V
V chemical symbol, vanadium; symbol, volt; vision; visual acuity.
v. [L.] vena (vein); pl. venae (vv.) [L.].
V domain the variable region or domain of immunoglobulins.
V factor see diphosphopyridine nucleotide.
V region variable region of immunoglobulins.
v tach ventricular tachycardia.
VAC vincristine, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide; a cancer chemotherapy regime.
vaccigenous producing a vaccine.
vaccina [vak-si’n ] vaccinia virus.
] vaccinia virus.
vaccinable susceptible of being successfully vaccinated.
vaccinate [vak’s -nāt] to inoculatewith vaccine to produce immunity.
-nāt] to inoculatewith vaccine to produce immunity.
v.-associated sarcoma see sarcoma.
core v. one that should always be included in the basic immunization program for the species.
dead v. inactivated vaccine; one with organisms that have been killed.
inactivated v. see dead vaccine (above).
killed virus (KV) v. see dead vaccine (above).
live v. a vaccine prepared from live, usually attenuated, microorganisms.
mixed v. see mixed bacterial vaccine.
modified live virus (MLV) v. see attenuated vaccine (above).
polyvalent v. one prepared from more than one strain or species of microorganisms.
recombinant v. one created by recombinant DNA technology.
subunit v. one containing only specific antigenic proteins of the infectious agent.
vaccinial [vak-sin’e- l] pertaining to or characteristic of vaccinia.
l] pertaining to or characteristic of vaccinia.
vacciniform [vak-sin’ -form] resembling vaccinia.
-form] resembling vaccinia.
vacciniola generalized vaccinia.
vaccinotherapy [vak“s -no-ther’
-no-ther’ -pe] therapeutic use of vaccines.
-pe] therapeutic use of vaccines.
vacuolar [ak“u-o’l r] containing, or of the nature of, vacuoles.
r] containing, or of the nature of, vacuoles.
vacuolated [vak’u-o-lāt“ d] containing vacuoles.
d] containing vacuoles.
vacuolation [vak“u-o-la’sh n] the process of forming vacuoles; the condition of being vacuolated.
n] the process of forming vacuoles; the condition of being vacuolated.
vacuole [vak’u-ōl] a space or cavity in the cytoplasm of a cell.
vacuolization [vak“u-o-l -za’sh
-za’sh n] vacuolation.
n] vacuolation.
vacuum [vak’ūm] a space devoid of air or other gas.
v. collection use of a handheld vacuum to recover ectoparasites from the coat of animals.
v.-dehydrated freed of moisture while in a vacuum. Used in the packaging of food.
v. gauge pressure gauge in a milking machine which indicates the level of vacuum in the system.
vagal [va’g l] pertaining to the vagus nerve.
l] pertaining to the vagus nerve.
v. attack see vasovagal attack.
v. bulbi (1) see Tenon’s capsule.
vaginal pertaining to the vagina, the tunica vaginalis testis, or to any sheath.
v. anulus see anulus vaginalis.
v. aplasia manifested by imperforate hymen or residual strands of hymen. See imperforate hymen.
v. cyclic changes see vaginal cytology (below).
v. cysts see Gartner’s ducts, Bartholin’s glands.
v. hypertrophy see vaginal prolapse.
v. hypoplasia segmental see müllerian duct aplasia.
v. inflammation see vaginitis (1).
v. neoplasm include papilloma, sarcoma, leiomyoma.
v. prolapse see vaginal prolapse.
v. retainer see bearing retainer.
v. stricture cicatricial contraction after traumatic injury.
vaginalitis [vaj“ -n
-n -li’tis] inflammation of the tunica vaginalis testis; periorchitis.
-li’tis] inflammation of the tunica vaginalis testis; periorchitis.
vaginate [vaj’ -nāt] enclosed in a sheath.
-nāt] enclosed in a sheath.
vaginectomy [vaj“ -nek’t
-nek’t -me] 1. resection of the tunica vaginalis testis. 2. excision of the vagina.
-me] 1. resection of the tunica vaginalis testis. 2. excision of the vagina.
vaginismus [vaj“ -niz’m
-niz’m s] painful spasms of the muscles of the vagina.
s] painful spasms of the muscles of the vagina.
vaginitis [vaj“ -ni’tis] 1. inflammation of the vagina; colpitis. 2. inflammation of a sheath.
-ni’tis] 1. inflammation of the vagina; colpitis. 2. inflammation of a sheath.
contagious v. see infectious pustular vulvovaginitis, epivag.
pustular v. see infectious pustular vulvovaginitis.
vaginoabdominal [vaj“ -no-ab-dom’
-no-ab-dom’ -n
-n l] pertaining to the vagina and abdomen.
l] pertaining to the vagina and abdomen.
vaginocele [vaj’ -no-sēl“] colpocele; vaginal hernia.
-no-sēl“] colpocele; vaginal hernia.
vaginofixation [vaj“ -no-fik-sa’sh
-no-fik-sa’sh n] vaginopexy; colpopexy.
n] vaginopexy; colpopexy.
vaginolabial [vaj“ -no-la’be-
-no-la’be- l] pertaining to the vagina and labia.
l] pertaining to the vagina and labia.
vaginomycosis [vaj“ -no-mi-ko’sis] any fungal disease of the vagina.
-no-mi-ko’sis] any fungal disease of the vagina.
vaginopathy [vaj“ -nop’
-nop’ -the] any disease of the vagina.
-the] any disease of the vagina.
vaginoperineal [vaj“ -no-per“
-no-per“ -ne’
-ne’ l] pertaining to the vagina and perineum.
l] pertaining to the vagina and perineum.
vaginoperineotomy [vaj’ -no-per“
-no-per“ -ne-ot’
-ne-ot’ -me] incision of the vagina and perineum.
-me] incision of the vagina and perineum.
vaginoperitoneal [vaj“ -no-per“
-no-per“ -to-ne’
-to-ne’ l] pertaining to the vagina and peritoneum.
l] pertaining to the vagina and peritoneum.
vaginoplasty [vaj’ -no-plas“te] colpoplasty; plastic repair of the vagina.
-no-plas“te] colpoplasty; plastic repair of the vagina.
vaginoscopy [vaj“ -nos’k
-nos’k -pe] viewing of the vaginal lining with a vaginoscope.
-pe] viewing of the vaginal lining with a vaginoscope.
vaginotomy [vaj“ -not’
-not’ -me] colpotomy; incision of the vagina.
-me] colpotomy; incision of the vagina.
vaginovesical [vaj“ -no-ves’
-no-ves’ -k
-k l] pertaining to the vagina and bladder.
l] pertaining to the vagina and bladder.
vagolysis [va-gol’ -sis] surgical destruction of the vagus nerve.
-sis] surgical destruction of the vagus nerve.
v. agents includes atropine sulfate, glycopyrrolate, propantheline, isopropamide.
vagotomy [va-got’ -me] interruption of the impulses carried by the vagus nerve or nerves.
-me] interruption of the impulses carried by the vagus nerve or nerves.
vagotonia [va“go-to’ne- ] irritability of the vagus nerve.
] irritability of the vagus nerve.
vagotropic [va“go-tro’pik] having an effect on the vagus nerve.
vagus [va’g s] the tenth cranial nerve. For vagus nerve, see Table 14.
s] the tenth cranial nerve. For vagus nerve, see Table 14.
valerian [v -lēr’e-
-lēr’e- n] see Valeriana.
n] see Valeriana.
valine (Val) [va’lēn, val’ēn] a naturally occurring amino acid.
valinemia [val“in-e’me- ] hypervalinemia; elevated concentration of valine in the blood and urine.
] hypervalinemia; elevated concentration of valine in the blood and urine.
vallate [val’āt] having a wall or rim; rim-shaped. See also vallate papilla.
vallecula [v -lek’u-l
-lek’u-l ] pl. valleculae [L.] a depression or furrow.
] pl. valleculae [L.] a depression or furrow.
v. cerebelli a large groove on the ventral cerebellum, in which the medulla oblongata is lodged.
v. epiglottica the depressions on either side of the median glossoepiglottic fold.
v. unguis the sulcus of the matrix of the nail.
valley fever coccidioidomycosis.
valproic acid [val-pro’ik] an anticonvulsant drug.
absolute v. the size of an observation or measurement regardless of its sign.
valva [val’v ] pl. valvae [L.] a valve.
] pl. valvae [L.] a valve.
Adam’s pressure reducing v. see reducing valve (below).
coronary v. a valve at entrance of the coronary sinus into right atrium.
ileocecal v., ileocolic v. see ileocecal valve.
nonreturn v. in anesthetic circuits, it prevents exhaled gas from returning to the patient.
portal v. regulates the amount of venous blood entering the avian kidney.
pressure reducing v. see reducing valve (below).
valvotomy [val-vot’ -me] incision of a valve.
-me] incision of a valve.
valvular [val’vu-l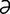 r] pertaining to, affecting or of the nature of a valve.
r] pertaining to, affecting or of the nature of a valve.
valvulitis [val“vu-li’tis] inflammation of a valve, especially of a valve of the heart.
valvuloplasty [val’vu-lo-plas“te] plastic repair of a valve, especially a valve of the heart.
valvulotome [val’vu-lo-tōm“] an instrument for cutting a valve.
valvulotomy [val“vu-lot’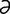 -me] valvotomy.
