22 Anatomy and Normal Reproductive Physiology
I. EMBRYOLOGY AND ANATOMY OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT
The reproductive anatomy of the male dog consists of the paired testes-epididymes within the scrotum, the vasa deferentia, the prostate, the penis, and the prepuce (Figure 22-1). The testes consist of multiple seminiferous tubules in which spermatogenesis takes place. The seminiferous tubules empty into a fibrous center space, the rete testis. The rete testis connects to the head of the epididymis. The testicular tissue is surrounded by a tight capsule, such that the testes have the consistency of a peeled hard-boiled egg when palpated. An epididymis is tightly adhered to each testis. Fluid and spermatozoa from the testis enter the head of the epididymis; move through the body of the epididymis, which lies laterally on each testis; and are stored in the tail of the epididymis.
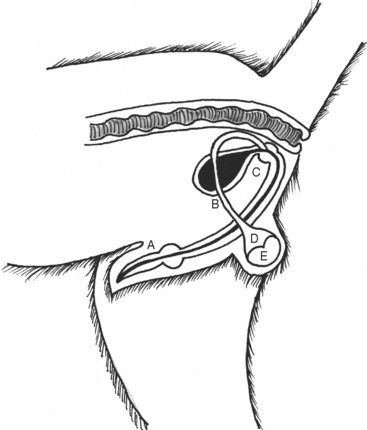
Figure 22-1 Anatomy of the male reproductive tract. A, Penis; B, urinary bladder; C, prostate; D, testis; E, epididymis.
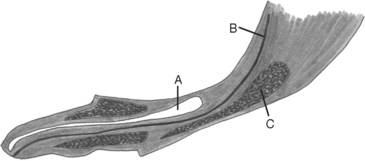
The urethra runs through the center of the penis. It is surrounded throughout its length by cavernous tissue. Cavernous tissue is an empty honeycomb space within the penis that fills with blood during erection. The urethra also is surrounded by part of its length within the penis by a bone, the os penis (Figure 22-2). The os penis allows the male to introduce the penis before erection is complete; this allows the extreme increase in size of the penis to occur within the vagina, permitting formation of the copulatory lock, or tie.
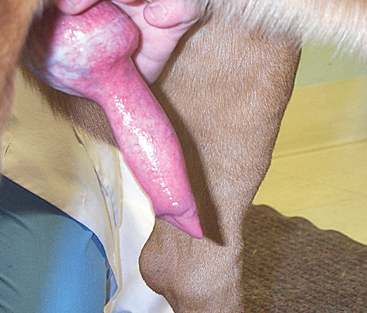
The proximal portion of the penis, which always is larger than the rest of the shaft of the penis, is the bulbus glandis. This tissue will treble in size when the penis is erect and is the portion of the penis that is caught within the vulvar lips during the tie that usually occurs during breeding (Figure 22-3). The tip of the penis contains the external urethral orifice, visible as a small opening or slit. When the penis is erect, the tip takes on the appearance of a thick leaf; it is thought that this shape helps promote ejaculation of spermatozoa toward the cervix of the female during natural service. The prepuce is a piece of haired skin that encloses the flaccid penis at rest.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree