Chapter 2 Clinical Evaluation of the Urinary Tract
Introduction and Terminology
A. Azotemia is defined as an increased concentration of nonprotein nitrogenous compounds in blood, usually urea and creatinine.
1. Prerenal azotemia is a consequence of reduced renal perfusion (e.g., severe dehydration, heart failure).
2. Postrenal azotemia results from interference with excretion of urine from the body (e.g., obstruction, uroabdomen).
B. Renal failure refers to the clinical syndrome that occurs when the kidneys are no longer able to maintain their regulatory, excretory, and endocrine functions, resulting in retention of nitrogenous solutes and derangements of fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance. Renal failure occurs when 75% of more of the nephron population is nonfunctional.
C. Uremia refers to clinical signs and biochemical abnormalities associated with a critical loss of functional nephrons, and includes the extrarenal manifestations of renal failure (e.g., uremic gastroenteritis, hyperparathyroidism).
D. Renal disease refers to the presence of morphologic or functional lesions in one or both kidneys, regardless of extent.
Clinical Approach
History
Urination
a. Frequency and volume.
(2) Polyuria (usually an indicator of upper urinary tract disease). Normal urine output ranges from 10 to 20 mL/lb/day in dogs and cats.
(5) Oliguria (may be indicative of partial obstruction, dehydration, and some forms of acute renal failure).
b. Initiation of urination. How easily does the animal initiate urination? Difficulty starting the urine stream could be due to partial obstruction, inflammation, or neurologic disease.
c. Diameter of urine stream, with or without interruption of flow. A narrow stream could indicate partial obstruction, urethral spasm, or neurologic disease.
Water Intake
d. Exposure to nephrotoxins such as ethylene glycol (EG) in antifreeze, Easter lily (cats only), aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin), and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be identified. Administration of drugs that could cause polydipsia and polyuria (e.g., glucocorticoids, diuretics) also should be determined.
Physical Examination
A. Evaluation of hydration status is important for interpretation of laboratory data, especially urine specific gravity (USG). Dehydration is suggested by decreased skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, and sunken appearance of the eyes in their orbits.
C. The oral cavity is examined for ulcers, tongue tip necrosis, and pallor of the mucous membranes that may occur in uremia.
D. Presence of retinal edema, detachment, hemorrhage, or vascular tortuosity noted during fundic examination is compatible with systemic hypertension, which may accompany renal disease. The animal may be blind or have impaired vision.
E. Musculoskeletal evaluation.
1. Fibrous osteodystrophy may develop in young animals with renal failure, but is rare in older dogs.
2. Fibrous osteodystrophy is characterized by enlargement and deformity of the maxilla and mandible (so-called rubber jaw).
G. Urinary bladder.
2. The bladder should be evaluated for degree of distension, pain, wall thickness, and presence of intramural (e.g., tumors) or intra-luminal (e.g., calculi, clots) masses.
H. The prostate gland of male dogs and pelvic urethra of males and females are evaluated by rectal examination. The prostate gland should be within the pelvic canal, smooth, bilobed, moveable, and free of pain. Rectal examination is not routine in cats, but should be performed in cats with persistent lower urinary tract signs. The normal pelvic urethra is difficult to identify on rectal palpation.
Laboratory Evaluation of Renal Function
Glomerular Function (values for glomerular function tests in the dog and cat are presented in Table 2-2)
1. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is directly related to functional renal mass. GFR is the gold standard for the assessment of renal function and detection of renal disease progression. Determination of renal blood flow (RBF) also can be useful in detecting progression of renal disease, but is less commonly evaluated than GFR. Unfortunately, GFR is not routinely measured in the evaluation of renal function. Instead, surrogates for GFR such as blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine concentrations are used because they are more easily determined than is GFR. An ideal substance for estimation of GFR should be produced at a constant rate in the body, have little binding to plasma proteins, be freely filtered, and not undergo tubular reabsorption or secretion.
a. BUN concentration. Normal BUN concentrations are 8 to 25 mg/dL in the dog and 15 to 35 mg/dL in the cat.
(1) Renal excretion of urea occurs by glomerular filtration, and BUN concentrations are inversely proportional to GFR. Urea clearance is not a reliable estimate of GFR and, in the face of volume depletion, decreased urea clearance may occur without a decrease in GFR due to increased tubular reabsorption of urea.
(2) Production and excretion of urea are not constant.
(a) Production and excretion increase after a high protein meal. A BUN concentration of 30 to 40 mg/dL may occur 4 to 8 hours after feeding a high-protein meal in dogs. Therefore, an 8- to 12-hour fast is recommended before measurement.
(b) Gastrointestinal bleeding can increase BUN concentration because blood represents an endogenous protein load.
(c) Clinical conditions characterized by increased catabolism (e.g., starvation, infection, fever) also can increase BUN concentration.
(d) Some drugs may increase BUN concentration by increasing tissue catabolism (e.g., glucocorticoids, azathioprine) or decreasing protein synthesis (e.g., tetracyclines) but these effects are minimal.
b. Serum creatinine concentration. Normal serum creatinine concentrations are 0.3 to 1.3 mg/dL in the dog and 0.8 to 1.8 mg/dL in the cat. An individual patient’s serum creatinine concentration will increase over time with progression of renal disease, and increasing serum creatinine concentrations should not be ignored even if the results still are within the reference range.
(1) Methods of measurement.
(a) Automated colorimetric method (Jaffe reaction): Up to half of the measured creatinine actually may represent noncreatinine chromogens.
(b) Lloyd’s reagent may be used to remove non-creatinine chromogens and provide a more accurate determination of the true serum creatinine concentration.
(2) Young animals have lower serum creatinine concentrations, whereas males and well-muscled individuals have higher concentrations.
(a) Serum creatinine concentration in puppies younger than or equal to 16 weeks of age often is 0.4 to 0.5 mg/dL.
(3) Cachectic animals that have experienced severe loss of lean muscle mass often have lower serum creatinine concentrations than they otherwise would have if their muscle mass were normal.
(4) Normal reference ranges may differ somewhat among breeds. Greyhound dogs have slightly higher serum creatinine concentrations than do other breeds. In one study, serum creatinine concentrations were 1.8 ± 0.1 mg/dL in greyhounds and 1.5 ± 0.1 mg/dL in other breeds and in another study serum creatinine concentrations ranged from 1.2 to 1.9 mg/dL (mean, 1.6 mg/dL) in greyhounds as compared with 0.6 to 1.7 mg/dL (mean, 1.0 mg/dL) in non-greyhound dogs.
TABLE 2-2 Normal Values for Clinical Glomerular Function Tests
| Test (units) | Dog | Cat |
|---|---|---|
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 8-25 | 15-35 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.3-1.3 | 0.8-1.8 |
| Serum cystatin C (mg/dL) | 0.5-1.5 | NA |
| Endogenous creatinine clearance (mL/min/kg) | 2-5 | 2-5 |
| Exogenous creatinine clearance (mL/min/kg) | 3-5 | 2-4 |
| Iohexol clearance (mL/min/kg) | 1.7-4.1 | 1.3-4.2 |
| 24-hour urine protein excretion (mg/kg/d) | <30 | <20 |
| UPr/UCr | <0.4 | <0.4 |
| Microalbuminuria (mg/dL) | <1 | <1 |
NA, not available.
(5) Serum creatinine concentration (in contrast to BUN concentration) is not affected appreciably by diet.
c. BUN and serum creatinine concentrations often both increase during disease processes. Neither one is more sensitive than the other.
(1) A normal BUN or serum creatinine concentration does not exclude the possibility of renal disease.
(2) A normal BUN or serum creatinine concentration implies that at least 25% of renal mass is functional, but how much more renal mass is functional cannot be determined by these tests.
(3) In some situations, either the BUN or serum creatinine concentration is increased, but not both at the same time. It is not always possible to explain discordant results between BUN and serum creatinine concentrations (Table 2-3).
(4) Individual patient BUN or serum creatinine concentrations may increase progressively during development of chronic renal disease, but the results still may remain within the normal reference range.
TABLE 2-3 Discordant Results Between Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) and Serum Creatinine (SCr) Concentration
| Disproportionate ↑ BUN Relative to SCr | Disproportionate ↑ SCr Relative to BUN |
|---|---|
| Severe dehydration and volume depletion (common) | Liver disease |
| Gastrointestinal hemorrhage | Anorexia or low protein diet |
| Emaciated animal | Massive muscle injury (acute) |
| Young animal | Well-muscled individual |
(a) If available, serial test results should be evaluated to identify a trend toward progressively increasing concentrations.
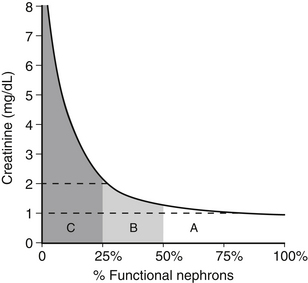
d. The relationship of BUN and serum creatinine concentrations to GFR is a rectangular hyperbola.
(1) The slope of the curve is small when GFR is mildly or moderately decreased but large when GFR is severely reduced (Figure 2-1). Thus, large changes in GFR early in the course of renal disease cause small increases in BUN or serum creatinine concentration. Small changes in GFR in advanced renal disease cause large changes in BUN or serum creatinine concentration.
(2) An increase in BUN or serum creatinine concentration above normal implies that at least 75% of the nephrons are not functioning.
(a) The magnitude of a single BUN or serum creatinine concentration cannot be used to predict whether azotemia is prerenal, primary renal, or postrenal in origin, and cannot be used to distinguish between acute and chronic, reversible and irreversible, or progressive and non-progressive processes.
(b) The BUN/creatinine ratio usually is 20:1 to 30:1.
(i) It may be increased in prerenal and postrenal azotemia as a result of increased tubular reabsorption of urea at lower tubular flow rates or easier absorption of urea than creatinine across peritoneal membranes in animals with uroabdomen.
(ii) Hyperthyroid cats also may have an increased ratio due to increased GFR and loss of lean muscle mass.
(iii) It may be increased during cachexia as a result of lower serum creatinine concentration due to loss of lean muscle mass.
e. Normal cystatin C concentration in dogs is approximately 1 mg/dL.
(1) Cystatin C is a protease inhibitor that is freely filtered by the glomeruli. It does not undergo tubular secretion, and filtered cystatin C is almost completely reabsorbed by the proximal tubular cells.
(2) Cystatin C is produced at a constant rate in all tissues and its excretion is not dependent on age, sex, or diet.
Renal Clearance
1. The renal clearance of a substance is that volume of plasma that would have to be filtered by the glomeruli each minute to account for the amount of that substance appearing in the urine each minute. The renal clearance of a substance (x) that is neither reabsorbed nor secreted by the tubules is equal to the GFR. Thus, GFR = UxV/Px.
2. Creatinine is produced endogenously and excreted by glomerular filtration. Thus, its clearance can be used to estimate GFR.
3. Endogenous creatinine clearance determination:
a. Collect all urine for 12 or 24 hours and record volume (failure to collect all urine produced will decrease the calculated clearance value).
4. Exogenous creatinine clearance.
a. Administer creatinine (100 mg/kg) SQ or IV to increase serum creatinine concentration approximately 10-fold.
b. Approximately 40 minutes later, collect at least 1 timed urine sample using an indwelling urinary catheter (e.g., all urine produced in 20 minutes). The average of three 20-minute collection periods is recommended to minimize collection errors.
Single Injection Methods for Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate
1. Single injection plasma clearance methods using inulin, iohexol, or creatinine have been used to estimate GFR. Inulin clearance is the gold standard, but it is not easily measured and not available at commercial laboratories.
2. Plasma clearance of the substance is calculated using the area under the plasma-concentration-versus-time curve.
3. These methods do not require urine collection, but accuracy depends on the number of plasma samples and the timing of their collection.
4. Iohexol is readily available for clinical use, but a laboratory equipped to measure it must be available.
a. Iohexol is given at dosage of 300 mg/kg IV (using a 300 mg/mL solution), and plasma samples are collected 2, 3, and 4 hours after administration.
c. Because 1 mL/kg of iohexol is given IV relatively rapidly, caution should be used in overhydrated patients or those with marginal cardiac function.
Effects of Sedatives and Anesthetics on Glomerular Filtration Rate
Radioisotopes
1. Radioisotopes (e.g., 125I- or 131I-iothalamate, 51Cr-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid [EDTA], DTPA) have been used to estimate GFR in dogs and cats using both plasma clearance and dynamic renal scintigraphic methods.
2. Plasma clearance of isotopes.
a. The plasma clearance approach has the same advantages and limitations as described earlier for iohexol or exogenously administered creatinine.
b. Procedures using radioisotopes require technical expertise and equipment available primarily at referral institutions.
c. Methods using 99mTc-DTPA to estimate GFR are clinically useful because the short half-life (6 hours) of 99mTc allows the animal to be released within 24 to 48 hours after the procedure. Very low dose protocols allow the animal to be released safely on the same day. The percentage of an injected dose of 99mTc-DTPA extracted by the kidneys over a finite time period correlates well with inulin clearance.
3. Dynamic renal scintigraphy.
a. This method correlates less well with inulin clearance than does the plasma clearance method in dogs with renal disease. Renal scintigraphy is less accurate than plasma clearance because a very short sampling period (usually 1 to 3 minutes postinjection) is used, and data obtained over such a short time may not accurately reflect steady state GFR. Characteristics of the gamma camera itself can lead to inaccuracies, and partial obstruction can delay excretion of the tracer from the kidneys and lead to overestimation of GFR.
b. Nuclear imaging using 99mTc-DTPA has been employed to determine GFR in normal dogs, dogs with renal disease, and in normal cats and those with renal dysfunction.
c. Quantitative renal scintigraphy and determination of plasma disappearance after single-injection using 99mTc-mercaptoacetyltriglycine have been used to estimate renal plasma flow in dogs. Hepatic uptake of 99mTc-mercaptoacetyltriglycine in cats may limit the value of this tracer for evaluation of renal plasma flow in this species.
Serum Phosphorus Concentration
1. Measurement of serum phosphorus concentration can provide information about renal function in addition to that obtained from determination of BUN and serum creatinine concentrations.
2. Increased serum phosphorus concentration is not seen until > 85% of the nephrons are nonfunctional.
3. Phosphorus is filtered by the glomeruli and reabsorbed by the tubules. Tubular reabsorption of phosphorus is regulated by parathyroid hormone, and renal secondary hyperparathyroidism maintains serum phosphorus concentration within the normal range by promoting excretion of phosphorus into urine until renal disease is advanced.
4. A serum phosphorus concentration that is disproportionately increased relative to serum creatinine concentration may be observed in acute renal failure. Rust inhibitors in anti-freeze products may account for an increase in serum phosphorus concentration in animals shortly after EG ingestion.
5. Thyroxine increases proximal renal tubular reabsorption of phosphate and may contribute to hyperphosphatemia in cats with hyperthyroidism.
6. Serum phosphorus concentrations are 2.5 to 5.0 mg/dL in normal adult dogs and cats. Serum phosphorus concentrations may be as high as 8.5 mg/dL in immature animals as a consequence of bone growth. Most laboratories do not determine separate normal reference ranges for adults and immature animals resulting in a somewhat higher than expected upper limit of normal for serum phosphorus concentration.
Urine Protein
1. The presence of protein in the urine may indicate a disease process anywhere in the urinary tract, or may be a consequence of genital contamination. When the urinary sediment is inactive, the presence of protein in the urine is suggestive of renal disease.
2. Dipstick screening measures mostly albumin and often produces positive results in highly concentrated urine. Trace to +1 proteinuria (i.e., 10 to 30 mg/dl) may be normal in highly concentrated urine. With dipstick screening, a protein concentration of 20 to 30 mg/dL is required for a positive reaction. Dipstick screening for proteinuria may be negative despite the presence of pathologic amounts of protein if the urine is dilute.
3. If persistent proteinuria is present on dipstick analysis in the absence of hematuria and pyuria, the severity of proteinuria may be assessed by measuring 24-hour urine protein excretion or performing a urine protein-to-urine creatinine ratio (UPr/UCr).
4. Urine protein excretion (normal values for 24-hour urine protein excretion and UPr/UCr ratio are presented in Table 2-2).
b. Dogs with primary glomerular disease (e.g., glomerulonephritis, glomerular amyloidosis) often have markedly increased 24-hour urine protein excretion and those with amyloidosis generally have the highest 24-hour urine protein excretion.
5. Urine protein/urine creatinine ratio (UPr/UCr).
a. Determination of UPr/UCr eliminates the necessity of a 24-hour urine collection and is highly correlated with 24-hour urine protein excretion.
c. UPr/UCr ratios often are normal in animals with high USG and positive dipstick protein reaction. Urine protein and creatinine concentrations are increased to the same extent in highly concentrated urine, and the UPr/UCr is unaffected because it is a ratio of the 2 concentrations.
d. In dogs, UPr/UCr results are not affected by differences in sex, method of urine collection, fasted versus fed state, or by time of day of collection.
e. Pyuria and marked blood contamination of urine samples can result in abnormal UPr/UCr ratios in the absence of glomerular disease. Thus, both the urine protein concentration and UPr/UCr ratio must be evaluated in conjunction with urinary sediment findings.
f. Induction of renal failure in experimental studies in cats increased mean UPr/UCr ratio from 0.13 to 0.36, and in both groups of cats UPr/UCr ratios were higher on 52% as compared with 28% protein diets. Administration of prednisone to normal dogs increased UPr/UCr ratios from normal to a mean of 1.2 at 30 days and 0.9 at 42 days.