Chapter 1 Invertebrates
TABLE 1-1 Antimicrobial and Antifungal Agents Used in Invertebrates.a–e
| Agent | Dosage | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Benzalkonium chloride | 0.5 mg/L long-term66 | Quaternary amine with broad disinfection properties |
| 10 mg/L for 10 min56 | ||
| Ceftazidime (Fortaz, Pfizer) | 20 mg/kg intracardiac q72h × 3 wk56 | Spiders/cephalosporin with good activity against Gram-negative bacteria (e.g., Pseudomonas); although this regimen appears safe, efficacy has not been determined |
| Chloramphenicol | 75 mg/kg PO, IM q12h × 6 days59 | Cephalopods |
| 10-50 mg/L as an immersion treatment for several days10,62,64 (prepare fresh solution with 100% water change q24h) | Corals/reduce lighting for treated animals if possible (slows metabolic rate and may reduce stress and improve drug tolerance); rinse animals well with fresh seawater before return to primary habitat; properly treat any effluent before discharge; florfenicol may be a better alternative (risk to humans from chloramphenicol) | |
| Enrofloxacin (Baytril, Bayer) | 5 mg/kg IM, IV28,59 | Cuttlefish and possibly other cephalopods |
| 5 mg/kg IV56 | Spiders | |
| 10 mg/kg PO28,59 | Cuttlefish and possibly other cephalopods | |
| 10-20 mg/kg IM65 | Chinese mitten crabs/PD | |
| 10-20 mg/kg PO q24h56 | Spiders | |
| 2.5 mg/L × 5 hr immersion q12-24h28,59 | Cuttlefish and possibly other cephalopods | |
| Fluconazole | 3 mg/kg q4d × 6 treatments60 | Horseshoe crabs |
| Formalin | 1-1.5 ppm37 | Horseshoe crabs/ectocommensals |
| Furazolidone | 50 mg/L q12h for 10 min immersion59 | Cephalopods |
| Iodine, Lugol’s 5% solution | 5-10 drops/L of seawater; use as an immersion for 10-20 min10,64 | Corals/antiseptic; cauterize wounds; strong oxidizing agent; some corals are sensitive, including pulse corals (Xenia sp), Anthelia spp, and star polyps (Pachyclavularia spp); remove corals at first signs of stress (polyp expulsion) |
| Topically at full strength (5%) for 20-30 sec64 | ||
| Itraconazole (Sporanox, Janssen) | 10 mg/kg IV1 | Horseshoe crabs/PD |
| Nitrofurazone | 1.5 mg/L for 72 hr59 immersion | Cephalopods/nitrofuran; carcinogenic; drug inactivated in bright light; water soluble formulations preferred |
| 25 mg/L q12h for 1 hr59 immersion | ||
| Nystatin | 50 mg/mL for surface “sterilization” of aquatic nematodes8,47 | |
| Oxolinic acid | 10 mg/kg intrasinus67 | Kuruma shrimp/PD; quinolone; Gram-negative bacteria; decreased uptake in hard water; better uptake pH <6.9 |
| 50 mg/kg PO67 | ||
| Oxytetracycline | 10 mg/kg intrasinus67,68 | Tiger shrimp/PD; cooking reduced muscle levels by 30-60% and shell levels by 20% |
| 25 mg/kg intrasinus67 | Kuruma shrimp/PD | |
| 25-50 mg/kg IV52 | Horseshoe crabs/PD | |
| 50 mg/kg PO67,68 | Kuruma shrimp/PD; tiger shrimp/PD; cooking reduced muscle levels by 30-60% and shell levels by 20% | |
| 100 mg/kg PO57 | White shrimp/PD | |
| 200 mg/colony q4-5d × 3 treatments70 | Honeybees/for treating American and European foulbrood; withdrawal time of 6 wk; should not be used on hives where honey will be consumed by humans | |
| 10-15 mg/L q48-72h × 3-5 treatments33 | Chocolate chip sea stars/cutaneous ulcerations; may be applicable to other echinoderms with bacterial lesions | |
| 1 g/lb of feed51 | American lobsters/gaffkemia; approved for use in food animals by the FDA | |
| Silver sulfadiazine cream (Silvadene, Marion Merrill Dow) | Apply topically to lesions | Proceed with caution (biotest if possible) as treatments are empirical |
| Sulfadimethoxine | 50-100 mg/kg in feed × 14 days51 | Penaeid shrimp |
| Sulfadimethoxine/ormetoprim (Romet-30, Alpharma) | 42 mg/kg intrapericardial4 | American lobster/PD |
| Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim | Bioencapsulated in brine shrimp PO q12h13,40,49,50 | White shrimp/PD; combine 20-40% trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole with a lipid emulsion (Selco, INVE Aquaculture) at a concentration of 1:5 |
| Tetracycline | 10 mg/kg PO q24h59 | Cephalopods |
| 10 mg/L bath36,64 | Corals/efficacy questionable in saltwater; anecdotal evidence of successful treatment for bacterial infections | |
| Trifluralin | 0.01-0.1 ppm as an immersion51 | Penaeid shrimp/larval oomycetosis |
| Tris EDTA and neomycin (Tricide-Neo, Molecular Therapeutics) | 100 mL/L for 45 min q24h × 7 days as an immersion33 | Cushion sea stars/cutaneous ulcers; may be applicable to other echinoderms |
| Tylosin (Tylan, Elanco) | 200 mg/colony q7d × 3 treatments70 | Honeybees/antibiotic applied topically to the brood chamber for control of American foulbrood (Paenibacillus larvae); approved by the FDA; should not be used in hives where the honey will be consumed by humans |
| Winter savory extract (Satureja montana) | 0.01% in microcrystalline sugar15 | Honeybees/chalkbrood fungal disease (Ascosphaera apis); a number of plant aromatic oils have been tested, some with more promise than others, on various diseases of honeybees20,70 |
a Not to be used with invertebrates intended for human consumption unless government approved.
b Preferable to treat a single animal of a species (biotest) to determine toxicity.
c Tank treatment: when treating the invertebrates’ resident aquarium, disconnect activated carbon filtration to prevent drug removal. Many drugs adversely affect the nitrifying bacteria, so water quality should be monitored closely (especially ammonia and nitrite concentrations). Keep water well aerated when appropriate and monitor patient(s) closely. Perform water changes and reconnect filtration to remove residual drug following treatment. Discard carbon following drug removal.
d Bath (immersion) treatment: remove invertebrates from resident aquarium and place in container with known volume of water and concentration of therapeutic agent. Watch closely for signs of toxicity.
e Invertebrate species, temperature, and water quality parameters can influence the pharmacodynamics of many drugs, especially antimicrobials.
TABLE 1-2 Antiparasitic Agents Used in Invertebrates.a–e
| Agent | Dosage | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Acetic acid, glacial | 3-5% solution for 1 hr12 | Horseshoe crabs |
| Amitraz | Use as directed70 | Honeybees/acariasis; commercial packaging should be consulted prior to use |
| Chromic acid | 0.2% immersion for several min9,58 | Turbellarians/Urceolaria protozoans |
| Formalin | 50-100 μL/L for 4 hr or 25 μL/L indefinitely51 | Shrimp/protozoal ectoparasites; approved for use by the FDA in food animals |
| Formic acid | Use as directed70 | Honeybees/acariasis; commercial packaging should be consulted prior to use |
| Freshwater | 1-3 min dip64 | Stony corals, some soft corals/flatworms, and other ectoparasites; buffer to pH 8.2 and use clean, dechlorinated water; do not use on small polyp corals or xenids; biotest first, if possible, especially when attempting with a new species |
| Fumagillin | Use as directed70 | Honeybees/nosemosis (caused by microsporidian parasites); commercial packaging should be consulted prior to use |
| Ivermectin | Stock solution of 1:1 (1% ivermectin and propylene glycol); dilute 1:50 with distilled water prior to topical use56 | Spiders/for the treatment of individual parasitic mites; apply carefully to mites with fine paintbrush or similar implement |
| Levamisole (Levasole, Schering Plough) | 8 mg/L immersion for 24 hr64 | Corals/metazoan parasites; well tolerated by Acropora spp, Montipora digitata, M. capricornis, Seriatopora histrix, Stylophora pistillata |
| Menthol | Use as directed70 | Honeybees/acariasis; commercial packaging should be consulted prior to use |
| Metronidazole | 50 mg/kg intracardiac × 1 treatment56 | Spiders/appears safe, but efficacy is unknown |
| 100 mg/L for 16 hr59 | Cephalopods/antiprotozoal | |
| Milbemycin oxime (Interceptor, Novartis) | 0.625 mg/L as an immersion24,32,38 | Stony corals (Acropora)/“red bug” (Tegastes acroporanus) |
| Potassium permanganate | 25-30 ppm for 30-60 min51 | Penaeid shrimp/external parasiticide |
| Povidone iodine | 0.75% solution for topical treatment56 | Spiders/fungal infections; use water based solution |
| Thymol | Use as directed70 | Honeybees/acariasis; commercial packaging should be consulted prior to use |
| Triton X-100 (Sigma) | Culture turbellarian eggs in 0.25-1% solution for 4 days9 | Turbellarian eggs/protozoan (Thraustochytrium caudivorum) |
a Not to be used with invertebrates intended for human consumption unless government approved.
b Preferable to treat a single animal of a species (biotest) to determine toxicity.
c Tank treatment: when treating the invertebrates’ resident aquarium, disconnect activated carbon filtration to prevent drug removal. Many drugs adversely affect the nitrifying bacteria, so water quality should be monitored closely (especially ammonia and nitrite concentrations). Keep water well aerated when appropriate and monitor patient(s) closely. Perform water changes and reconnect filtration to remove residual drug following treatment. Discard carbon following drug removal.
d Bath (immersion) treatment: remove invertebrates from resident aquarium and place in container with known volume of water and concentration of therapeutic agent. Watch closely for signs of toxicity.
e Invertebrate species, temperature, and water quality parameters can influence the pharmacodynamics of many drugs.
TABLE 1-3 Chemical Restraint/Anesthetic/Analgesic Agents Used in Invertebrates.
| Agent | Dosage | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Benzocaine | 100 mg/L2,30 | Abalone/anesthesia; not sold as anesthetic in United States; available from chemical supply companies; do not use topical anesthetic products marketed for mammals; prepare stock solution in ethanol (benzocaine is poorly soluble in water); store in dark bottle at room temperature |
| 400 mg/L19 | Leeches/this could be applied, with caution, to other aquatic annelids | |
| 2.5-3 g/L59 | Cephalopods/euthanasia | |
| Butorphanol | Fish, amphibian, and reptile dosages can be employed with care | Analgesia; use with caution as dosing regimens are empirical; biotest when possible |
| Carbon dioxide | Blow gas over animal9,41 | Terrestrial turbellarians/euthanasia |
| 3-5%31 | Terrestrial arthropods/euthanasia; isoflurane and sevoflurane may be preferable with regard to recovery; an anesthetic chamber has been developed/described for use in the fruit fly71 | |
| Chloretone | 0.1%9,55 | Turbellarians/anesthesia |
| Clove oil (eugenol) | 0.125 mL/L (approx. 125 mg/L) as an immersion26 | Crustaceans/stock solution: 100 mg/mL of eugenol by diluting 1 part clove oil with 9 parts 95% ethanol (eugenol is poorly soluble in water); over-the-counter preparation (pure) available at most pharmacies contains approximately 1 g eugenol per mL clove oil |
| Ethanol | 1.5-3% solution34 | Cuttlefish/may not be effective for cold water cephalopods30 |
| 3% solution30 | Abalone | |
| 5% solution25,31 | Aquatic gastropods | |
| 5% solution16,42 | Oligochaetes/adequate for terrestrial earthworms such as Lumbricus terrestris | |
| 10% solution6,9,55,73 | Turbellarians/anesthesia | |
| 10% solution59 | Cephalopods/euthanasia | |
| Ethanol/menthol (Listerine, McNeil-PPC) | 10% in saline74 | Aquatic gastropods/anesthesia |
| Hydroxylamine hydrochloride | 1% solution9,55 | Turbellarians/anesthesia |
| Ice | Used to effect;9,22 pure ice water can also be used9,55 | Turbellarians/sedation; cover ice with filter paper to protect the flatworms |
| Isoflurane | Can be used with an anesthetic chamber | Terrestrial gastropods,27 arachnids17,23,45,56/anesthesia; fast induction with a possible excitatory period; anesthetic depth may not be appropriate for invasive surgery;27 usually applied at a 5% concentration for arachnids |
| Ketamine | 40-90 mcg/g IM11 | Crayfish/induction time of less than 1 min and anesthetic duration of 10 min at low dose and 2 hr at high dose |
| 0.025-1 mg/kg26 | Australian giant crabs/fast induction (less than 30 sec) with an excitatory phase; dose dependent anesthetic duration of 8-40 min | |
| Lidocaine | 0.4-1 mg/g IM11 | Crayfish/induction time of less than 2 min and duration of anesthesia of 5-30 min when injected into the tail |
| Magnesium chloride | Intracoelomic14 | Sea hares/short induction time (2-5 min) and good muscle relaxation |
| 6.8 g/L28,30 | Cephalopods/induction time of 6-12 min in cuttlefish | |
| 30-50 g/L35 | Scallops/fast induction and recovery | |
| 1:1 isotonic salt and seawater as an immersion7,9 | Marine turbellarians | |
| 1:1 mixture of 7.5% with seawater33,44 | Echinoderms/concentration adjustments may be required for prolonged anesthesia | |
| 7.5% immersion40,48 | Polychaetes | |
| 10% solution prn59 | Cephalopods/euthanasia | |
| Magnesium sulfate | Intracoelomic14 | Sea hares (sea snails; Aplysia)/short induction time (2-5 min) and good muscle relaxation |
| 4-22 g/100 mL72 | Abalone/fast induction and good recovery | |
| MS-222 (Finquel, Argent) | — | See tricaine methanesulfonate |
| 2-phenoxyethanol | 0.5-3 mL/L72 | Abalone/quick induction and short recovery |
| 1-2 mL/L30 | Quick induction and short recovery | |
| Potassium chloride | 1 g/kg (330 mg/mL solution) IV5 | Lobsters/euthanasia; inject at base of second walking leg |
| Procaine | 25 mg/kg IV54 | Crabs/very short induction time (less than 30 sec) and prolonged anesthesia (2-3 hr) |
| Propylene phenoxetol | 1-3 mL/L of a 1% solution30,46,53 | Oysters/anesthesia; this concentration should produce anesthesia in less than 15 min; recovery time is short (under 30 min); higher doses can be used but induce a deeper level of anesthesia; can also be used for giant clams46 |
| 2 mL/L30,69 | Echinoderms | |
| Sevoflurane | Can be used with an anesthetic chamber at a 5% concentration30 | Terrestrial arthropods/see isoflurane for details of administration |
| Sodium azide | 100 mM3,8 | Nematodes (Caenorhabditis elegans)/anesthesia; can survive for 2 hr without apparent harm; sodium azide is a plant and animal cell mutagen; proper hygiene and handling is advised |
| Sodium bicarbonate tablets (Alka-Seltzer, Bayer) | 2-4 tablets/L bath29 | Euthanasia; generates CO2; use when other agents unavailable; keep aquatic invertebrate in solution >10 min after respiration stops; dosage based on piscine literature |
| Sodium pentobarbital | 400 mg/L43 | Aquatic gastropods/anesthesia; very slow onset but apparently safe; controlled drug |
| 1 mL/L2 | Abalone | |
| Tricaine methanesulfonate (MS-222; Finquel, Argent) | Dosages and efficacy vary widely depending on species and application; consult taxon-specific literature30,31 | Anesthesia; stock solution: 10 g/L, buffer the acidity by adding sodium bicarbonate at 10 g/L or to saturation; store stock in dark container; shelf-life of stock extended by refrigeration or freezing; stock that develops an oily film should be discarded; aerate water to prevent hypoxemia; euthanasia: keep animal in solution >20 min after respiration stops |
| Xylazine | 16-22 mg/kg IV26 | Giant crabs/fast induction (3-5 min) and approx 30 min of anesthesia (dose dependent) |
TABLE 1-4 Miscellaneous Agents Used in Invertebrates.
| Agent | Dosage | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Barium sulfate | 4 mL/15 g food21 | Tarantulas, scorpions, millipedes, hissing cockroaches/contrast radiography; inject into a strawberry and feed to millipedes; inject into crickets and/or other prey for carnivorous invertebrates |
| Benzocaine topical (Orabase, Colgate-Palmolive) | Topically64 | Corals and, potentially, other aquatic invertebrates/used as a water-resistant paste; chemotherapeutics can be combined for topical therapy |
| Carbon, activated | 75 g/40 L tank water51 | Removal of medications and other organics from water; usually added to filter system; discard after 2 wk; 75 g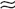 250 cc dry volume 250 cc dry volume |
| Chlorine/chloramine neutralizer | Use as directed | See sodium thiosulfate |
| Diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium (Hypaque-76, Amersham Health) | 4 mL/15 g food21 | Tarantulas, scorpions, millipedes, hissing cockroaches/contrast radiography; combine with/inject into the food item and feed 1-3 hr prior to radiography |
| Hydrogen peroxide (3%) | 0.25 mL/L water50 | Acute environmental hypoxia; dose from the piscine literature |
| Iohexol | 12 mL/kg IV | Horseshoe crabs/contrast radiography |
| 15 mL PO61 | ||
| Methylmethacrylate | Apply topically as needed18,56 | Arthropods (spiders, scorpions, insects)/repair fractured exoskeleton; there are numerous references for the application of surgical adhesives, so consult the appropriate taxon-based literature |
| Mineral oil | 1 mL/kg PO | Insects/laxative18 |
| Nitrifying bacteria | Use as directed for commercial products | Seed or improve development of biological filtration to detoxify ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate; numerous commercial preparations; do not expose products to extreme temperatures; use before expiration date |
| Add material (e.g., floss, gravel) from a tank with an active biological filter and healthy fish to new tank50 | Must evaluate risk of disease transmission with this technique | |
| Oxygen (100%) | Fill plastic bag with O2 containing 1/3 vol of water29 | Acute environmental hypoxia common with transportation; close bag tightly with rubberband; keep animals in bag until normal swimming and respiratory behavior |
| Sodium thiosulfate | Use as directed for chlorine/chloramine neutralizers | Active ingredient in numerous chlorine/chloramine neutralizers; chlorine and chloramine are common additions to municipal water supplies and are toxic to many aquatic invertebrates; ammonia released by detoxification of chloramine is removed by functioning biological filter (see nitrifying bacteria) or chemical means (see zeolite) |
| 10 mg/L tank water39 | ||
| 10 g neutralizes chlorine (up to 2 mg/L) in 1000 L water39 | ||
| 100 mg/L tank water63 | Chlorine exposure | |
| Zeolite (i.e., clinoptilite) (Ammonex, Argent) | Use as directed | Ion-exchange resin that exchanges ammonia for sodium ions; clinoptilite is an active form of zeolite; used to reduce or prevent ammonia toxicity |
| 20 g/L tank water50 |
TABLE 1-5 Common Captive Invertebrate Taxa.a



