48 VAGINAL CYTOLOGY
7 What are the cytologic features of proestrus in dogs?
a. Admixture of parabasal cells, small and large intermediate cells, and superficial epithelial cells
(2) As proestrus advances closer to estrus, the absolute number and percentage of large intermediate cells and superficial cells increase, and these cells become the predominant cell types present on the cytology smears.
b. Usually a few up to many red blood cells (RBCs) and neutrophils are present, although they may be absent. Their numbers decrease in late proestrus.
c. Bacteria, generally small bacterial rods, often are present in high numbers both adhered to the epithelial cells and free throughout the smear. Although generally present in high numbers, bacterial numbers may range from none to many on cytology smears.
11 What are the cytologic features of estrus in dogs?
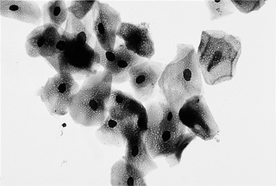
a. Greater than 90% of the epithelial cells are superficial cells (Figure 48-1). These may all be superficial epithelial cells with small pyknotic nuclei, all anucleate cells, or any mixture of the types. Occasionally the cells more closely resemble large intermediate cells (larger nucleus).
b. Neutrophils should be absent. The presence of neutrophils is an abnormal finding and suggests inflammation.
d. Bacteria are often present in high numbers, although the numbers are variable and bacteria may be absent.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree