.
(a) Lateral view of bioluminescence measurement on intracranial meningioma. Mouse on left with high activity and mouse on right with low activity. (b) Axial view of same mice, once again left mouse with high activity and right with low activity.
3.4 Analysis
3.4.1 Magnetic Resonance Imaging
1.
Follow institution’s animal handling protocol.
2.
One day after final intracranial BLI, sacrifice mice with an overdose of intraperitoneal phenobarbital.
3.
Five minutes before phenobarbital injection, administer 100 μl of gadolinium via tail vein injection for contrast-enhanced MR images.
4.
Center each mouse in a radiofrequency wrist-coil and image with T1- and T2-weighted 1-mm imaging sequences in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes on a 3-T magnet.
3.4.2 Immunohisto chemical Staining for Vimentin, EMA, GFAP, and Ki 67
1.
Cut paraffin-fixed tissue slides at 4 μm.
2.
Melt slides at 55–60°C for 30 min.
3.
Deparaffinize in xylene for 5 min.
4.
Rehydrate in graded alcohols, washing twice in both 100 and 95%, and once in 70% for 1 min each.
5.
Using the Ventana ES at 40°C, apply heat-induced epitope retrieval in citrate buffer (pH 6.0) in microwave oven for 15 min at 50% power.
6.
Allow to cool for 15 additional minutes.
7.
Apply the primary antibodies for 32 min as follows: vimentin (1:300, mouse monoclonal Ab, Cline Vim 3B4, Dako Cytomation); EMA (1:200, mouse monoclonal Ab, Clone E29, Dako Cytomation); GFAP (1:400, mouse monoclonal Ab, Clone 6 F2, Dako Cytomation); Ki 67 (1:160, mouse monoclonal Ab, Dako).
8.
Follow primary antibody application with the appropriate secondary antibody for 8 min.
9.
Using the IView DAB Detection Kit, determine staining.
10.
Counterstain with hematoxylin for 4 min.
11.
Dehydrate slides with graded alcohol, washing once in 70%, and twice each in 95 and 100% for 30 s each, dehydrate in alcohol and xylene.
12.
Cover with a coverslip.
13.
After staining using the above procedure, stain normal skin, normal pancreatic, brain, and colon cancer cells for EMA, GFAP, and Ki 67, respectively.
14.
For the negative controls, follow the same procedure used for the positive control tissue samples, but without the primary antibody.
15.
Take three random pictures of each slide at 400× magnification with an Olympus Microfire camera.
16.
Analyze the images using Image-Pro Plus 5.0 graphic analysis software.
17.
To calculate the MIB-1 (Ki 67) index, divide the number of MIB-1 (Ki 67)-stained cells by the total number of stained cells (Fig. 2).
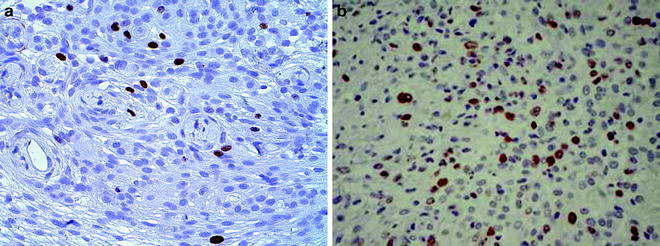

Fig. 2.
MIB-1-stained meningiomas taken from intracranial mouse model. (a) Low MIB-1 index. (b) Higher MIB-1 activity.
3.4.3 Transmission Electron Microscopy for Desmosomes
1.
Harvest the tumor samples.
2.
Cut into 1-mm3 blocks.
3.
Fix in 2.5% paraformaldehyde with 1% glutaraldehyde.
4.




After at least 24 h, rinse samples twice for 10 min each in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate buffer with sucrose and calcium chloride (pH 7.4).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


