29 Extraction of permanent teeth
ORAL EXAMINATION – CONSCIOUS
The dog was well behaved and allowed conscious examination, which revealed the following:
1. Skeletal malocclusion
• The upper jaw was extremely long and narrow with respect to the lower jaw, which was of relatively normal length and width for the breed, i.e. relative mandibular brachygnathism.
• The lower canines occluded with the palatal mucosa, distal to the upper canines, causing deep indentations in palate.
ORAL EXAMINATION – UNDER GENERAL ANAESTHETIC
In summary, examination under general anaesthesia identified the following list:
1. Skeletal malocclusion
• The upper jaw was extremely long and narrow with respect to the lower jaw, which was of a relatively normal length and width for the breed, i.e. relative mandibular brachygnathism.
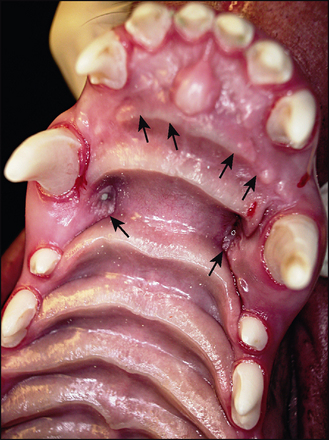
• The lower canines occluded with the palatal mucosa, distal to the upper canines, causing ulcerated indentations in the palate (Fig. 29.1).
• The lower incisors occluded with the palatal mucosa, causing non-ulcerated indentations (Fig. 29.1). There were also indentations in the palatal mucosa where the lower carnassials occluded.
Careful examination with a sharp explorer did not allow communication into the pulp.
FURTHER INVESTIGATIONS
Radiographs were taken of 204 (UCF) and of 104 (contralateral healthy tooth).
RADIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
The shape and diameter of the pulp system of 104 (contralateral healthy) and 204 (UCF) were the same. Both were immature teeth, as expected in a 7-month-old dog.