CHAPTER 42. Orthopedic Disorders
Rebecca S. McConnico
Please refer toChapter 47for further review of equine orthopedic diseases.
THRUSH
I. Affects the central and lateral sulci of the frog (Figure 42-1)
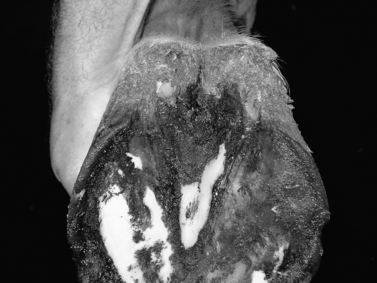 |
| Figure 42-1 Typical case of thrush affecting most of the frog. (From Floyd A, Mansmann R. Equine Podiatry. St Louis, 2007, Saunders.) |
II. Dermatitis of the frog
III. Occurs in horses kept in confinement in unsanitary conditions
IV. Clinical findings
A. Soft, spongy, flaky frog (advanced cases)
B. Fetid odor
C. In some cases, lameness results
D. Advanced cases may involve inflammation of the coronary band
E. Discharge of pus from fissures in the coronary band may exist
V. Causes
A. Fusobacterium necrophorum possibly plays a role in the pathogenesis
B. Unhygienic conditions, loafing in wet or unhygienic conditions
C. Poor foot care
D. Lameness leads to decreased exercise, causing further predisposition to thrush
VI. Diagnosis is based on clinical findings
VII. Treatment
A. Pare out foot and remove dead or necrotic frog and sole
B. Drying and antiseptic products to include copper sulfate, iodines
C. If sensitive laminae become exposed, bandaging may be necessary
VIII. Prevention: Hygiene, keep feet picked out, dry bedding and pasture
LAMINITIS
I. Occurs in ponies and horses (may be more common in ponies)
II. Inflammation of the sensitive lamina in foot
III. Clinical signs
A. Shifting leg lameness
B. Short strided walk
C. Progressive cases spend a lot of time in recumbency
D. Bounding digital pulses
E. Increased heat to the hoof walls
F. Pain on hoof tester pressure
G. Heel-to-toe placement
IV. Chronic laminitis
A. May be more common in overweight horses
B. Recurrent episodes of lameness
C. Hoof wall rings
D. Dropped or flattened sole
E. Long toe
V. Lameness grading system
A. Obel grade 1: No lameness except for a short stilted gait
B. Obel grade 2: Discomfort and lameness at the walk; can lift each forefoot without difficulty
C. Obel grade 3: Reluctance to move and resistance to lifting forefeet
D. Obel grade 4: Planted feet; difficult to get the horse to move
E. Obel grade 5: Horse is recumbent
VI. Causes
A. Systemic disease such as septicemia, endometritis, colitis (salmonellosis, clostridiosis)
B. Carbohydrate overload
C. Predisposing factors
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


