Z
Z zeta, capital letter; sixth letter in the Greek alphabet; symbol for atomic number.
ζ zeta, small letter; sixth letter in the Greek alphabet.
Z-linkage genes with loci on the Z chromosome.
Z-myoplasty a technique for surgical correction of quadriceps muscle contracture.
Z-tenectomy a technique for tendon shortening.
Z-tenotomy a technique for tendon lengthening.
tree z. Cycas armstrongii, C. media.
zang-fu organs see yin organs and yang organs.
zearalanol [z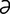 -ral′
-ral′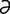 -nol] see zeranol.
-nol] see zeranol.
z. marks faint striping in coats of horses, usually on the legs, also the neck and withers.
zebronkey a cross between zebra and donkey.
Zeis glands [tsīs] see glands of Zeis.
Zenker’s necrosis, degeneration [tseng′ker] see Zenker’s necrosis.
zeony progeny of a zebra and a pony.
Zephyranthes see Cooperia pedunculata.
zernike condenser special condenser used in phase contrast microscope.
zeta [za′t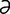 ] seventh letter in the Greek alphabet, Z or ζ.
] seventh letter in the Greek alphabet, Z or ζ.
zeta potential see zeta potential.
zetamethrin a beta-cypermethrin. Used in ear tags for control of ectoparasites on cattle.
zeugopodium [zoo″go-po′de-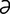 m] the segment of the limb corresponding to either the forearm or the leg.
m] the segment of the limb corresponding to either the forearm or the leg.
Zieria an Australian genus of shrubs and trees of the Rutaceae family.
Z. laevigata, Z. smithii suspected of causing cyanide poisoning.
zigadenine, zigadine, zygadenine plant toxin found in Zigadenus spp.
Zimmerman’s aluminum wire suture [ts ′mer-mahn] see Zimmerman’s aluminum wire suture.
′mer-mahn] see Zimmerman’s aluminum wire suture.
zinc (Zn) [zingk] a chemical element, atomic number 30, atomic weight 65.37. See Table 4. Zinc is a trace element that is a component of several enzymes, including DNA and RNA polymerases, and carbonic anhydrase. Zinc salts are used in skin lotions, eye washes, the treatment and prevention of footrot of sheep and facial eczema of sheep and cattle.
z. acetate a salt used as an astringent and styptic.
z. carbonate a mild astringent; used mainly as calamine.
z. finger protein DNA-binding proteins that contain zinc-finger motifs.
z. gluconate a source of supplementary zinc.
hereditary z. deficiency lethal trait A46; Adema disease; see inherited parakeratosis.
z. oversupplementation causes hemolytic anemia, anorexia and vomiting.
z. phosphate used as a phosphate-bonded cement in restorative dentistry.
z.-responsive dermatoses see parakeratosis, zinc-responsive dermatosis.
zipper structure leucine [zip′ r] see leucine zipper.
r] see leucine zipper.
zipper worm [zip′ r] Spirometra erinacei.
r] Spirometra erinacei.
zirconium (Zr) [zir-ko′ne- m] a chemical element, atomic number 40, atomic weight 91.22. See Table 4.
m] a chemical element, atomic number 40, atomic weight 91.22. See Table 4.
z. chlorhydrate an astringent.
zona [zo′n ] pl. zonae [L.] zone.
] pl. zonae [L.] zone.
z. alba the white line in the horse’s hoof.
z. fasciculata the thick middle layer of the adrenal gland.
z. glomerulosa the outermost layer of the adrenal cortex. Called also zona multiformis.
z. multiformis see zona glomerulosa (above).
z. pellucida 1. the transparent, noncellular, secreted layer surrounding an ovum. 2. area pellucida.
z. reaction caused by the penetration of the zona pellucida by the spermatozoa.
z. reticularis the innermost layer of the adrenal cortex.
z. striata see zona radiata (above).
epileptogenic z. an area, stimulation of which may provoke an epileptic seizure.
zonifugal [zo-nif′ -g
-g l] passing outward from a zone or region.
l] passing outward from a zone or region.
zonipetal [zo-nip′ -t
-t l] passing toward a zone or region.
l] passing toward a zone or region.
zonisamide [zo-nis′ -mīd“] a sulfonamide anticonvulsant.
-mīd“] a sulfonamide anticonvulsant.
zonula [zo′nu-l ] pl. zonulae [L.] zonule.
] pl. zonulae [L.] zonule.
z. occludens see tight junction.
zonulitis [zo″nu-li′tis] inflammation reflected on the ciliary zonule.
zonulotomy [zon″u-lot′o-me] incision of the ciliary zonule.
zo(o)- word element. [Gr.] animal.
zoogenous [zo-oj′ -n
-n s] 1. acquired from animals. 2. viviparous.
s] 1. acquired from animals. 2. viviparous.
zoogeny [zo-oj′ -ne] the development and evolution of animals.
-ne] the development and evolution of animals.
zoogony [zo-og′ -ne] the production of living young from within the body.
-ne] the production of living young from within the body.
zoografting [zo′o-graft″ing] the grafting of animal tissue.
zoology [zo-ol′ -je] the biology of animals.
-je] the biology of animals.
zoom control in ultrasonography, a means of magnifying part of the image.
reverse z. disease transmitted from humans to animals, such as tuberculosis.
zooparasite [zo″o-par′ -sīt] any parasitic animal organism or species.
-sīt] any parasitic animal organism or species.
zoopathology [zo″o-p -thol′
-thol′ -je] the science of the diseases of animals.
-je] the science of the diseases of animals.
zoophagous [zo-of′ -g
-g s] carnivorous.
s] carnivorous.
zoophilic [zo″o-fil′ik] preferring animals to humans; said of certain fungi.
zoophobia [zo″o-fo′be- ] abnormal fear of animals.
] abnormal fear of animals.
zoospores see ruminal zoospores.
zootoxicosis disease caused by a zootoxin.
Zr chemical symbol, zirconium.
zwoegersiekte [Dutch] see maedi.
zygacine one of the toxic alkaloids in Zigadenus.
zygadine one of the toxic alkaloids in Zigadenus.
zygal [zi′g l] shaped like a yoke.
l] shaped like a yoke.
zygapophysis [zi″g -pof′
-pof′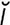 -sis] the articular process of a vertebra. See also facet joints.
-sis] the articular process of a vertebra. See also facet joints.
zygion [zij’e-on] the most lateral point on the zygomatic arch.
zyg(o)– word element. [Gr.] yoked, joined, a junction.
zygodactylous having two toes directed forwards and two backwards as in some birds, e.g. parrots.
zygomatic [zi″go-mat′ik] pertaining to zygomatic bone.
z. arch the arch formed by the processes of the zygomatic and temporal bones.
z. bone the bone forming the hard part of the cheek and the lower, lateral portion of the rim of the orbit. See also Table 10.
zygomaticofacial [zi″go-mat“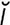 -ko-fa′sh
-ko-fa′sh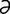 l] pertaining to the zygoma and face.
l] pertaining to the zygoma and face.
zygomaticotemporal [zi″go-mat“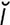 -ko-tem′p
-ko-tem′p r-
r- l] pertaining to the zygoma and temporal bone.
l] pertaining to the zygoma and temporal bone.
Zygomycetes [zi″go-mi-se’tēz] see Phycomycetes.
zygomycotes members of the Zygomycota phylum of fungi. Includes Mucor, Rhizopus spp.
zygon [zi′gon] the stem connecting the two branches of a zygal fissure.
zygospore [zi′go-spor] a thick-walled sexual spore produced by fungi in the class Zygomycetes.
zymase enzyme found in yeasts that catalyzes the fermentation of sugar to alcohol and CO2.
zymic pertaining to enzymes or fermentation.
zym(o)- word element. [Gr.] enzyme, fermentation.
zymodemes populations of parasites with identical isoenzymes.
z. cells the secretory cells that secrete the zymogens.
Zymonema farciminosum see Histoplasma farciminosum.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
 -ral′
-ral′ -nōn] an estrogenic substance produced during the fermentation of stored grain by the fungus Fusarium graminearum. The effects of the toxin are enlargement of the pudenda, infertility and death of the newborn. See also zeranol.
-nōn] an estrogenic substance produced during the fermentation of stored grain by the fungus Fusarium graminearum. The effects of the toxin are enlargement of the pudenda, infertility and death of the newborn. See also zeranol. -nol] a synthetic zearalenone (6′-reduced zearalenone) marketed as Ralgro used as a growth promotant in cattle. Called also zearalanol.
-nol] a synthetic zearalenone (6′-reduced zearalenone) marketed as Ralgro used as a growth promotant in cattle. Called also zearalanol.
 -pam] a benzodiazepine tranquilizer most commonly used in a fixed-ratio combination with tiletamine.
-pam] a benzodiazepine tranquilizer most commonly used in a fixed-ratio combination with tiletamine. r el′
r el′ -s
-s n] a triad comprising intractable, sometimes fulminating, upper gastrointestinal ulceration, extreme gastric hyperacidity, and nonbeta cell, gastrinsecreting, islet cell tumors (gastrinomas) of the pancreas. Clinical signs in affected dogs include vomiting, often with blood, anemia, diarrhea, weight loss, and sometimes signs of peritonitis.
n] a triad comprising intractable, sometimes fulminating, upper gastrointestinal ulceration, extreme gastric hyperacidity, and nonbeta cell, gastrinsecreting, islet cell tumors (gastrinomas) of the pancreas. Clinical signs in affected dogs include vomiting, often with blood, anemia, diarrhea, weight loss, and sometimes signs of peritonitis. -sis, zo″nu-li′sis] dissolution of the ciliary zonule by use of enzymes, to permit surgical removal of the lens.
-sis, zo″nu-li′sis] dissolution of the ciliary zonule by use of enzymes, to permit surgical removal of the lens. -fe] defining the location and numbers of animal populations, and their variability with time.
-fe] defining the location and numbers of animal populations, and their variability with time. -gof′
-gof′ -r
-r ] a group of protozoa (zooflagellates), including all of the flagellates that parasitize higher animals.
] a group of protozoa (zooflagellates), including all of the flagellates that parasitize higher animals. -sis] disease or infection that is naturally transmissible from vertebrate animals to humans. It can be bacterial, viral, or parasitic, or may involve unconventional agents. Zoonoses are a public health concern, but also create obstacles to international trade in animal products.
-sis] disease or infection that is naturally transmissible from vertebrate animals to humans. It can be bacterial, viral, or parasitic, or may involve unconventional agents. Zoonoses are a public health concern, but also create obstacles to international trade in animal products. -le] union of digits by soft tissues (skin), without bony fusion of the phalanges involved.
-le] union of digits by soft tissues (skin), without bony fusion of the phalanges involved. ] 1. the zygomatic process of the temporal bone. 2. zygomatic arch. 3. a term sometimes applied to the zygomatic bone.
] 1. the zygomatic process of the temporal bone. 2. zygomatic arch. 3. a term sometimes applied to the zygomatic bone. -te] the condition relating to conjugation, or to the zygote, as (1) the state of a cell or individual in regard to the alleles determining a specific character, whether identical (homozygosity) or different (heterozygosity); or (2) in the case of twins, whether developing from one zygote (monozygosity) or two (dizygosity).
-te] the condition relating to conjugation, or to the zygote, as (1) the state of a cell or individual in regard to the alleles determining a specific character, whether identical (homozygosity) or different (heterozygosity); or (2) in the case of twins, whether developing from one zygote (monozygosity) or two (dizygosity). n] an inactive precursor that is converted into an active enzyme, usually by cleavage of a small polypeptde by action of an acid or another enzyme or by other means; a proenzyme.
n] an inactive precursor that is converted into an active enzyme, usually by cleavage of a small polypeptde by action of an acid or another enzyme or by other means; a proenzyme.