-me] valvotomy.
balloon v. see balloon valvuloplasty.
vanadium (V) [v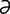 -na’de-
-na’de-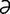 m] a chemical element, atomic number 23, atomic weight 50.942. See Table 4. Its salts have been used in treating various diseases.
m] a chemical element, atomic number 23, atomic weight 50.942. See Table 4. Its salts have been used in treating various diseases.
vanadiumism [v -na’de-
-na’de- m-iz-
m-iz- m] poisoning by vanadium.
m] poisoning by vanadium.
Vangueira pygmaea Pachystigma pygmaeum.
vapor [va’p r] steam, gas or exhalation.
r] steam, gas or exhalation.
vaporize [va’p r-īz] to convert into vapor or to be transformed into vapor.
r-īz] to convert into vapor or to be transformed into vapor.
vapotherapy therapeutic use of steam, vapor or spray.
VA/Q see ventilation:perfusion ratio.
Vaqueta see Thiloa glaucocarpa.
Vaquez–Osler disease [vah-ka’- ōs’l r] primary polycythemia.
r] primary polycythemia.
variability [var“e- -bil’
-bil’ -te] the state of being variable.
-te] the state of being variable.
discontinuous v. see discrete variable (below).
endogenous v. dependent variable.
exogenous v. independent or predetermined variable.
spatial v. a measurement relating to area or location.
temporal v. one relating to chronological time.
v. ratio distribution see f distribution.
Varicellovirus a genus in the subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae.
varices [vār’ -sēz] [L.] plural of varix.
-sēz] [L.] plural of varix.
variciform [var-is’ -form] resembling a varix; varicose.
-form] resembling a varix; varicose.
varicoblepharon [var“ -ko-blef’
-ko-blef’ -ron] a varicose swelling of the eyelid.
-ron] a varicose swelling of the eyelid.
varicocelectomy [var“ -ko-s
-ko-s -lek’t
-lek’t -me] excision of a varicocele.
-me] excision of a varicocele.
varicomphalos [var“ -kom’f
-kom’f -l
-l s] a varicose tumor of the umbilicus.
s] a varicose tumor of the umbilicus.
v. scrotal tumor benign vascular proliferation in dogs; resembles cavernous hemangioma.
varicotomy [var“ -kot’
-kot’ -me] excision of a varix or of a varicose vein.
-me] excision of a varix or of a varicose vein.
varicula [v -rik’u-l
-rik’u-l ] a varix of the conjunctiva.
] a varix of the conjunctiva.
variety [v -ri’
-ri’ -te] a taxonomic subcategory of a species.
-te] a taxonomic subcategory of a species.
variegated tick see Amblyomma variegatum.
varix [var’iks] pl. varices [L.] an enlarged, tortuous vein, artery or lymphatic vessel.
arterial v. a racemose aneurysm or varicose artery.
varization a surgical procedure that decreases the angle of inclination of a part.
varkoor see Zantedeschia aethiopica.
varnish tree Aleurites moluccana.
varolian [v -ro’le-
-ro’le- n] pertaining to the pons varolii.
n] pertaining to the pons varolii.
varroosis a disease of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) caused by the mite Varroa destructor, which parasitizes bee larvae and adults causing developmental deformities, reduced life span and ultimately destruction of the colony or hive. A disease notifiable to the OIE (see Table 22).
vas [vas] pl. vasa [L.] a vessel.
v. afferentia vessels that convey fluid to a structure or part.
v. brevia short vessels such as the gastric arteries.
v. efferentia vessels that convey fluid away from a structure or part.
v. lymphatica lymphatic vessels.
v. vasorum the small nutrient arteries and veins in the walls of the larger blood vessels.
vasa [va’s ] [L.] plural of vas.
] [L.] plural of vas.
vascular [vas’ku-l r] pertaining to blood vessels or indicative of a copious blood supply.
r] pertaining to blood vessels or indicative of a copious blood supply.
v. clamps see hemostatic forceps.
v. disease see arteritis, phlebitis, lymphangitis, thrombosis, aneurysm, capillary fragility.
v. grafts see vascular conduit.
v. hemophilia von Willebrand disease.
v. malformation includes hamartoma, arteriovenous fistula, telangiectasia.
v. pole the point on the renal glomerulus where the blood vessels enter and exit.
v. prosthesis see vascular conduit.
v. ring anomaly see vascular ring.
v. stasis serious slowing, or complete cessation, of blood or lymph flow through vessels.
v. tone the state of contractile tension in the vessel walls.
v. tumor see vascular neoplasm (above).
v. tunic of the eye; the uvea. Consists of the choroid, the ciliary body and iris.
vascularity [vas“ku-lar’ -te] the condition of being vascular.
-te] the condition of being vascular.
vascularization [vas“ku-l r-
r- -za’sh
-za’sh n] the formation of new blood vessels in tissues.
n] the formation of new blood vessels in tissues.
vascularize [vas’ku-l r-īz] to supply with vessels.
r-īz] to supply with vessels.
leukocytoclastic v. see hypersensitivity angiitis.
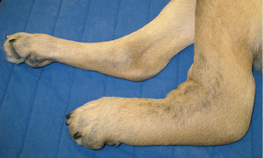
V-3: Cutaneous vasculitis. Peripheral edema caused by vascular leakage associated with vasculitis.
From Medleau L, Hnilica KA, Small Animal Dermatology, 2nd Edition. Saunders, 2006.
vasculopathy [vas“ku-lop’ -the] any disorder of blood vessels.
-the] any disorder of blood vessels.
v. of Greyhounds see idiopathic cutaneous and renal glomerular disease.
vasectomized [v -sek’t
-sek’t -mīzd] subjected to vasectomy.
-mīzd] subjected to vasectomy.
Vaseline trademark for white petrolatum (USP), petroleum jelly.
vasey grass Paspalum urvillei.
Vasgotaspets see Swedish Vallhund.
vasiform [vas’ -form] resembling a vessel.
-form] resembling a vessel.
vasitis [v -si’tis] inflammation of the vas (ductus) deferens.
-si’tis] inflammation of the vas (ductus) deferens.
vas(o)- word element. [L.] vessel, duct.
vasoactive [vas“o-ak’tiv] exerting an effect on the caliber of blood vessels.
v. fibers adrenergic nerve fibers in the walls of all blood vessels except capillaries.
vasodepression [vas“o-de-presh’ n] decrease in vascular resistance with hypotension.
n] decrease in vascular resistance with hypotension.
vasodilatation [vas“o-d -l
-l -ta’sh
-ta’sh n] vasodilation.
n] vasodilation.
vasodilation [vas“o-di-la’sh n] a state of increased caliber of blood vessels.
n] a state of increased caliber of blood vessels.
vasoformative [vas“o-for’m -tiv] pertaining to or promoting the formation of blood vessels.
-tiv] pertaining to or promoting the formation of blood vessels.
vasoganglion [vas“o-gang’gle-on] a vascular ganglion or rete.
vasogenic [va“zo-jen’ik] emanating from or pertaining to blood vessels.
v. circulatory failure see vasogenic shock.
vasography [va-zog’r -fe] radiography of the blood vessels.
-fe] radiography of the blood vessels.
vasohypertonic [vas“o-hi“p r-ton’ik] vasoconstrictor.
r-ton’ik] vasoconstrictor.
vasoinhibitor [vas“o-in-hib’ -t
-t r] an agent that inhibits vasomotor nerves.
r] an agent that inhibits vasomotor nerves.
vasoligation [vas“o-li-ga’sh n] ligation of the vas (ductus) deferens.
n] ligation of the vas (ductus) deferens.
vasomotion [vas“o-mo’sh n] change in caliber of blood vessels.
n] change in caliber of blood vessels.
v. system the part of the nervous system that controls the caliber of the blood vessels.
vasoneurosis [vas“o-n
 -ro’sis] angioneurosis.
-ro’sis] angioneurosis.
vaso-orchidostomy anastomosis of the epididymis to the severed end of the vas (ductus) deferens.
vasoparesis [vas“o-p -re’sis] paralysis of vasomotor nerves.
-re’sis] paralysis of vasomotor nerves.
v. test see antidiuretic hormone response test.
vasopuncture [vas“o-punk’ch r] surgical puncture of the vas (ductus) deferens.
r] surgical puncture of the vas (ductus) deferens.
vasoreflex [vas“o-re’fleks] a reflex of blood vessels.
vasorelaxation [vas“o-re-lak-sa’sh n] decrease of vascular pressure.
n] decrease of vascular pressure.
vasorrhaphy suture of the vas (ductus) deferens.
vasosensory [vas“o-sen’s r-e] supplying sensory filaments to the vessels.
r-e] supplying sensory filaments to the vessels.
vasospasm [vas’o-spaz“ m] spasm of blood vessels, decreasing their caliber.
m] spasm of blood vessels, decreasing their caliber.
vasostimulant [vas“o-stim’u-l nt] stimulating vasomotor action.
nt] stimulating vasomotor action.
vasostomy [vas-os’t -me] surgical formation of an opening into the ductus (vas) deferens.
-me] surgical formation of an opening into the ductus (vas) deferens.
vasotomy [va-zot’ -me] incision of the vas (ductus) deferens.
-me] incision of the vas (ductus) deferens.
vasotonia [vas“o-to’ne- ] tone or tension of the vessels.
] tone or tension of the vessels.
vasotonic [vas“o-ton’ik] pertaining to, characterized by, or increasing vasotonia.
vasovagal [vas“o-va’g l] vascular and vagal.
l] vascular and vagal.
vasovasostomy [vas“o-va-zos’t -me] anastomosis of the ends of the severed vas (ductus) deferens.
-me] anastomosis of the ends of the severed vas (ductus) deferens.
VCI Veterinary Council of Ireland.
vCJD variant Creutzfeld-Jakob disease caused by the agent of bovine spongiform encephalopathy.
VCNZ Veterinary Council of New Zealand.
VCPR veterinarian-client-patient relationship.
VDH valvular disease of the heart.
Western v. calves see heavy veal calves (above).
vealer young calf destined to be marketed as veal.
vection [vek’sh n] the carrying of disease germs from an infected animal to a well animal.
n] the carrying of disease germs from an infected animal to a well animal.
v. data representation see vector data representation.
vedaprofen a propionic acid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent used in horses and dogs.
VEE Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis.
v. drugs derived from plants; includes alkaloids, glycosides, resins, gums and oils.
vegetal [vej’ -t
-t l] 1. pertaining to plants or a plant. 2. vegetative.
l] 1. pertaining to plants or a plant. 2. vegetative.
vegetarian [vej“ -tar’e-
-tar’e- n] a person who eats no meat, eggs or dairy food.
n] a person who eats no meat, eggs or dairy food.
lacto-ovo v. a person who eats no meat, but does consume dairy products and eggs.
inherited v. dermatosis see dermatosis vegetans.
v. nervous system autonomic nervous system.
cloning v. see cloning vector.
v. cell fibroblast-like cells which surround small vessels in the dermis.
vein [vān] a vessel through which blood passes from various organs or parts back towards the heart, in the systemic circulation carrying blood that has given up most of its oxygen. Veins, like arteries, have three coats, an inner, middle and outer, but the coats are not so thick and they collapse when the vessel is cut. Many veins, especially the superficial, have valves formed of reduplication of their lining membrane. For a complete list of the named veins of the body, see Table 15.
afferent v’s veins that carry blood to an organ.
precardinal v’s paired venous trunks in the embryo cranial to the heart.
pulp v’s vessels draining the venous sinuses of the spleen.
sublobular v’s tributaries of the hepatic veins that receive the central veins of hepatic lobules.
trabecular v’s vessels coursing in splenic trabeculae, formed by tributary pulp veins.
velamen [ve-la’m n] pl. velamina [L.] a membrane, meninx or velum.
n] pl. velamina [L.] a membrane, meninx or velum.
velamentous [vel“ -men’t
-men’t s] membranous and pendent; like a veil.
s] membranous and pendent; like a veil.
veldt sickness see heartwater.
vellein coumarin glycoside of uncertain toxicity in Velleia discora.
velopharyngeal [ve“lo-f -rin’je-
-rin’je- l] pertaining to the velum palatinum (soft palate) and pharynx.
l] pertaining to the velum palatinum (soft palate) and pharynx.
Velpeau sling see Velpeau sling.
velum [ve’l m] pl. vela [L.] a covering structure or veil.
m] pl. vela [L.] a covering structure or veil.
v. abomasicum two folds on either side of the omasoabomasal orifice.
v. interpositum the membranous roof of the third ventricle of the brain.
palatine v., v. palatinum soft palate.
v. uteri see intracornual frenulum.
vena [ve’n ] pl. venae [L.] vein. See also Table 15.
] pl. venae [L.] vein. See also Table 15.
caudal v. caval syndrome vena caval thrombosis (below).
v. cava spontaneous rupture recorded as a cause of sudden death in horses.
v. caval hiatus see vena cava foramen.
v. caval syndrome see caval syndrome.
posterior v. cava caudal vena cava.
venectasia [ve“n k-ta’zh
k-ta’zh ] phlebectasia.
] phlebectasia.
venectomy [ve-nek’t -me] phlebectomy.
-me] phlebectomy.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
 -n
-n l] 1. pertaining to vaccinia, to vaccine, or to vaccination. 2. having protective qualities when used by way of inoculation.
l] 1. pertaining to vaccinia, to vaccine, or to vaccination. 2. having protective qualities when used by way of inoculation. -na’sh
-na’sh n] the introduction of vaccine into the body to produce immunity to a specific disease. The vaccine may be administered by subcutaneous or intradermal injection, by infusion into the mammary gland, by mouth, by inhalation of an aerosol or administration in food or drinking water. The term vaccination comes from the Latin vacca, cow, and was coined when the first inoculations were given with organisms that caused the mild disease cowpox to produce immunity against smallpox. Today the word has the same meaning as immunization.
n] the introduction of vaccine into the body to produce immunity to a specific disease. The vaccine may be administered by subcutaneous or intradermal injection, by infusion into the mammary gland, by mouth, by inhalation of an aerosol or administration in food or drinking water. The term vaccination comes from the Latin vacca, cow, and was coined when the first inoculations were given with organisms that caused the mild disease cowpox to produce immunity against smallpox. Today the word has the same meaning as immunization. ] the vaccinia virus; a laboratory generated virus, antigenically related to the cowpox virus, that causes a lesion on the teat skin of affected cows. It is indistinguishable from cowpox lesions and used to be used to vaccinate humans against smallpox.
] the vaccinia virus; a laboratory generated virus, antigenically related to the cowpox virus, that causes a lesion on the teat skin of affected cows. It is indistinguishable from cowpox lesions and used to be used to vaccinate humans against smallpox. -ji’n
-ji’n ] 1. any sheath or sheathlike structure. 2. the canal in the female that runs from the vestibule in the external genitalia (vulva) to the cervix uteri.
] 1. any sheath or sheathlike structure. 2. the canal in the female that runs from the vestibule in the external genitalia (vulva) to the cervix uteri. -nog’r
-nog’r -fe] radiography of the vagina using a contrast agent. Retrograde passage of the contrast agent can be used to demonstrate ectopic ureters in bitches.
-fe] radiography of the vagina using a contrast agent. Retrograde passage of the contrast agent can be used to demonstrate ectopic ureters in bitches. -no-per“
-no-per“ -ne-or’
-ne-or’ -fe] suture of the vagina and perineum; colpoperineorrhaphy.
-fe] suture of the vagina and perineum; colpoperineorrhaphy. -no-pek“se] colpopexy; vaginofixation; suturing of the vagina to the abdominal wall in cases of vaginal relaxation.
-no-pek“se] colpopexy; vaginofixation; suturing of the vagina to the abdominal wall in cases of vaginal relaxation. -no-skōp] illuminated tubular instrument designed for examining the interior of the vagina. A common alternative is to use a vaginal speculum and a flashlight.
-no-skōp] illuminated tubular instrument designed for examining the interior of the vagina. A common alternative is to use a vaginal speculum and a flashlight. -met’ik] having an effect resembling that produced by stimulation of the vagus nerve.
-met’ik] having an effect resembling that produced by stimulation of the vagus nerve. -thet’ik] the combined vagus nerve and the sympathetic trunk, invested in a common fascial sheath in the neck. In cats the two nerves remain separate.
-thet’ik] the combined vagus nerve and the sympathetic trunk, invested in a common fascial sheath in the neck. In cats the two nerves remain separate. l] arising as a result of afferent and efferent impulses mediated through the vagus nerve.
l] arising as a result of afferent and efferent impulses mediated through the vagus nerve. n-se, va’lens] 1. the numerical measure of the capacity to combine; in chemistry, an expression of the number of atoms of hydrogen (or its equivalent) that one atom of a chemical element can hold in combination, if negative, or displace in a reaction, if positive. 2. in immunology, an expression of the number of antigenic determinants with which one molecule of a given antibody can combine.
n-se, va’lens] 1. the numerical measure of the capacity to combine; in chemistry, an expression of the number of atoms of hydrogen (or its equivalent) that one atom of a chemical element can hold in combination, if negative, or displace in a reaction, if positive. 2. in immunology, an expression of the number of antigenic determinants with which one molecule of a given antibody can combine. s] [L.] bent outward; twisted; denoting a deformity in which the angulation is away from the midline of the body, as in coxa valga.
s] [L.] bent outward; twisted; denoting a deformity in which the angulation is away from the midline of the body, as in coxa valga.
 ] a forcible expiratory effort in combination with a closed glottis as occurs in coughing.
] a forcible expiratory effort in combination with a closed glottis as occurs in coughing. ] pl. valvulae [L.] a small valve; a single cusp of one of the semilunar valves of the heart.
] pl. valvulae [L.] a small valve; a single cusp of one of the semilunar valves of the heart. -nil’
-nil’ l-m
l-m n-del’ik] an excretory product of the catecholamines found in the urine; used as a test in the diagnosis of phaeochromocytoma.
n-del’ik] an excretory product of the catecholamines found in the urine; used as a test in the diagnosis of phaeochromocytoma. r-
r- -za’sh
-za’sh n] 1. the conversion of a solid or liquid into a vapor without chemical change; distillation. 2. treatment by vapors; vapotherapy.
n] 1. the conversion of a solid or liquid into a vapor without chemical change; distillation. 2. treatment by vapors; vapotherapy. r] part of the apparatus used to deliver volatile anesthetic agents to patients. It is the vessel that vaporizes the liquid anesthetic and adds it to the flow of gas to the patient. The objective of them all is to deliver a suitable, accurately calibrated, quantity of anesthetic at all times and under all conditions. See also EMO vaporizer, Dräger vaporizer, Goldman vaporizer, Vapor vaporizer.
r] part of the apparatus used to deliver volatile anesthetic agents to patients. It is the vessel that vaporizes the liquid anesthetic and adds it to the flow of gas to the patient. The objective of them all is to deliver a suitable, accurately calibrated, quantity of anesthetic at all times and under all conditions. See also EMO vaporizer, Dräger vaporizer, Goldman vaporizer, Vapor vaporizer. -b
-b l] 1. any type of measurement, quantitative or qualitative, of which a series of individual observations is made so that it has, as a principal characteristic, the potential for variability. 2. has the quality of variability.
l] 1. any type of measurement, quantitative or qualitative, of which a series of individual observations is made so that it has, as a principal characteristic, the potential for variability. 2. has the quality of variability. ns] one of the measures of the dispersion of data; the mean squared deviation of a set of values from the mean.
ns] one of the measures of the dispersion of data; the mean squared deviation of a set of values from the mean. nt] an organism or tissue that is different from the majority of the population but is still sufficiently similar to the common mode to be considered to be one of them, e.g. a variant strain of classical swine fever (hog cholera) virus.
nt] an organism or tissue that is different from the majority of the population but is still sufficiently similar to the common mode to be considered to be one of them, e.g. a variant strain of classical swine fever (hog cholera) virus. n] divergence among individual animals of a group. The differences in the morphology or function of an organ or organism, are small enough to stay within the variability of the type organism or organ.
n] divergence among individual animals of a group. The differences in the morphology or function of an organ or organism, are small enough to stay within the variability of the type organism or organ. -sel’
-sel’ ] a member of the family Herpesviridae, genus Varicellovirus that causes chicken pox in humans early in life and herpes zoster (shingles), as a reactivation of latent virus, in later life; also infects gorillas, orangutans and chimpanzees.
] a member of the family Herpesviridae, genus Varicellovirus that causes chicken pox in humans early in life and herpes zoster (shingles), as a reactivation of latent virus, in later life; also infects gorillas, orangutans and chimpanzees. -ko-sēl“] varicosity of the pampiniform plexus of the spermatic cord, forming a swelling in the scrotal neck that feels like a ‘bag of worms’.
-ko-sēl“] varicosity of the pampiniform plexus of the spermatic cord, forming a swelling in the scrotal neck that feels like a ‘bag of worms’. -kōs] of the nature of or pertaining to a varix; unnaturally and permanently distended (said of a vein); variciform.
-kōs] of the nature of or pertaining to a varix; unnaturally and permanently distended (said of a vein); variciform. -kos’
-kos’ -te] 1. a varicose condition; the quality or fact of being varicose. 2. a varix, or varicose vein.
-te] 1. a varicose condition; the quality or fact of being varicose. 2. a varix, or varicose vein. -ri’o-l
-ri’o-l ] a viral disease of humans and primates characterized by fever, rash and scab formation. Called also smallpox.
] a viral disease of humans and primates characterized by fever, rash and scab formation. Called also smallpox. s] [L.] bent inward; denoting a deformity in which the angulation of the part is toward the midline of the body, as in coxa vara, genu varum.
s] [L.] bent inward; denoting a deformity in which the angulation of the part is toward the midline of the body, as in coxa vara, genu varum.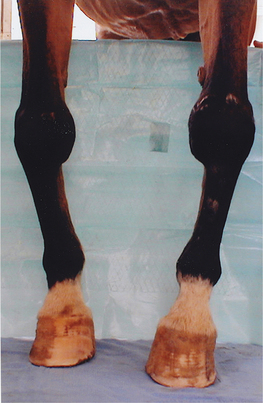
 -ch
-ch r] 1. the vascular system of the body, or any part of it. 2. the supply of vessels to a specific region.
r] 1. the vascular system of the body, or any part of it. 2. the supply of vessels to a specific region. -sek’t
-sek’t -me] excision of the vas (ductus) deferens, or a portion of it; bilateral vasectomy results in sterility.
-me] excision of the vas (ductus) deferens, or a portion of it; bilateral vasectomy results in sterility. n-strik’sh
n-strik’sh n] decrease in the caliber of blood vessels; may be general or local, e.g. pulmonary, peripheral.
n] decrease in the caliber of blood vessels; may be general or local, e.g. pulmonary, peripheral. n-strik’t
n-strik’t r] 1. causing constriction of the blood vessels. 2. a vasoconstrictive agent.
r] 1. causing constriction of the blood vessels. 2. a vasoconstrictive agent. r] 1. having the effect of lowering the blood pressure through reduction in peripheral resistance. 2. An agent that causes vasodepression.
r] 1. having the effect of lowering the blood pressure through reduction in peripheral resistance. 2. An agent that causes vasodepression. r] 1. causing dilatation of blood vessels. 2. a nerve or agent that causes dilatation of blood vessels.
r] 1. causing dilatation of blood vessels. 2. a nerve or agent that causes dilatation of blood vessels. -did“
-did“ -mog’r
-mog’r -fe] radiography of the vas deferens and epididymis after injection of a contrast medium.
-fe] radiography of the vas deferens and epididymis after injection of a contrast medium. -did-
-did- -mos’t
-mos’t -me] anastomosis of the vas (ductus) deferens and the epididymis.
-me] anastomosis of the vas (ductus) deferens and the epididymis. r] 1. having an effect on the caliber of blood vessels. 2. a vasomotor agent or nerve.
r] 1. having an effect on the caliber of blood vessels. 2. a vasomotor agent or nerve.
 -rop’
-rop’ -the] a condition caused by combined vascular and neurological defect, resulting from simultaneous action or interaction of the vascular and nervous systems.
-the] a condition caused by combined vascular and neurological defect, resulting from simultaneous action or interaction of the vascular and nervous systems. -bil’
-bil’ -te] the permeability of a blood vessel; the extent to which a blood vessel is permeable.
-te] the permeability of a blood vessel; the extent to which a blood vessel is permeable. r] 1. stimulating contraction of the muscular tissue of the capillaries and arteries. 2. a vasopressor agent.
r] 1. stimulating contraction of the muscular tissue of the capillaries and arteries. 2. a vasopressor agent. n] the severing of a vessel or vessels, especially of the vasa deferentia (ductus deferentes).
n] the severing of a vessel or vessels, especially of the vasa deferentia (ductus deferentes). -sik“u-lek’t
-sik“u-lek’t -me] excision of the vas (ductus) deferens and seminal vesicle.
-me] excision of the vas (ductus) deferens and seminal vesicle. s] [L.] great.
s] [L.] great. r] 1. a carrier, especially the animal (usually an arthropod) which transfers an infective agent from one host to another, e.g. the tsetse fly, which carries trypanosomes from animals to humans, dogs, bats and other animals that transmit the rabies virus. In molecular biology, a DNA molecule which serves to transfer DNA into a host cell. 2. a quantity possessing magnitude, direction and sense (positivity or negativity).
r] 1. a carrier, especially the animal (usually an arthropod) which transfers an infective agent from one host to another, e.g. the tsetse fly, which carries trypanosomes from animals to humans, dogs, bats and other animals that transmit the rabies virus. In molecular biology, a DNA molecule which serves to transfer DNA into a host cell. 2. a quantity possessing magnitude, direction and sense (positivity or negativity). r-kahr’de-o-gram“] the record, usually a photograph, of the loop formed on the oscilloscope in vectorcardiography.
r-kahr’de-o-gram“] the record, usually a photograph, of the loop formed on the oscilloscope in vectorcardiography. r-kahr“de-og’r
r-kahr“de-og’r -fe] the registration, usually by formation of a loop on an oscilloscope, of the direction and magnitude (vector) of the moment-to-moment electromotive forces of the heart during one complete cycle.
-fe] the registration, usually by formation of a loop on an oscilloscope, of the direction and magnitude (vector) of the moment-to-moment electromotive forces of the heart during one complete cycle. m] a derivative of pancuronium, used as a short-acting neuromuscular blocking agent.
m] a derivative of pancuronium, used as a short-acting neuromuscular blocking agent. n] a person who advocates and consumes a purely vegetarian diet and does not use animal products in clothing or use any other animal-derived product.
n] a person who advocates and consumes a purely vegetarian diet and does not use animal products in clothing or use any other animal-derived product. -t
-t -b
-b l] 1. pertaining to or derived from plants. 2. any plant or species of plant, especially one cultivated as a source of food.
l] 1. pertaining to or derived from plants. 2. any plant or species of plant, especially one cultivated as a source of food. -ta’sh
-ta’sh n] 1. any plant-like fungoid neoplasm or growth; a luxuriant fungus-like growth of pathological tissue. 2. plant growth.
n] 1. any plant-like fungoid neoplasm or growth; a luxuriant fungus-like growth of pathological tissue. 2. plant growth. -ta“tiv] 1. concerned with growth and nutrition. 2. functioning involuntarily or unconsciously. 3. resting; denoting the portion of a cell cycle during which the cell is not replicating. 4. pertaining to plants. 5. asexual reproduction.
-ta“tiv] 1. concerned with growth and nutrition. 2. functioning involuntarily or unconsciously. 3. resting; denoting the portion of a cell cycle during which the cell is not replicating. 4. pertaining to plants. 5. asexual reproduction. -k
-k l] 1. a transporting agent, especially the component of a medication (prescription) serving as a solvent or to increase the bulk or decrease the concentration of the mixture. 2. any medium through which an impulse is propagated.
l] 1. a transporting agent, especially the component of a medication (prescription) serving as a solvent or to increase the bulk or decrease the concentration of the mixture. 2. any medium through which an impulse is propagated.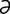 ] plural of velum.
] plural of velum. s] 1. fine hairs that appear on human skin after the lanugo hairs are cast off. 2. any fine, downy hair.
s] 1. fine hairs that appear on human skin after the lanugo hairs are cast off. 2. any fine, downy hair.