73 Urinary incontinence – an introduction
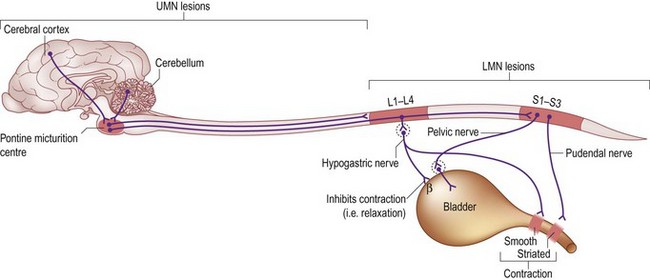
Urination becomes a voluntary action in the young animal. It is governed by interactions of the CNS and PNS, many of them reflex. Cerebral influences inhibit or initiate urination. The pontine micturition centre is the major coordinator of the storage and voiding phases. The spinal cord transmits sensory and motor impulses. The pelvic, hypogastric and pudendal nerves directly innervate the smooth and skeletal muscle of the bladder and sphincter. Fast conduction through the tight connections between bladder muscle fibres facilitates bladder contraction (Fig. 73.1).
PRESENTING SIGNS
No attempt to urinate, leaks, dribbles urine, strains to urinate and increased urgency to urinate.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree