35 Introduction to the colon and colonic disorders
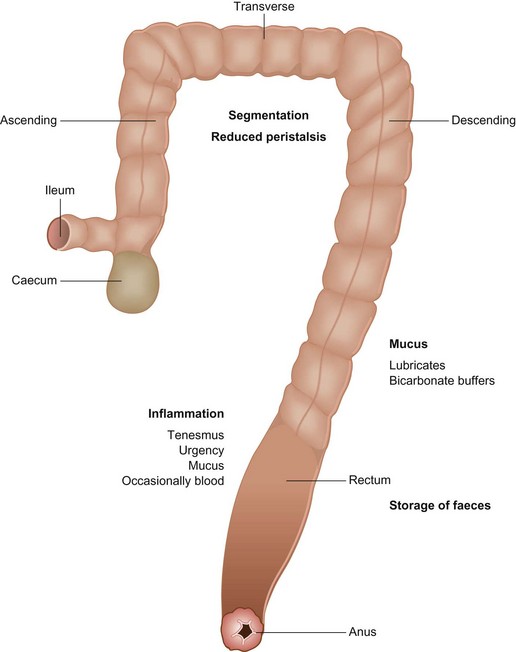
The large intestine comprises the caecum, colon, rectum and anus (Fig 35.1). The primary role of the colon is the resorption of water and electrolytes. Colonic bacteria break down fermentable fibre to produce short chain fatty acids – acetate, butyrate and proprionate. Butyrate is an essential energy source for colonocytes.
Diseases of the colon include:
Causes of large bowel diarrhoea include:
Clinical signs of large intestinal disease include:
Investigation of large intestinal disorders
An initial minimum data base, especially faecal testing, as for small intestinal diarrhoea (see page 116) may be helpful in chronic cases. In cats, a fresh saline faecal preparation should be examined for Tritrichomonas foetus under the microscope and a sample sent for PCR test.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree