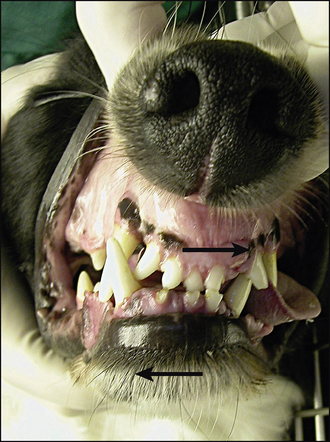
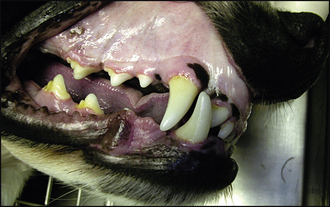
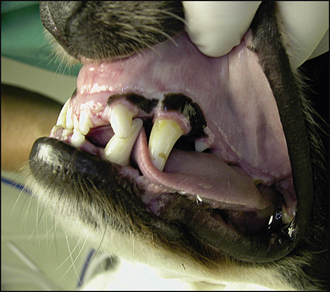
30 Iatrogenic malocclusion
ORAL EXAMINATION – CONSCIOUS
• Marked muscle wastage of muscles of mastication (temporal, masseter and pterygoid) on the left side.
ORAL EXAMINATION – UNDER GENERAL ANAESTHETIC
In summary, examination under general anaesthesia identified the following:
1. The mandibular fracture had healed. The jaw was stable and there was a palpable callus at the ventral border of the left and right mandible level with apices of canine teeth.
3. Full closure of the mouth was not possible due to the mechanical obstruction from the malocclusion (Figs 30.1, 30.2 and 30.3):
4. There was no swelling, abnormal movement or crepitus from the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) on either opening or partial closure of the jaws. When evaluating the TMJ, it is useful to place the animal in dorsal recumbency and manipulate jaw opening, closure and lateral movement while a second person holds the head and upper jaw in a fixed position. The tongue needs to be folded caudally to avoid interference with jaw closure.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree