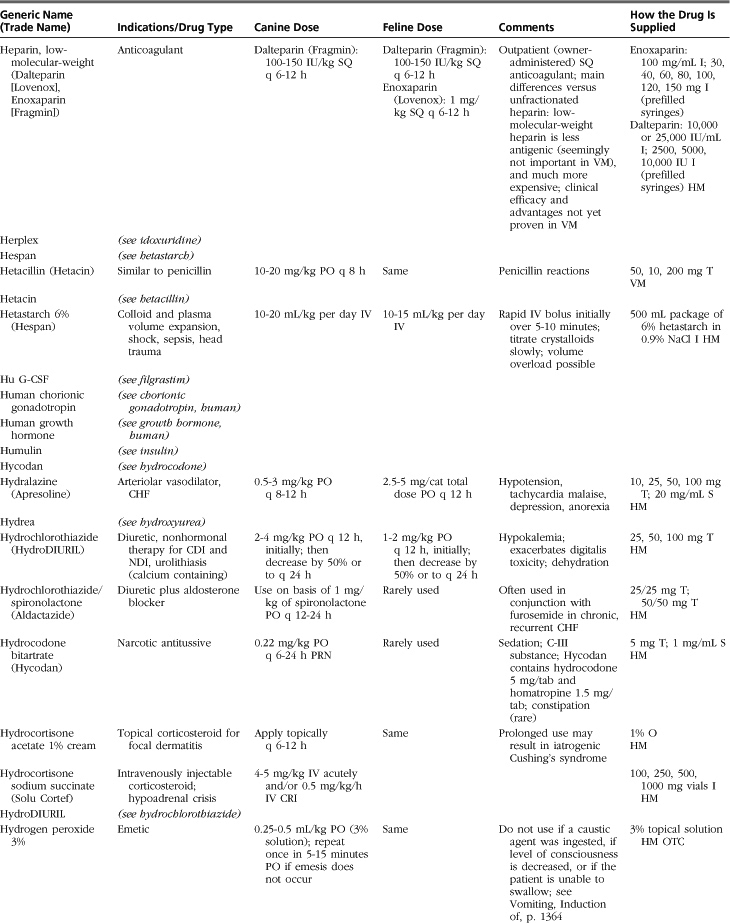
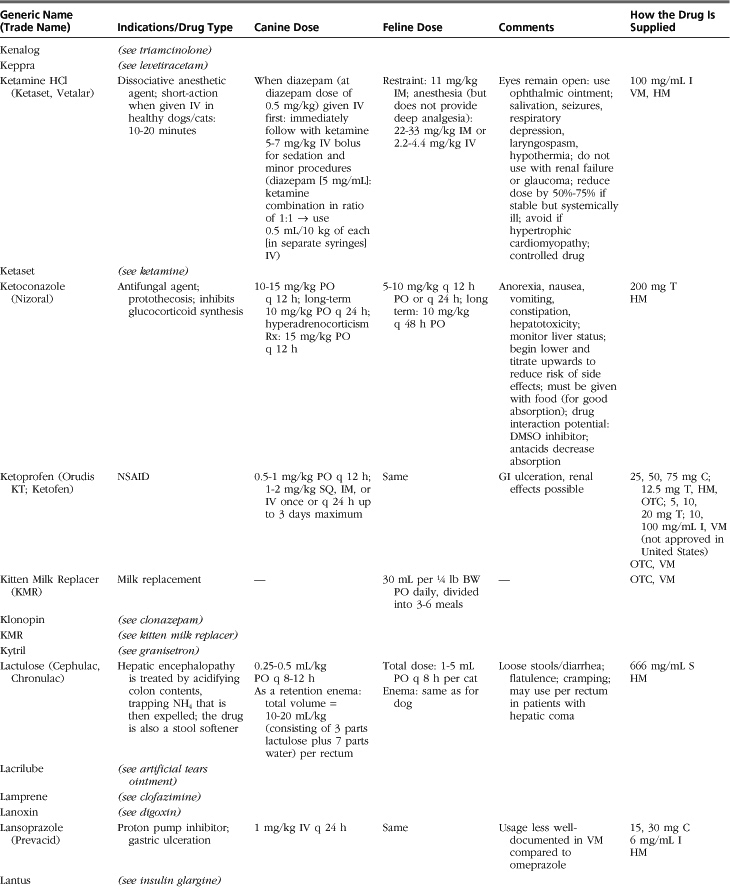
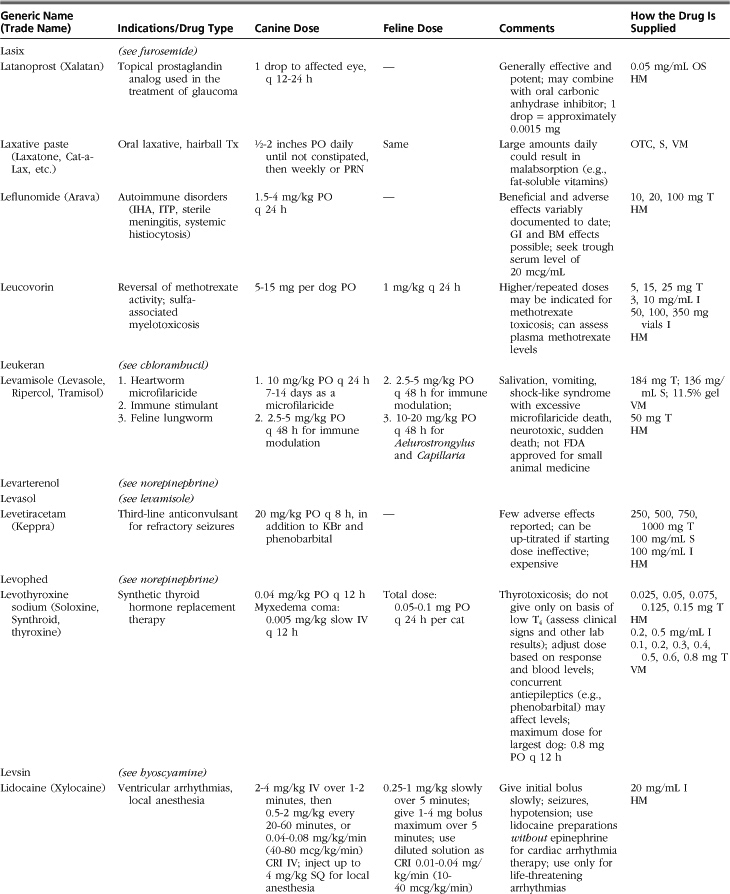
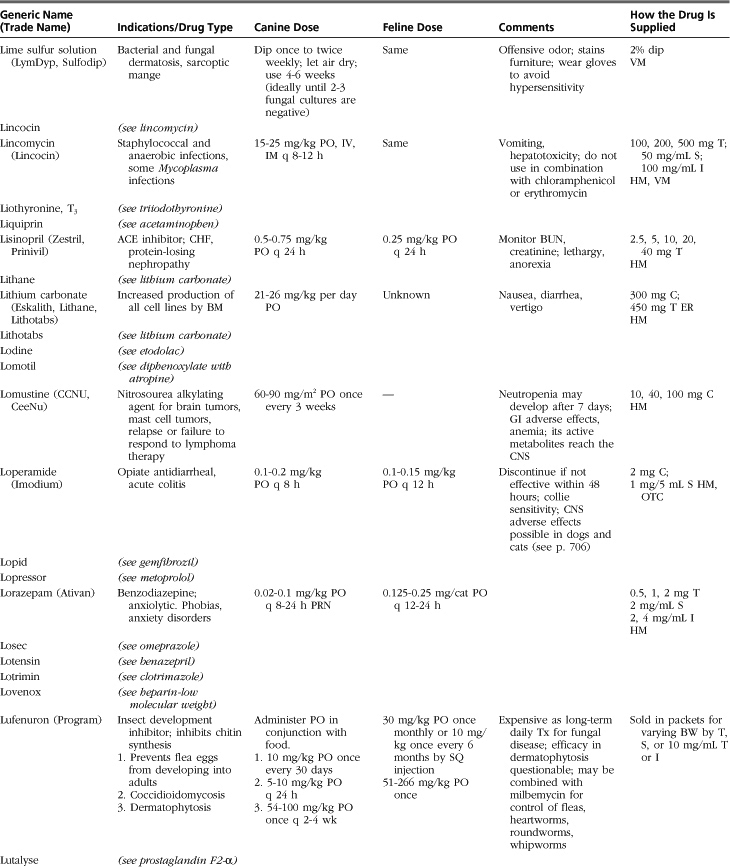
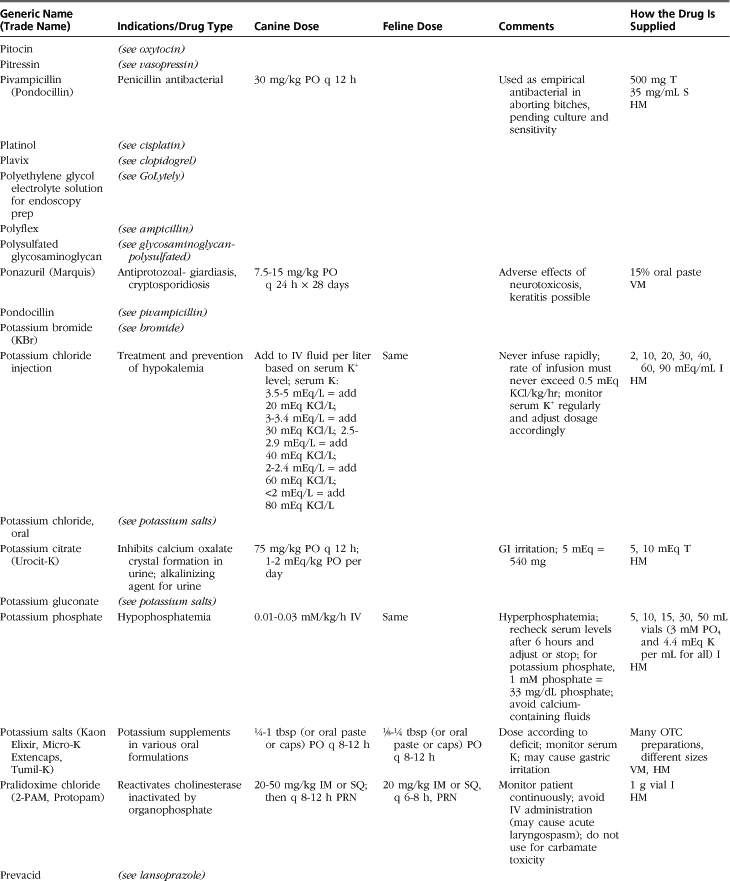
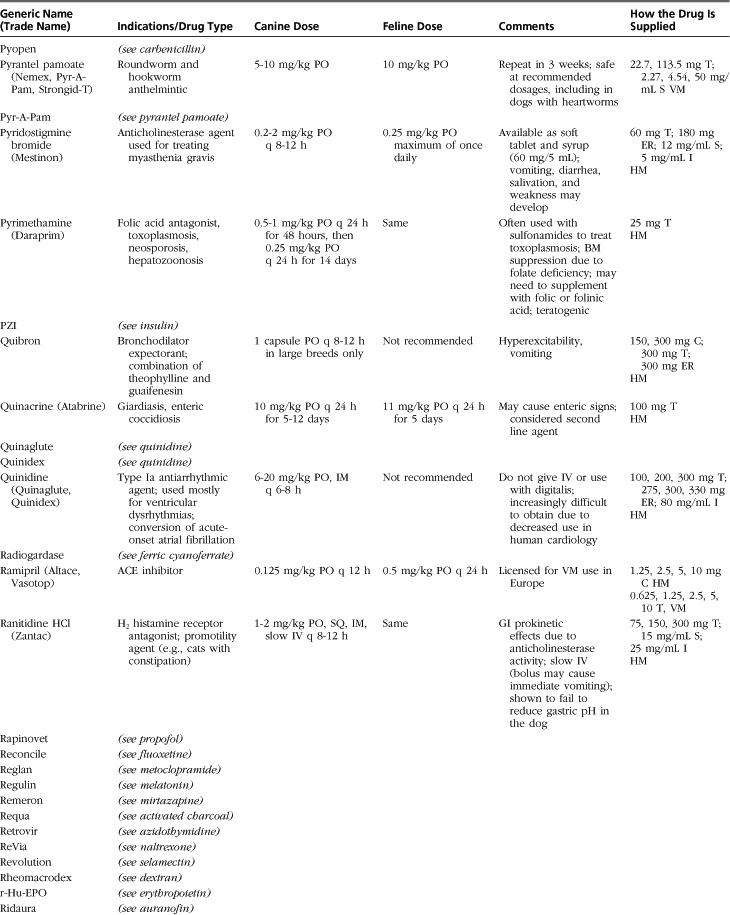
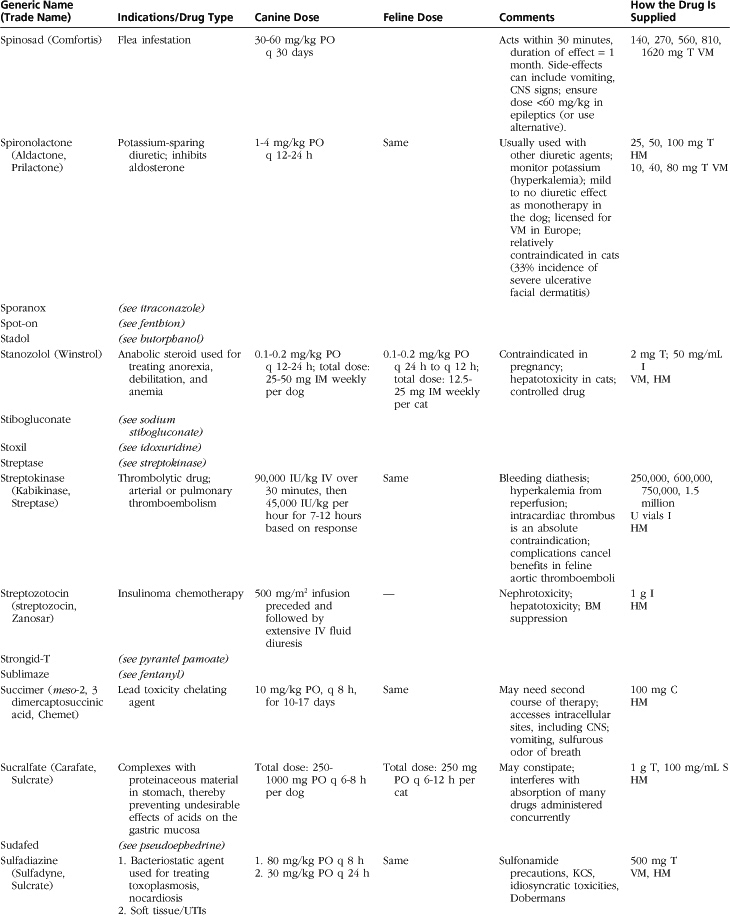
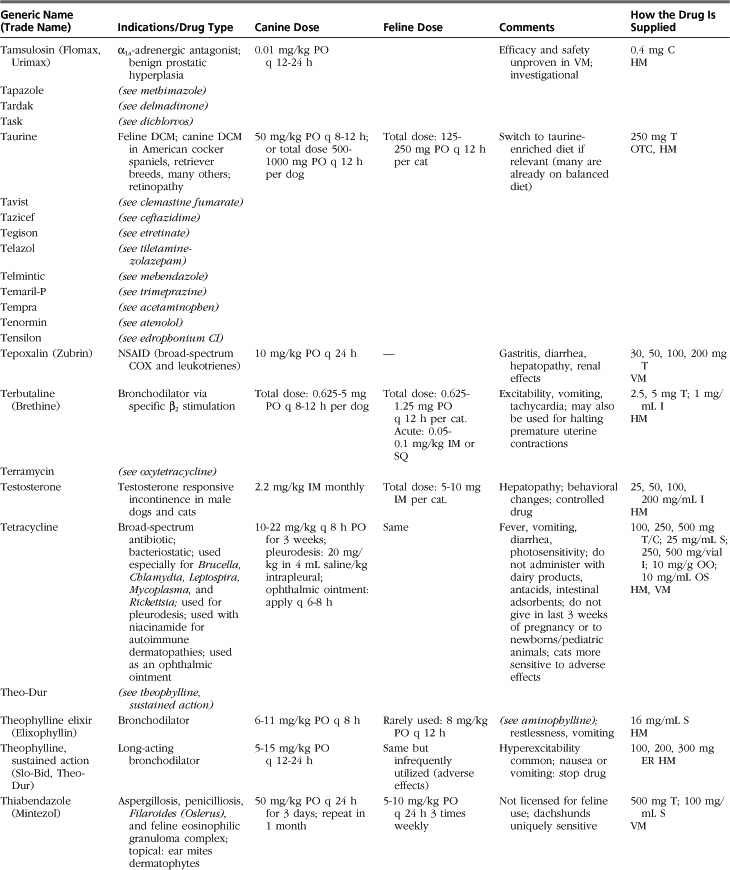
Introduction to Drug Formulary
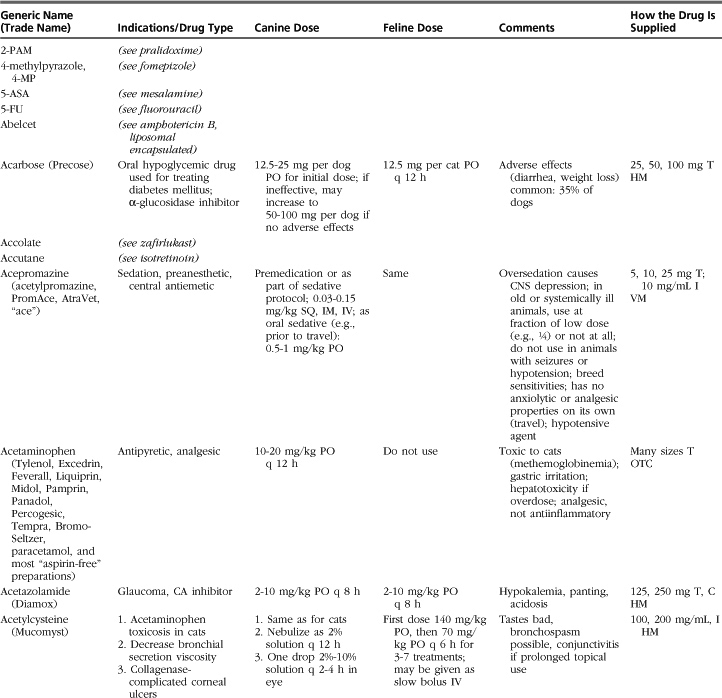
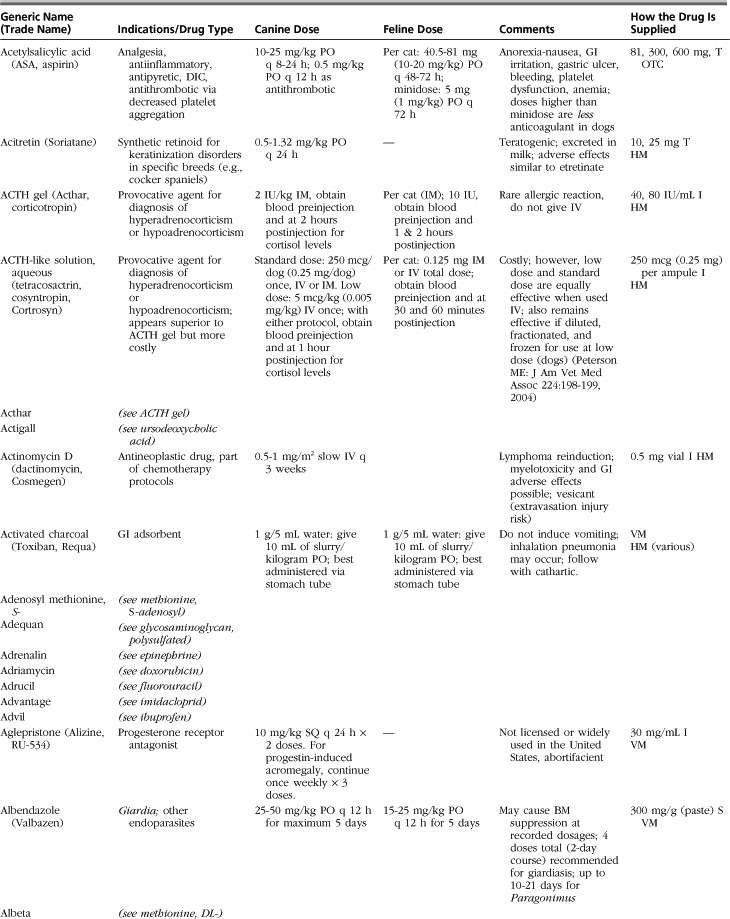
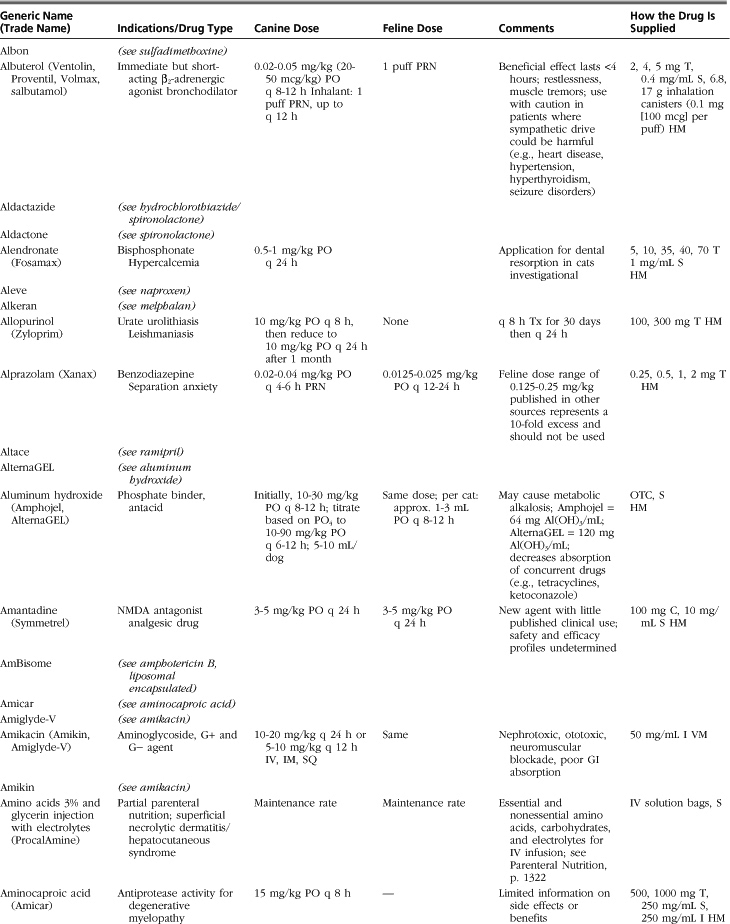
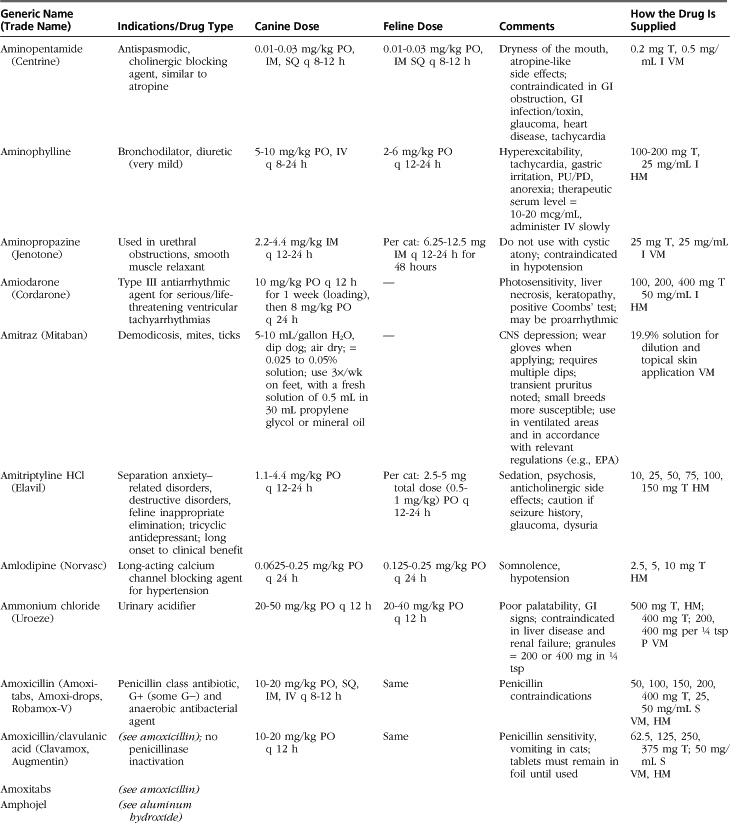
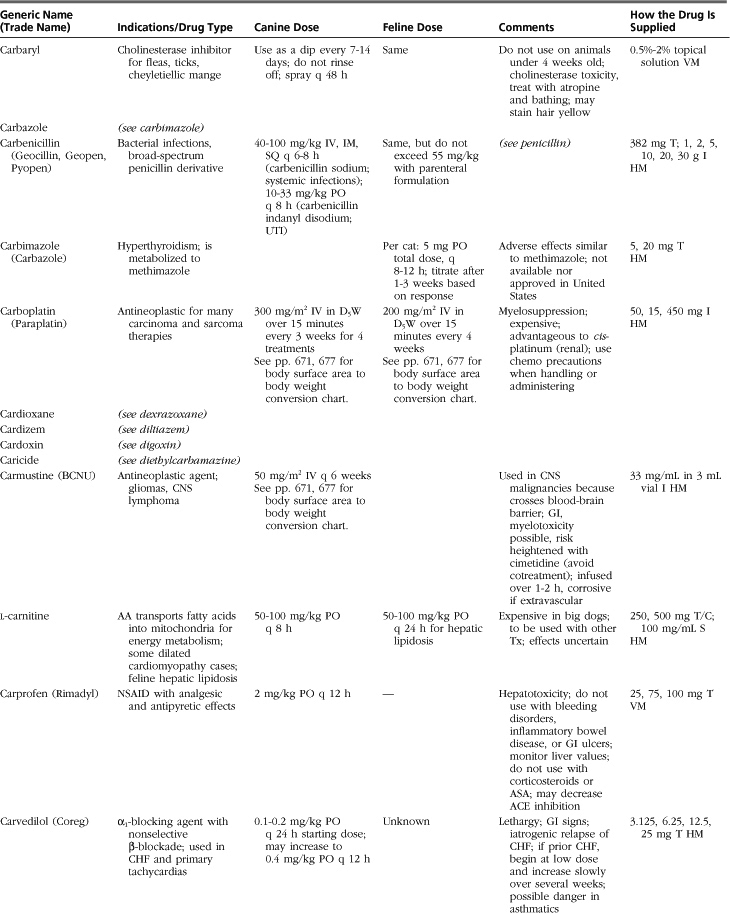
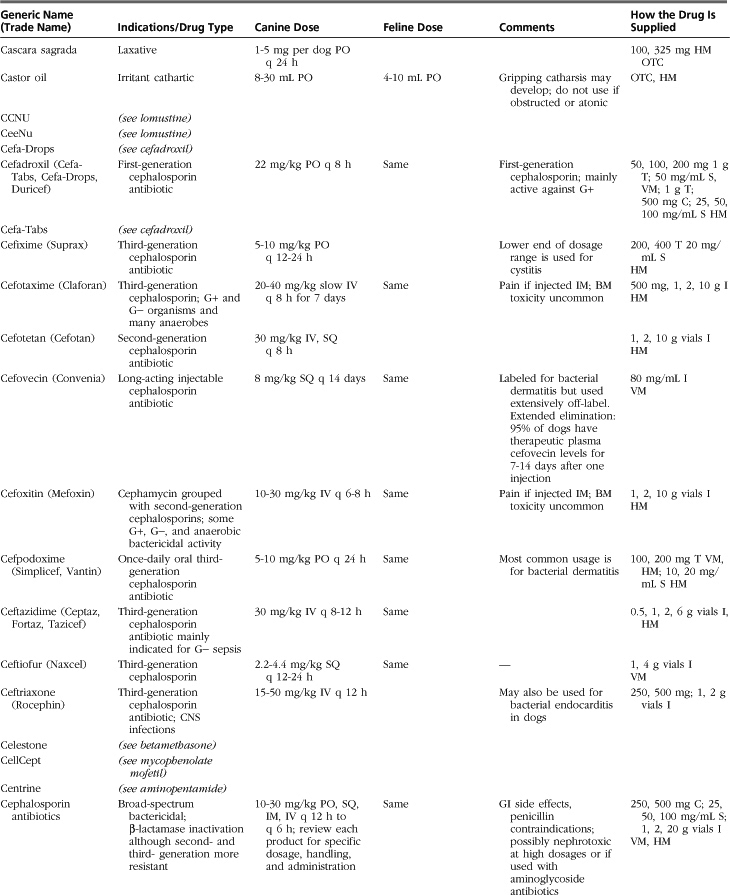
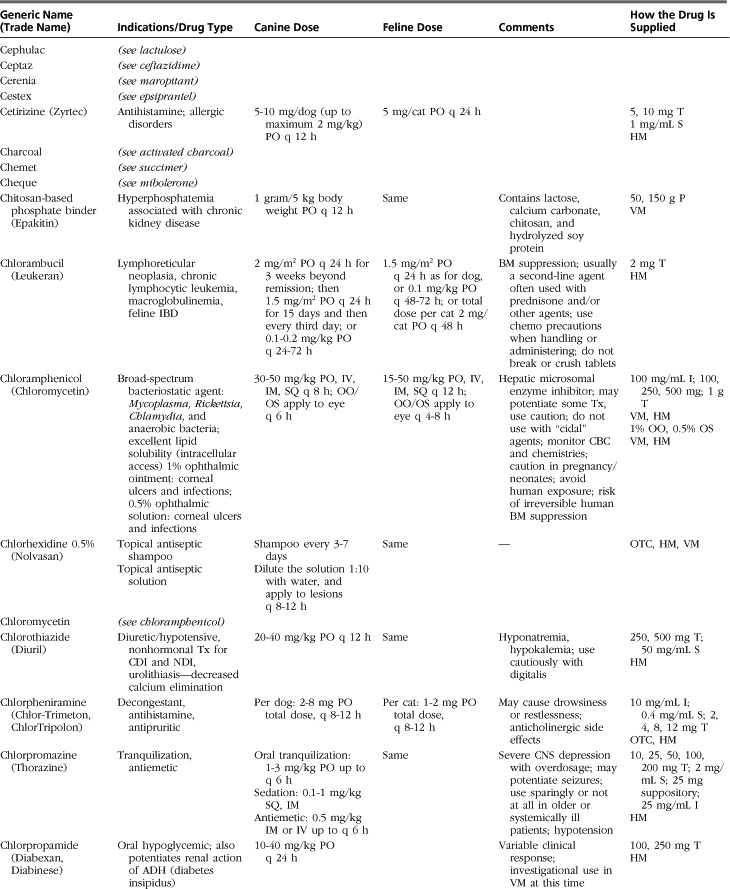
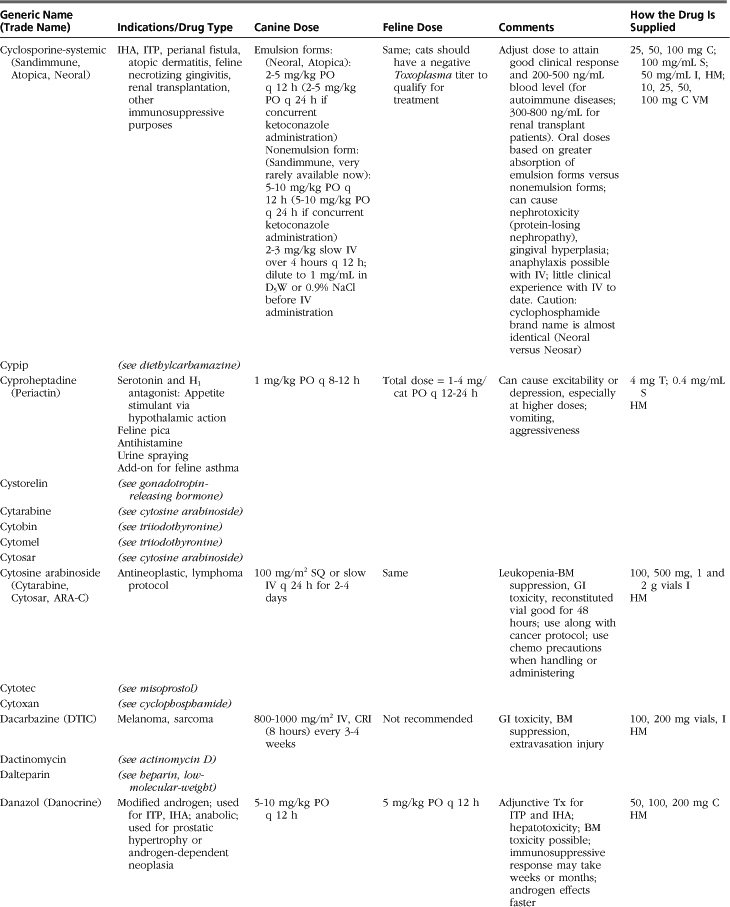
The drugs listed in this formulary represent a compilation of the more commonly used therapeutic agents in small-animal practice, without implying endorsement (or lack thereof) of specific medications. Not all drugs used in veterinary practice are included, and clinicians may infrequently or never use some of those listed.
Drugs, dosages, comments, and side effects are taken from several sources: (1) the clinical experience of the editor and previous redactors of this formulary; (2) drug-related information from the other sections of this textbook; (3) Ettinger SJ, Feldman, EC: Textbook of veterinary internal medicine, ed 6, St Louis, 2005, Saunders; (4) PDR Staff: Physician’s desk reference, ed 64, Williston, VT, 2009, PDR Network; (5) Plumb DC: Veterinary drug handbook, ed 6, Ames, Iowa, 2008, Blackwell; (6) Kirk RW, Bonagura JD, editors: Current veterinary therapy IX-XIV, Philadelphia and St Louis, 1986-2008, Saunders; (7) Greene CE, editor: Infectious diseases of the dog and cat, ed 3, St Louis, 2006, Saunders; and (8) websites medlineplus.gov, www.medicinenet.com, www.drugs.com, and www.rxlist.com.
ABBREVIATIONS
ACE: angiotensin-converting enzyme
ACS: American Chemical Society
ACT: activated coagulation time
ACTH: adrenocorticotropic hormone
APTT: activated partial thromboplastin time
C-III: class 3 controlled drug
CDI: central diabetes insipidus
CDS: cognitive dysfunction syndrome
CLL: chronic lymphocytic leukemia
D5W: sterile 5% dextrose in water
DIC: disseminated intravascular coagulation
DJD: degenerative joint disease
DOCA: deoxycorticosterone acetate
EDTA: ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
EPA: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
FAIDS: feline immunodeficiency virus–induced acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
FDA: U.S. Food and Drug Administration
FIP: feline infectious peritonitis
FIV: feline immunodeficiency virus
HDDST: high-dose dexamethasone suppression test
HPA: hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal
IBD: inflammatory bowel disease
IHA: immune-mediated hemolytic anemia
ITP: immune-mediated thrombocy topenia
KCS: keratoconjunctivitis sicca
LDDST: low-dose dexamethasone suppression test
LES: lower esophageal (gastroesophageal) sphincter
LRS: lactated Ringer’s solution
MVO2: myocardial oxygen consumption
NDI: nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
NSAID: nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug
OTC: over-the-counter, nonprescription item
PDH: pituitary-dependent hyperadrenocorticism
PSS: physiologic saline solution
PTE: pulmonary thromboembolism
PU/PD: polyuria and polydipsia
RAAS: renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
SIBO: small-intestinal bacterial overgrowth/antibiotic-responsive enteritis
SLE: systemic lupus erythematosus
SVT: supraventricular tachycardia
TCC: transitional cell carcinoma
TVT: transmissible venereal tumor
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree